Tim Mektrakarn
February 26, 2025
What is GRC in Cybersecurity? Why It Matters in 2025!
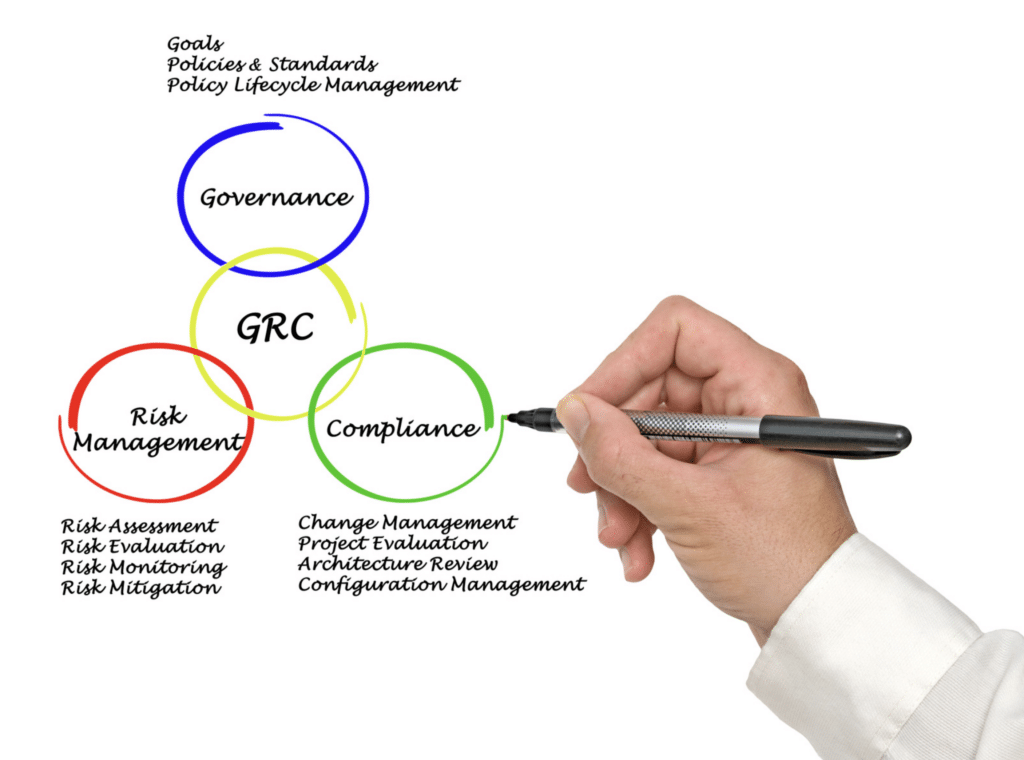
GRC in cybersecurity stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance. It is a framework that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity efforts efficiently.
Governance focuses on keeping policies, processes, and roles consistent with the organization’s goals. Risk management involves identifying, addressing, and reducing cyber threats to minimize harm. Compliance focuses on adhering to laws, regulations, and industry standards like GDPR or HIPAA. Together, GRC provides a structured approach to protect sensitive` data, address risks, and meet regulatory requirements.
With 60% of organizations experiencing at least one data breach in the past year and 60% struggling to meet compliance requirements, GRC undeniably stands as one of the most crucial elements of cybersecurity at this moment.
In this blog post, we will discuss everything there is to know about GRC.
Let’s dive right in!
Key Takeaways
- 60% of organizations experienced a data breach last year, showing the need for strong GRC practices to manage cybersecurity risks and compliance.
- GRC helps businesses manage risks, follow regulations, and keep security policies in line with business goals.
- 40% of organizations expect major cyber threats, making risk management through qualitative and quantitative assessments essential.
- Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 is critical to avoiding penalties and maintaining trust.
- 62% of organizations now see risk as an opportunity rather than just a threat, using GRC strategies to strengthen security.
- GRC services like Bright Defense help businesses with compliance, risk tracking, and security governance.
The Components of GRC
Let’s look at the three specific factors that make up GRC and discuss each one in greater detail:
1. Governance
Governance is the system an organization uses to manage and regulate its operations. It includes policies, rules, frameworks, and the organizational culture that guide behavior and decision-making. Here’s how governance plays a role:
- Clear Policies on Acceptable Use: Can employees install random software on work systems? Visit any website during their breaks? Connect gaming consoles to the network? Governance lays out clear rules to address these scenarios, ensuring consistency and security. Without these guidelines, organizations risk security breaches and operational chaos.
- Behavioral and Organizational Guidelines: Governance shapes how employees and IT resources operate, defining what is acceptable and expected within the organization.
- Ethics and Accountability Frameworks: It also promotes ethical conduct and accountability by introducing codes of ethics, performance evaluations, and compliance measures. For instance, it might require employees to declare conflicts of interest or report gifts received during work-related activities.
- Open and Consistent Information Sharing: Governance ensures transparency by mandating regular updates on budgets, projects, or policy changes. At the same time, it safeguards sensitive information, fostering trust and enabling public scrutiny.
- Defined Conflict Resolution Processes: With governance in place, organizations have clear protocols for addressing disputes. This includes steps for filing grievances, mediation processes, and escalation procedures to handle conflicts fairly.
- Not Just Rules, but a Cultural Element: Governance isn’t about tools or technical skills; it’s about building an organizational culture backed by leadership. For example, if a company mandates encryption for all stored data, governance ensures compliance by addressing any violations through set consequences.
In essence, governance brings structure and accountability, ensuring that decisions and behaviors align with organizational values and goals.
2. Risk Management
Risk management refers to the understanding and management of potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact an organization’s security. Nearly 40% of organizations surveyed by PwC anticipate significant cyber threats in the coming year, making risk management a crucial element within GRC and in cybersecurity as a whole. Risk management acknowledges that 100% security is unattainable due to various factors, such as:
- Human Vulnerabilities: Social engineering attacks.
- Technical Vulnerabilities: Exploitation of unpatched systems.
- Physical Security: Unauthorized physical access to systems.
Risk is assessed in two primary ways:
- Qualitative Risk: Assigns subjective labels to risks, such as “low,” “moderate,” or “high,” based on agreed-upon perceptions.
- Quantitative Risk: Uses measurable data to calculate risk levels. For example, an organization may determine that a specific control reduces risk from 34% to 17%. Decisions on acceptable risk thresholds, such as 20%, are made at the governance level.

Effective risk management includes:
- Auditing: Testing the effectiveness of implemented controls.
- Remediation Plans: Addressing gaps and weaknesses found during audits.
- Leadership Reporting: Communicating risk status and mitigation efforts to leadership or the board.
For example, purchasing a firewall or implementing a new tool may seem like a security improvement, but without assessing its impact on the organization’s risk posture, it might just add to the budget without significant benefits.
3. Compliance
Compliance involves adhering to federal, industry, or organizational regulations and standards. It ensures that organizations meet minimum security and privacy requirements to avoid penalties and maintain operational capabilities.
I. SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
Focuses on managing customer data securely based on security, confidentiality, and availability principles. Having SOC 2 compliance shows that an organization values data protection.
Example: A cloud storage provider complies with SOC 2 standards to reassure clients that their data is safe and accessible.
II. ISO 27001
This international standard outlines the requirements for implementing, maintaining, and improving an organization’s information security practices. Failing to comply can expose businesses to data breaches and regulatory penalties.
Example: A tech company handling sensitive user data implements ISO 27001 to minimize security risks and prevent reputational damage or fines.
III. PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
If a business processes credit card payments, it must comply with PCI DSS. Non-compliance could result in losing the ability to accept credit card payments, severely impacting operations.
Example: A food truck accepting credit cards must comply with PCI DSS to avoid being forced to switch to a cash-only model, which could hurt its business in a predominantly cashless society.
IV. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
In the healthcare sector, organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations to protect sensitive patient information. Non-compliance could lead to legal and financial penalties.
Example: A hospital implementing a new electronic health record system must follow HIPAA regulations to keep patient records secure and avoid lawsuits.
V. CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification)
CMMC applies to companies working with the U.S. Department of Defense, requiring them to follow strict cybersecurity protocols to protect sensitive information.
Example: A manufacturer bidding on defense contracts must obtain CMMC certification to remain eligible for federal projects.
VI. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR regulates the privacy and protection of personal data in the European Union, with non-compliance leading to hefty fines and eroded customer trust.
Example: A U.S.-based company serving EU customers complies with GDPR rules when collecting data on its website to avoid penalties and legal challenges.
Other important compliance frameworks include:
- NIST CSF (National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework): A widely adopted framework for managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): Provides guidelines for IT governance and management to align technology with business objectives.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): Ensures financial transparency and accountability for publicly traded companies.
- FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act): Mandates U.S. federal agencies and their contractors to secure government data and systems.
- GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act): Protects consumer financial data in the financial services industry.
- ISO 31000 (Risk Management Principles and Guidelines): Provides a framework for effectively identifying, analyzing, and addressing risks.
- CIS Controls (Center for Internet Security Controls): Offers prioritized actions to improve cybersecurity defenses.
Compliance often involves developing and following a minimum set of security controls, undergoing audits, and addressing gaps through an action plan. For instance, PCI DSS may require encrypting all credit card data. This policy would align with governance efforts, ensuring that encryption is enforced and deviations are addressed.
The Interconnection of Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) are deeply interconnected elements that together form the backbone of a robust cybersecurity posture for organizations. Governance sets the strategic direction and policies for cybersecurity, risk management identifies and mitigates potential threats to information security, and compliance ensures that the organization meets external legal and regulatory requirements as well as internal policies and standards. This synergy ensures that an organization’s cybersecurity efforts are aligned with its business objectives, legal obligations, and risk appetite.
The integration of GRC is crucial for enhancing an organization’s cybersecurity posture. When these elements work in concert, they create a comprehensive framework that addresses security from all angles. Governance provides the oversight and direction needed to align cybersecurity efforts with business goals. Risk management proactively identifies and addresses vulnerabilities and threats, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to protect critical assets. Compliance ensures that these efforts are in line with relevant laws, regulations, and standards, helping to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage. Together, they ensure that cybersecurity measures are not only effective but also strategic and compliant with external and internal requirements.
However, aligning governance, risk management, and compliance can present significant challenges. These include the complexity of regulatory environments, the dynamic nature of cyber threats, and the difficulty of integrating disparate processes and systems. Organizations often struggle with siloed departments that operate independently, leading to inefficiencies and gaps in the cybersecurity framework.
To overcome these challenges, organizations can adopt several strategies. Implementing a unified GRC platform can facilitate the integration of processes and data across governance, risk management, and compliance functions, providing a holistic view of the organization’s cybersecurity posture. Establishing cross-functional teams can enhance communication and collaboration between departments, ensuring that GRC efforts are aligned and cohesive. Furthermore, ongoing training and awareness programs can help embed a culture of security throughout the organization, ensuring that all employees understand their role in supporting GRC objectives.
By recognizing the interconnection of governance, risk management, and compliance and taking steps to integrate these components, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture, reduce risk, and ensure compliance. This integrated approach not only protects against cyber threats but also supports strategic business goals, making it a critical component of modern organizational strategy.
7 Reasons Why GRC is Important
GRC plays a pivotal role in shaping how organizations operate, make decisions, and safeguard their future. PwC’s Global Risk Survey 2023 revealed that 57% of organizations prioritize reviewing their risk landscape to prepare for upcoming technology investments, highlighting the growing importance of GRC in today’s evolving technological environment.
Here are 7 reasons why GRC is critical:
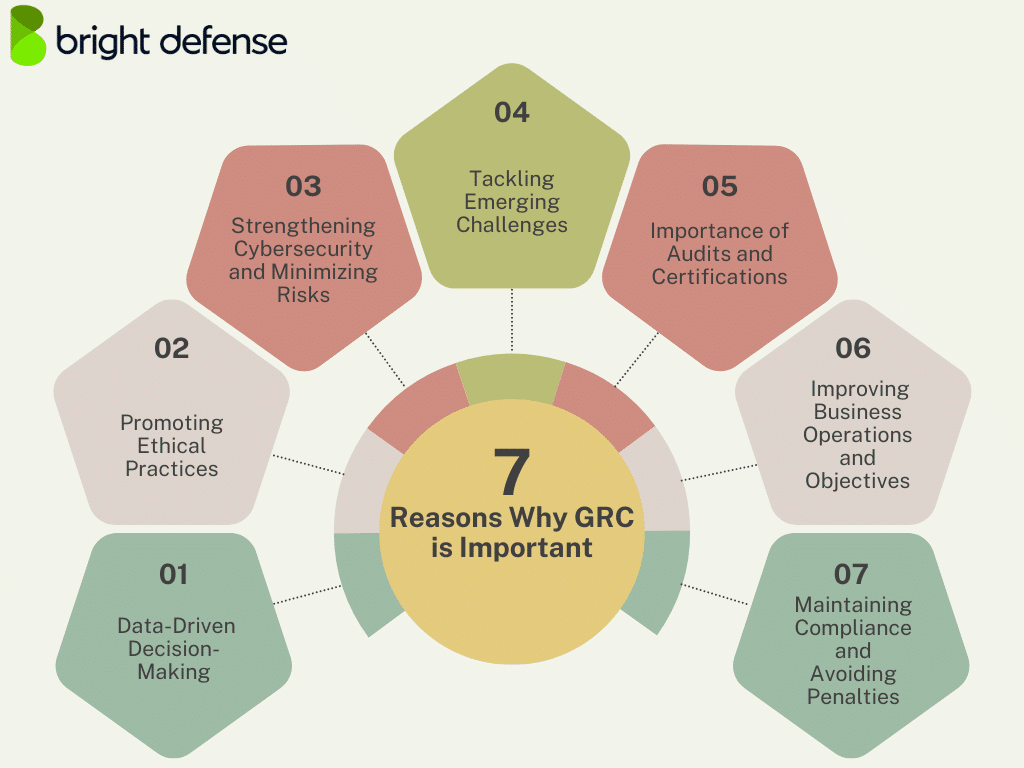
1. Data-Driven Decision-Making
GRC equips businesses with tools to make quicker and more informed choices. With GRC software, companies can track resources, assess risks, and implement policies based on real-time data, helping them make smarter decisions with confidence.
2. Promoting Ethical Practices
An effective GRC program fosters ethical behavior across the organization. Aligning operations with shared values creates an environment that supports sustainable growth and reinforces integrity in every action.
3. Strengthening Cybersecurity and Minimizing Risks
As cyber threats grow, GRC becomes critical for protecting sensitive data. With increasing cyber risks, organizations need a clear approach to identify, manage, and reduce risks. GRC tools and frameworks help businesses take a proactive stance on risk identification and mitigation, addressing vulnerabilities before they lead to data breaches or other critical issues.

4. Tackling Emerging Challenges
As AI and new technologies continue reshaping industries, GRC’s role is becoming even more crucial. In this context, businesses must oversee AI use, audit its applications, and address the shortage of skilled GRC professionals. To that end, clear policies are essential for managing risks introduced by innovation while ensuring that security and compliance remain intact.
5. Importance of Audits and Certifications
Audits and certifications play a key role in demonstrating a company’s dedication to security and compliance. They offer clear advantages:
- Building Trust: Certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2 prove that your security practices meet global standards.
- Reducing Risk: Verifying that third-party vendors follow established protocols lowers the chances of data breaches or compliance issues.
- Staying Competitive: Certifications often tip the scales in your favor, as many clients prefer working with certified vendors over those offering extra features.
For instance, take the case of two HR software vendors. On one hand, one vendor offers advanced features but lacks certifications. On the other hand, the competitor may have fewer features, but it holds recognized certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2.
Given these points, clients often gravitate toward the certified vendor, prioritizing security assurance over additional functionality. This demonstrates how GRC plays a crucial role in business growth and strengthens client confidence.
6. Improving Business Operations and Objectives
A well-implemented GRC program not only connects cybersecurity efforts with business processes but also ties them to broader business objectives. This improves operational efficiency while strengthening the organization’s ability to meet strategic goals, all while maintaining security.
7. Maintaining Compliance and Avoiding Penalties
Regulatory compliance is especially crucial for organizations in industries like finance, healthcare, and government. After all, failing to meet these requirements can result in hefty fines and significant reputational damage. To that end, adopting an integrated approach not only ensures compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR but also strengthens customer trust. Moreover, it reduces the risk of legal and financial consequences, making it a necessary strategy for long-term stability.
How To Develop a GRC Strategy?
A GRC strategy is a well-structured plan that integrates an organization’s Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance efforts. By doing so, it ensures these functions work together seamlessly to support business goals, reduce risks, and meet regulatory obligations more effectively. Moreover, this approach fosters collaboration while also keeping organizations proactive in addressing challenges before they escalate.
Step 1 – Select Key Decision-Makers and Influencers
For executives, IT leaders, and compliance officers, playing a critical role in cybersecurity decisions is essential. After all, their involvement directly ties the GRC strategy to broader business priorities. By aligning these efforts, organizations can promote a unified and practical approach to governance, risk, and compliance, ensuring security remains a top priority without compromising business objectives.
Step 2 – Define Core Security Objectives
To build an effective GRC strategy, set precise and actionable goals that address governance, risk management, and compliance needs. This means assigning specific responsibilities, strengthening threat detection, and most importantly, creating a culture of accountability. To do this, implement regular training and awareness programs that help teams stay proactive against risks.
Step 3 – Audit Existing Processes and Spot Security Gaps
Conduct a detailed review of your current tools, workflows, and security frameworks. Pinpoint weaknesses, inefficiencies, and vulnerabilities that need immediate attention. This step builds the groundwork for a more reliable and effective cybersecurity strategy.
Step 4 – Prioritize Cyber Threat Management
Assess your organization’s risk tolerance and identify critical threats to systems and data. Moving from reactive measures to proactive planning allows for quicker risk mitigation and minimizes potential disruptions.
Step 5 – Build GRC Roadmap
Develop a roadmap specific to your organization’s challenges. Use benchmarks such as ISO 27001 or GDPR for guidance. Include actionable initiatives like improving endpoint security or protecting cloud-based systems, and break them into manageable steps with clear deadlines.
Step 6 – Maintain Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Treat cybersecurity as a dynamic, ongoing effort. To maintain strong defenses, regularly review and adjust controls, compliance activities, and risk management strategies. Given that cyber threats constantly evolve, staying flexible and proactive ensures your organization is prepared to tackle new challenges.
Example of a GRC Strategy in Action
An organization might implement a GRC strategy using a centralized GRC tool, conducting regular risk assessments, automating compliance tracking, and training employees on policies and procedures. In other words, this structured approach streamlines compliance, minimizes vulnerabilities, and keeps daily operations focused on long-term objectives. At the same time, it prepares the organization for audits and strengthens its ability to handle regulatory changes.
Implementing GRC in Cybersecurity
Implementing Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) in cybersecurity is a critical step for organizations aiming to protect their digital assets effectively. To ensure the success of GRC implementation, several best practices and key strategies should be followed:
Key Strategies for Effective GRC Implementation
Here’s a straightforward guide to implementing GRC effectively.
Step 1: Assess Current GRC Processes
Start reviewing your existing GRC systems to find inefficiencies or disconnected workflows.
- Governance: Are policies transparent? Is management reviewing them regularly?
- Risk: What are the top risks, and how are they being mitigated?
- Compliance: Are employees trained on regulatory requirements?
Highlight areas needing improvement to create a clear starting point for GRC implementation.
Step 2: Develop a GRC Implementation Plan
Set GRC objectives that align with organizational goals. Your plan should include:
- A clear scope of work.
- Leadership support.
- Assigned team roles.
- KPIs to measure success.
- Training for employees.
- Adoption of automation tools.
This plan forms the foundation for an organized implementation process.
Step 3: Engage and Train Stakeholders
Appoint stakeholders to lead the implementation and clearly define their roles. Conduct training to help employees understand their part in achieving compliance and managing risks effectively. One thing to note, while risk was once solely viewed as something to be defended against, recent research found that a staggering 62% of organizations predominantly seek to uncover opportunities within risks, a departure from the previously practiced style.
This further underscores the importance of training your team with a new worldview towards risk – one that focuses on finding new opportunities within it.
Step 4: Select the Right GRC Technology
Choose GRC software that fits your organization’s needs. Look for features like:
- Automation for efficiency.
- Integration with existing systems.
- Ease of use.
Adopting an integrated GRC technology platform, such as compliance automation solutions like Drata, empowers organizations to streamline governance, risk management, and compliance processes.
These centralized platforms enhance visibility across an organization’s cybersecurity landscape, enabling more informed decision-making by automating and simplifying compliance tracking, risk assessments, and reporting.
This approach not only boosts efficiency but also ensures a more cohesive and responsive GRC strategy.
Step 5: Execute GRC Initiatives in Smaller Scale
Carry out tasks based on priority, focusing on:
- Governance: Create clear policies and involve senior management in oversight.
- Risk: Perform assessments and develop mitigation plans.
- Compliance: Monitor regulations, collect evidence, and prepare reports.
Test your GRC framework on a smaller scale, such as within a single department or a manageable project. Use this initial implementation to refine processes, identify unforeseen issues, and build momentum. This phase helps secure additional stakeholder buy-in and confidence before rolling out the program organization-wide.
Step 6: Gradually Scale the GRC Program
Once the small-scale implementation is successful, expand the GRC program to larger or more complex areas of the organization. Apply lessons learned from earlier phases to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the program. Scaling the framework gradually ensures that the organization adapts smoothly to new practices.
Step 7: Monitor and Improve
Treat GRC as a dynamic process by regularly reviewing and updating policies, processes, and controls. More importantly, adapt to evolving regulatory requirements, business strategies, and emerging risks. In light of ongoing industry shifts, gather feedback from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and refine your approach. A continuous cycle of iteration mak

Step 8. Foster a Culture of Risk Awareness and Compliance
Fostering a culture of risk awareness and compliance within an organization involves cultivating an environment where security, risk management, and regulatory adherence are core values shared by all employees. Integrating security awareness training programs, such as those offered by KnowBe4, plays a crucial role in this endeavor.
KnowBe4 specializes in empowering employees with the knowledge and tools needed to recognize and respond to cybersecurity threats effectively. By educating staff on their pivotal role in supporting GRC efforts, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture, ensuring that every team member is an active participant in safeguarding the organization’s digital assets and compliance status.
Step 9. Ensure Regulatory Compliance and Stay Updated
Ensuring regulatory compliance and staying updated on relevant laws, regulations, and standards is paramount for organizations navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity. Leveraging platforms like Drata plays a pivotal role in this process by continuously updating compliance frameworks to reflect the latest regulatory changes and industry standards.
This automated, dynamic approach allows organizations to maintain up-to-the-minute compliance, minimizing the risk of breaches and non-compliance penalties. Drata’s capability to adapt and update GRC policies and procedures in real time ensures that organizations can swiftly respond to new regulations, safeguarding their operations and reinforcing their commitment to cybersecurity excellence.
Importance of Continuous Improvement and Adaptability in GRC Practices
In an ever-changing cybersecurity environment, the need for dynamic Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) practices is critical. This brief overview highlights how continuous improvement and adaptability are crucial for evolving GRC strategies to meet future challenges:
1. Continuous Improvement
GRC is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that evolves. Organizations should regularly review and update their GRC strategies to reflect changes in the threat landscape, technological advancements, and business objectives. Implementing feedback mechanisms and performance metrics can help in identifying areas for improvement.
2. Adaptability
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly changing, with new threats and regulatory requirements emerging regularly. Organizations must remain adaptable, ready to adjust their GRC strategies in response to these changes. This adaptability ensures that the organization can quickly respond to new threats and compliance requirements, maintaining a robust security posture.
Incorporating these best practices into GRC implementation helps organizations create a resilient and flexible cybersecurity framework. By continuously improving and adapting GRC practices, organizations can protect themselves against evolving cyber threats while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, ultimately supporting their overall business objectives.

Future Trends in GRC and Cybersecurity
As we delve into the future of GRC in cybersecurity, several emerging trends and predictions come to the forefront. These insights not only highlight the evolving landscape of cyber threats but also underscore the necessity for GRC frameworks to adapt and transform in response to these challenges.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity and Their Implications for GRC
As cybersecurity threats evolve, so must the strategies for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC). This brief overview highlights key trends impacting GRC practices today:
1. Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are becoming pivotal in detecting and responding to cyber threats with greater speed and accuracy. For GRC, this means integrating these technologies to enhance risk detection capabilities and improve the efficiency of compliance processes.
2. Rising Significance of Cloud Security
As organizations continue to migrate to cloud platforms, managing security in multi-cloud and hybrid environments becomes critical. GRC strategies must evolve to address the unique risks and compliance challenges associated with cloud services, including data privacy and sovereignty issues.
3. Expansion of IoT and Edge Computing
The proliferation of IoT devices and the adoption of edge computing introduce new vulnerabilities. GRC frameworks will need to extend their reach to secure these devices and manage the data they generate, ensuring robust protection against attacks targeting these technologies.
4. Focus on Privacy and Data Protection
With increasing global attention on privacy rights, regulations like GDPR and CCPA are setting a precedent for data protection. GRC practices will increasingly need to prioritize data privacy, requiring organizations to be transparent and accountable in their data handling practices.
Predictions on How GRC Will Evolve to Meet Future Cybersecurity Challenges
As cybersecurity landscapes shift, Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC) must adapt. This brief overview discusses the pivotal trends shaping the future of GRC:
1. Greater Integration of GRC Functions
Anticipate a move towards more integrated GRC platforms that offer comprehensive visibility and management of risks, governance, and compliance activities across the entire organization. This consolidation aims to break down silos and foster a more coordinated approach.
2. Adoption of Predictive Analytics
GRC will likely leverage predictive analytics more extensively to anticipate potential risks and compliance violations before they occur. By analyzing patterns and trends, organizations can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks.
3. Emphasis on Cyber Resilience
The concept of cyber resilience will become integral to GRC strategies, shifting the focus from merely preventing attacks to ensuring that organizations can continue operating effectively during and after a cyber incident.
4. Increased Regulatory Complexity
As technology evolves, so too will the regulatory landscape. GRC frameworks will need to be agile and adaptable, capable of responding to new regulations and standards that address emerging technologies and cyber threats.
5. Enhanced Collaboration Across Borders
Cybersecurity is a global issue that requires cooperation beyond national boundaries. Future GRC practices will emphasize international collaboration, sharing threat intelligence and best practices to collectively enhance global cyber resilience.
The future of GRC in cybersecurity is poised to navigate a complex and rapidly changing landscape. By embracing these emerging trends and adapting to new challenges, GRC frameworks can provide organizations with the strategies and tools needed to secure their digital futures effectively.
Key Components of a GRC Framework in Cybersecurity
- GRC Software and Tools: These tools assist in managing compliance data, automating risk assessments, and continuously monitoring security gaps.
- Risk Assessments: Regular assessments provide insight into potential threats, enabling organizations to focus on risk mitigation strategies.
- Compliance Management: This involves keeping track of regulatory changes, and implementing effective compliance frameworks.
- Structured Approach: A structured GRC process makes sure that all components, from governance to compliance, work together.
What is a GRC Tool?
A GRC tool is software designed to help organizations manage Governance, Risk, and Compliance processes. More specifically, these tools provide a centralized platform that simplifies risk assessment, compliance monitoring, and governance management.
As a result, businesses can stay organized and meet regulatory requirements with greater efficiency. At the same time, a well-integrated GRC tool enhances visibility across operations, ensuring a proactive approach to risk and compliance.
What Are Some Common GRC Tools and Solutions?
Let’s check out some of the commonly used GRC tools and solutions:
1. Bright Defense: A Fully Managed GRC Service

Bright Defense helps businesses meet and maintain compliance with major security frameworks, including SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and more. Our CISSP and CISA-certified security experts create and execute customized cybersecurity plans, ensuring businesses stay protected and audit-ready.
Our monthly service includes:
- Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance – Risk assessments, policy implementation, business continuity planning, and remediation.
- Managed Compliance Automation – A single platform to monitor compliance across all frameworks in real time.
- Managed Security Awareness & Phishing – Employee training to reduce human risk factors.
- Virtual Chief Information Security Officer (vCISO) – Expert guidance to oversee cybersecurity strategy.
Bright Defense was built by managed service veterans who understand the unique challenges MSPs face, from security risks to budget constraints. That’s why our compliance solutions are designed to help service providers meet regulatory requirements efficiently without disrupting operations.
With Bright Defense, businesses can automate compliance, strengthen security, and stay ahead of evolving regulations.
2. Drata
It helps businesses stay compliant from the start and remain audit-ready with automated workflows and real-time monitoring. Designed by security and compliance experts, it supports frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Startups tackling compliance for the first time, growing companies expanding security measures, and enterprises looking to add automation to their GRC programs all find Drata adaptable to their needs. Companies like Notion, Lemonade, and TaskRabbit rely on it to keep compliance on track without the extra hassle.
3. Archer
Archer is a well-known GRC platform offering solutions for risk management, compliance tracking, and audit management. One of its standout features is its flexibility, as it provides customizable workflows that adapt to specific organizational needs. In particular, its ability to scale makes it suitable for businesses of all sizes, ensuring a tailored approach to governance, risk, and compliance.
4. MetricStream

MetricStream focuses on enterprise risk management, compliance, and internal audits. It equips organizations with tools to evaluate and reduce risks, complemented by intuitive dashboards to monitor key performance indicators effectively.
5. LogicGate Risk Cloud
LogicGate Risk Cloud caters to risk management and compliance requirements with a user-friendly and highly visual interface. Its customizable workflows make it a versatile solution for businesses seeking tailored processes.
Final Thoughts
As cyber threats grow more advanced and regulations become stricter, Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) has become essential to cybersecurity. It’s not just a system for meeting requirements—it’s a framework for protecting operations, reputation, and stakeholder trust.
GRC goes beyond shielding organizations from fines and breaches. It provides a way to manage risks, maintain compliance, and build confidence in security practices. In today’s unpredictable digital environment, the question isn’t whether GRC is needed—it’s how quickly organizations can put it into action.
With an effective GRC strategy, businesses can reduce vulnerabilities, strengthen decision-making, and secure long-term stability. For organizations looking to thrive in a changing cybersecurity world, GRC isn’t just helpful—it’s a necessity.
Need Help with GRC Implementation?
Bright Defense helps you meet your GRC objectives. Our services, including continuous compliance, penetration testing, and vulnerability management, address key GRC pillars. We help you manage risks, meet regulatory requirements, and maintain a strong security posture. Contact us for a free consultation.

Bright Defense GRC Services
Elevate your organization’s security posture and ensure continuous compliance with Bright Defense’s comprehensive GRC services. Our continuous compliance service plans are meticulously designed to cover all facets of implementing robust information security programs, governance, risk management, and compliance. Whether you’re looking to establish clear leadership, align GRC with your business objectives, or conduct comprehensive risk assessments, Bright Defense is your strategic partner in navigating the complexities of cybersecurity.
Don’t let the evolving landscape of cyber threats and regulations put your operations at risk. Take action today and secure your organization’s future with Bright Defense. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the tools, knowledge, and support needed to achieve and maintain compliance, mitigate risks, and align your cybersecurity efforts with your overall business strategy.
Contact Bright Defense now to learn more about our continuous compliance service plans and how we can tailor our GRC solutions to meet your unique needs. Let us help you turn cybersecurity challenges into opportunities for growth and resilience. Secure your peace of mind with Bright Defense — where continuous compliance and robust security are within your reach.
FAQs
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) frameworks are essential in cybersecurity, helping organizations manage risks and adhere to regulations. The GRC platform market is projected to reach $127.7 billion by 2033, reflecting its growing importance.
GRC professionals develop security policies, assess and mitigate risks, ensure compliance with laws, and continuously monitor security controls. Their role is vital in aligning cybersecurity measures with business objectives.
Yes, it’s a promising field. According to ZipRecruiter, the average annual salary for a Cyber Security GRC professional in the U.S. is approximately $122,890. Employment for information security analysts is projected to grow 33% from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations.
References
For further reading and research into the complexities and best practices of GRC in cybersecurity, consider exploring the following sources:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Provides comprehensive frameworks and guidelines for cybersecurity and risk management, including the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Offers a range of standards relevant to information security management, notably ISO 27001 and ISO 31000 for risk management.
- Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA): Offers resources on governance and management of enterprise IT, including the COBIT framework for managing and governing enterprise IT environments.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The official website for GDPR, providing detailed information on the regulation’s requirements and implications for data protection and privacy.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services provides guidelines and information on complying with HIPAA’s privacy and security rules.
Get In Touch





