Tamzid Ahmed | Security and Compliance Writer
April 18, 2025
Data Loss: Causes, Consequences, and 7 Prevention Tips
That sinking feeling. The sudden dread. One minute, your crucial document is there, the next, it’s gone. Poof. Vanished. Data loss. It’s a digital nightmare we all secretly fear, and unfortunately, one many of us experience firsthand.
The loss of important data can compromise the integrity of your work and lead to significant setbacks, making it essential to identify and protect such data.
But before you resign yourself to a life of panicked Ctrl+Z mashing, let’s break down the reality of data loss: what causes it, the devastating consequences it can bring, and, most importantly, how to build a fortress of protection around your precious information.
We’ll also go deep into Google Workspace data loss—how it happens, what risks are involved, and the best strategies for keeping your files safe.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Common causes of data loss and why it happens
- The real-world consequences of losing critical files
- How to prevent data loss with smart backup strategies
- Best practices for securing your data against cyber threats
- Google Workspace data loss: risks, recovery, and prevention
What is Data Loss?
Data loss refers to the unintended or accidental deletion, corruption, or loss of data due to various factors such as:
- Software and hardware failure
- Hardware failure
- Software corruption
- Cyberattacks
- Human error
It can lead to the permanent unavailability of important information, making data recovery difficult or impossible. Preventative measures like regular backups, cybersecurity protocols, disaster recovery plans, and reliable storage solutions help minimize the risk of data loss. Businesses should also implement access control, encryption, and real-time monitoring to strengthen information security and ensure business continuity.
What is Data Loss Prevention?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) encompasses strategies, tools, and processes aimed at identifying and stopping unauthorized access, transfer, or exposure of sensitive information.
A critical step in effective DLP strategies is to classify sensitive data, determining the confidentiality levels of various data types such as personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property.
This typically involves identifying sensitive information, monitoring how it is used, and blocking or flagging risky activities or data transfers, helping organizations safeguard critical data and maintain compliance with regulations.
What is a Data Loss Prevention Software?
Data Loss Prevention software, or DLP software, refers to a solution that shields sensitive information from misuse or unauthorized exposure. It detects, categorizes, and tracks critical data, whether at rest, in motion, or in use. This solution safeguards private data and helps organizations uphold compliance with data protection regulations.
Additionally, antivirus software plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information by detecting malware and preventing unauthorized access and corruption.
6 Common Causes of Data Loss
Data loss can stem from various sources, each presenting unique challenges and implications. Here’s an expanded overview of common causes, supplemented with relevant statistics:
Data leaks, resulting from overlooked vulnerabilities and human errors, pose a significant risk by unintentionally exposing sensitive information. Tailored prevention strategies, such as monitoring tools and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, are essential to mitigate these risks.
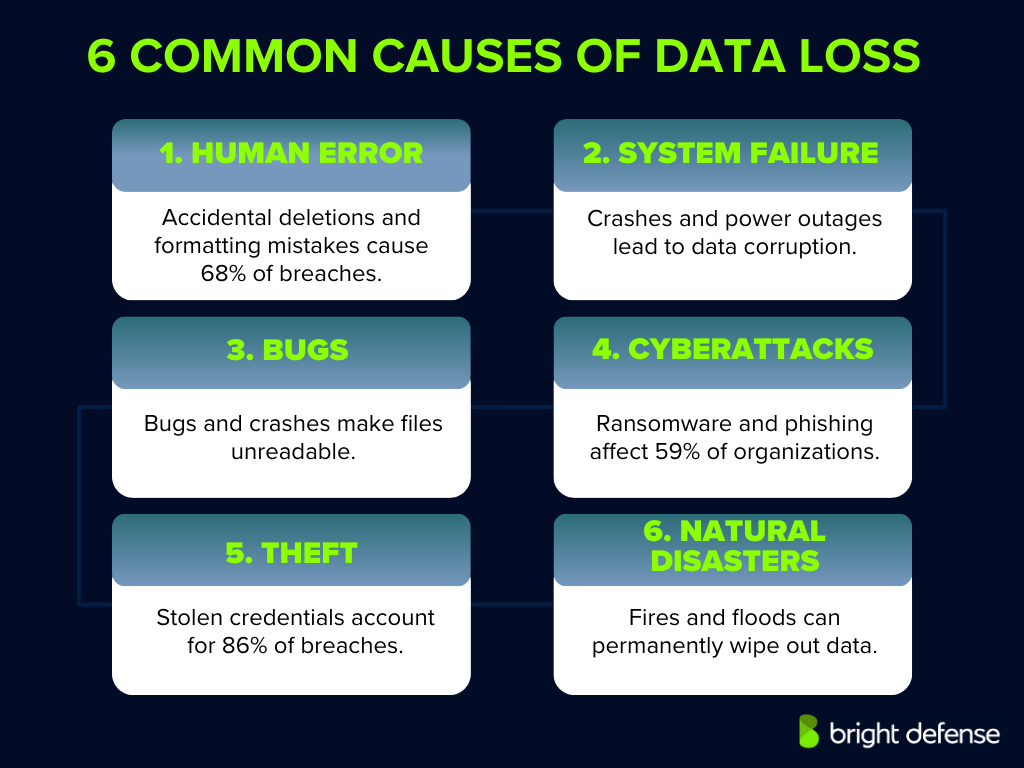
1. Human Error
Human error remains a leading cause of data breaches, accounting for 68% of incidents. These errors include accidental deletion of files, formatting incorrect drives, or overwriting essential data. Such mistakes can result in significant financial losses and operational disruptions.
2. Hardware or System Failure
Physical issues, such as hard drive crashes or sudden power outages, can lead to hardware failures, resulting in data corruption or loss. While specific statistics on hardware-induced data loss are limited, it’s widely recognized that hardware malfunctions contribute significantly to data loss incidents.
3. Software Corruption or Bugs
Software errors or crashes, including those in operating systems and applications, can damage files or render them unreadable. Improper shutdowns or software bugs might corrupt data, leading to loss. The prevalence of such incidents underscores the importance of robust software testing and reliable backup solutions.
4. Malware or Cyberattacks
Malicious software, including viruses, ransomware, and phishing attacks, poses significant threats to data security. Ransomware attacks have become increasingly prevalent, with 59% of organizations experiencing such incidents in the past year. Attackers utilize their collective intelligence to gain access to the organization’s network, allowing them to encrypt or steal data, leading to substantial financial and reputational damage.
5. Theft or Loss of Devices
Physical theft, intentional acts of vandalism, or loss of devices, such as laptops, external drives, or smartphones, can result in unauthorized access to sensitive data. Stolen credentials are a significant concern, with 86% of data breaches involving the use of stolen credentials. Stolen data can be published on the dark web, posing significant risks due to the high value of the information compared to the devices themselves. This highlights the need for strong authentication measures and device security protocols.
6. Natural Disasters
Events like fires, floods, or earthquakes can physically destroy data storage infrastructure, leading to irreversible data loss. While natural disasters are less common than other causes, their impact can be catastrophic, emphasizing the necessity for off-site backups and disaster recovery plans.
Impact of Data Loss on Businesses
Data loss can have profound repercussions for both individuals and organizations. Understanding these potential consequences is essential for implementing effective data protection strategies. Here’s an expanded overview:
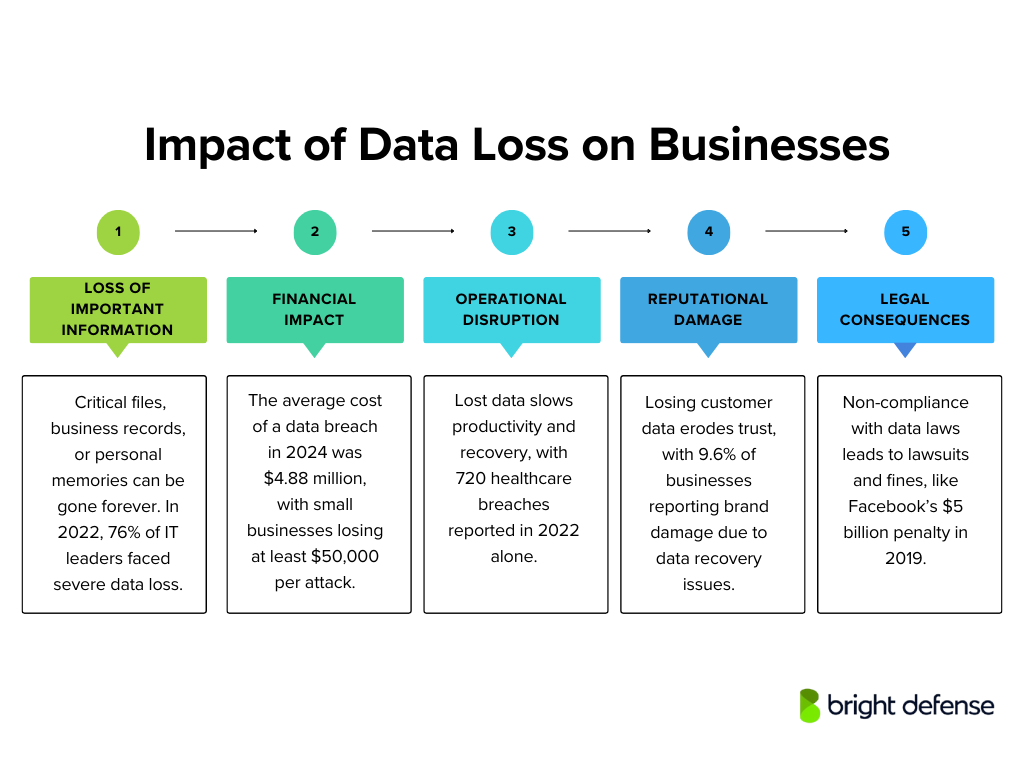
1. Permanent Loss of Sensitive Data
The immediate consequence of data loss is the irreversible disappearance of critical files, documents, or records. For individuals, this might mean losing cherished personal photos or essential financial documents.
Protecting sensitive data is crucial to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access or data breaches.
For businesses, the stakes are even higher; losing vital business documents can cripple operations. A 2022 survey found that 76% of IT leaders had faced a major loss of critical data within the past year, highlighting how widespread the problem is.
2. Financial Impact
Data loss often translates into significant financial repercussions. Businesses may face revenue losses due to operational downtime and incur substantial expenses in data recovery efforts or rebuilding lost work.
In 2024, the average cost of a data breach worldwide reached $4.88 million, marking a 10% rise from the previous year.
For small businesses, the financial strain can be particularly severe; in Australia, the average cost of a cyberattack on small businesses is at least $50,000. Individuals might bear expenses for data recovery services or suffer monetary losses if sensitive financial information is compromised.
3. Operational Disruption
For organizations, the loss of key data can lead to substantial operational disruptions. Such incidents may halt services or significantly reduce productivity while systems are restored and data is recovered.
Time and resources must be diverted to recovery efforts, causing delays in normal business activities. In healthcare settings, for instance, data breaches have been on the rise, with 720 incidents reported in 2022, potentially leading to prolonged recovery periods and operational challenges.
4. Reputational Damage Due to Data Breaches
Losing customer or client data can seriously harm an organization’s reputation and break the trust it has built. When personal data breaches occur, people may see the business as careless or unreliable. This loss of confidence can lead to lasting consequences, including losing clients or market share. In fact, 9.60% of organizations have reported brand damage due to data recovery problems.
5. Legal and Regulatory Consequences
When sensitive personal or customer data is compromised, organizations risk legal consequences and regulatory penalties. Businesses must protect customer data under data protection laws, and neglecting this responsibility can result in significant fines or legal action.
For instance, in 2019, Facebook faced a $5 billion fine from the FTC due to the Cambridge Analytica scandal and other privacy breaches. Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance also worsens reputational damage.

7 Ways to Prevent Data Loss
Data loss can happen in an instant—whether it’s a system crash, accidental deletion, or cyberattack. Recovering lost data can be time-consuming and expensive, but with the right precautions, you can avoid the headache altogether.
Here’s how to keep your data secure and accessible when you need it:
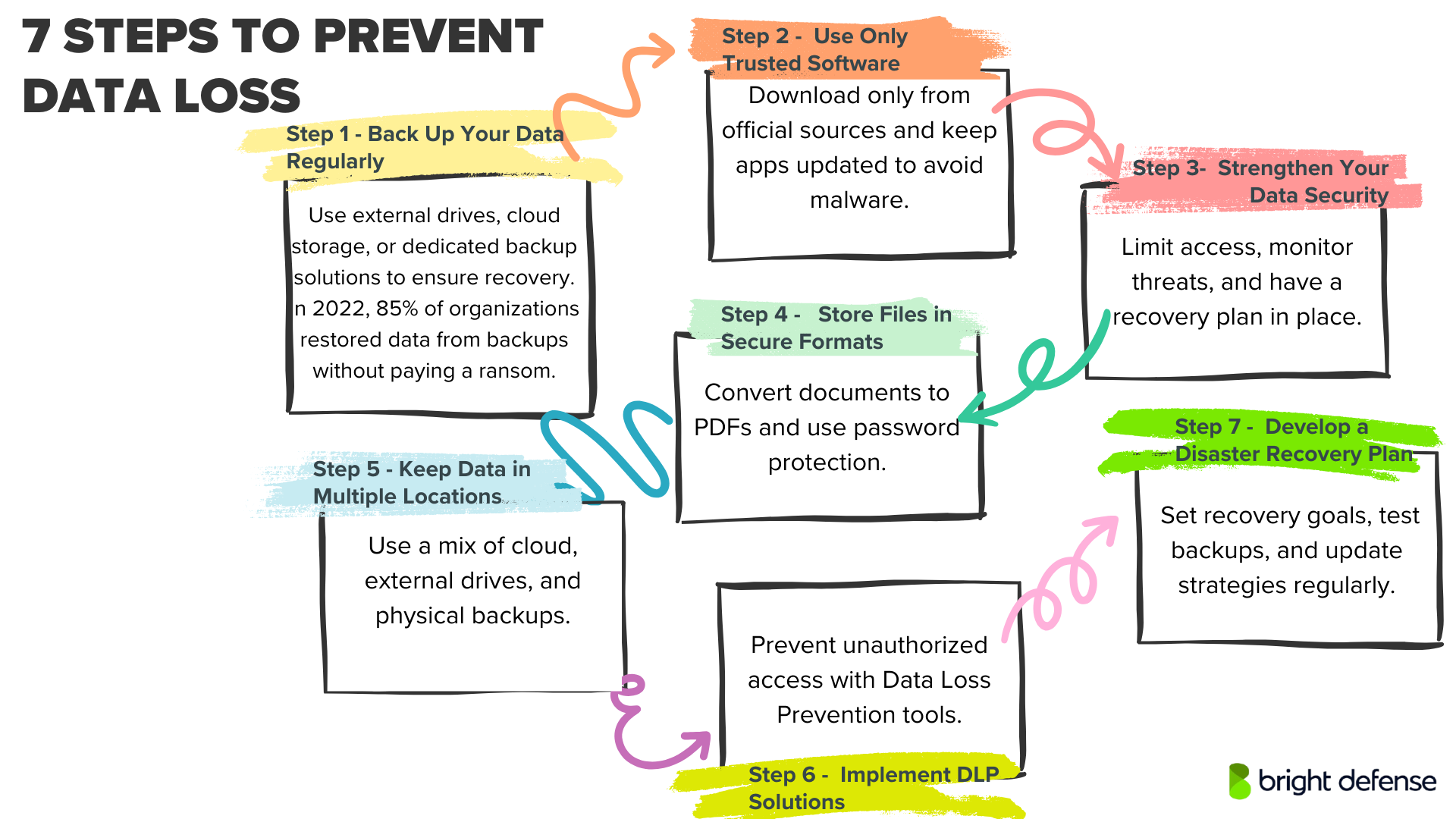
1. Back Up Your Data Regularly
Relying on a single storage location is a recipe for disaster. Instead, use a combination of backup methods to ensure your files are always recoverable:
- External Hard Drives: A simple and cost-effective solution for backups. However, these require manual updates and wear out over time, so plan for replacements periodically. In 2021, more than half of ransomware attack victims 57% managed to recover their files using backups. A separate report from 2022 revealed that organizations successfully restored at least some, if not all, of their data from backups in 85% of cases, avoiding any ransom payment.
- Cloud Storage: Services offering Backup as a Service (BaaS) automatically save your data, making it accessible from anywhere. This is an excellent option for businesses and individuals who want set-it-and-forget-it backups.
- Proprietary Backup Solutions: If you handle sensitive or business-critical data, investing in dedicated backup hardware and software gives you more control over your storage and recovery process.
Backing up data once a week is a good practice.
2. Use Only Trusted Software
Not all software is safe, and installing unverified applications can expose your data to malware, ransomware, or spyware. Follow these guidelines find out whether a software is trustworthy:
- Download apps and browser extensions only from official sources.
- If you’re unsure about a program’s security, research user reviews and security reports before installation.
- Keep your software updated, systems like macOS Gatekeeper prevent untrusted applications from running, but they need regular updates to stay effective.
3. Strengthen Your Data Security
Preventing data loss isn’t just about backups, it’s also about stopping breaches before they happen following appropriate data security practices.
Here’s what you can do in brief:
- Identify and classify your sensitive data, ensuring only authorized users can access it, and mitigate the risk of human errors such as accidental deletions or improper access revocation during employee offboarding.
- Use real-time monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity before it escalates.
- Develop a comprehensive security plan that includes preventive measures and incident response strategies.
- Have a data recovery plan ready so you can restore information quickly if a loss does occur. With the average cost of a data breach hitting $4.88 million, implementing thorough backup and recovery protocols can minimize the financial and operational impacts of such events.
4. Store Files in Secure Formats
How you save and share files can affect their security. To minimize risks:
- Convert Word, Excel, and PowerPoint files to PDFs to prevent accidental edits.
- Use password protection on PDFs to restrict unauthorized changes.
- PDFs also preserve formatting across devices, reducing issues caused by software updates or compatibility errors.
5. Keep Data in Multiple Locations
A single storage failure can wipe out everything if you don’t have backups in multiple locations. Here’s how to create a diversified storage strategy:
- Store copies on external hard drives, cloud services, and physical formats for added protection.
- Define a clear data storage and recovery plan so critical files remain accessible, even in worst-case scenarios. Nearly half of data breaches involve cloud-based systems. Ensuring data redundancy by storing information both in the cloud and on physical servers can safeguard your operations, even in the event of a breach.
6. Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are systems designed to detect and prevent unauthorized access, transmission, or loss of sensitive data. They operate across various domains to maintain data security:
- Data Identification and Classification: DLP tools use advanced algorithms to identify and categorize sensitive information within an organization’s data repositories. This process enables protection strategies based on data sensitivity levels.
- Policy Enforcement: Organizations can define specific policies regarding data handling, access, and sharing. DLP solutions enforce these policies by monitoring user activities and blocking actions that violate established guidelines.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Continuous monitoring of data in use, in motion, and at rest allows DLP systems to detect potential threats or breaches. Comprehensive reporting provides insights into data flow and security posture, facilitating informed decision-making.
7. Develop a Comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan
A well-structured disaster recovery plan is crucial for restoring data and maintaining operations after unforeseen events:
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or system failures, and evaluate their impact on business operations.
- Recovery Objectives: Define Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) to establish acceptable downtime and data loss thresholds.
- Backup Strategies: Implement regular data backups, utilizing both on-site and off-site storage solutions to ensure data availability in various scenarios.
- Testing and Maintenance: Regularly test disaster recovery procedures and update the plan to address evolving threats and organizational changes.
What is Data Loss in Google Workspace, and How Can it be Prevented?
Data loss in Google Workspace occurs when files, emails, or critical business information become inaccessible, corrupted, or permanently deleted due to human error, cyber threats, software malfunctions, or accidental overwrites. Since Google Workspace operates in a cloud-based environment, the assumption is that data is always secure. However, even with Google’s built-in security features, data can still be lost due to various factors, including:
- Accidental Deletion: Users may unintentionally delete emails or files, which can be permanently removed after a certain retention period.
- Malicious Insider Activity: Employees with access to sensitive data may delete or modify it deliberately.
- Ransomware and Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals can encrypt or delete data, making it inaccessible.
- Third-Party Application Conflicts: Integrations with unauthorized third-party apps can sometimes overwrite or delete existing data.
- Synchronization Errors: Issues with device syncing may cause file loss or corruption.
How to Prevent Data Loss in Google Workspace
Preventing data loss requires a combination of proactive security measures, employee training, and backup solutions. Here’s how organizations can safeguard their data:
1. Enable Google Vault for Data Retention
Google Vault allows businesses to retain, archive, and search emails and Google Drive files, ensuring that even deleted data remains accessible for legal or compliance purposes.
2. Implement a Third-Party Backup Solution
Relying solely on Google Workspace’s built-in protections isn’t enough. Using a third-party cloud backup service ensures multiple copies of data are stored securely, reducing the risk of permanent loss.
3. Apply Access Controls and Permissions
Setting up proper role-based access controls (RBAC) limits who can edit, delete, or share files. Google Admin Console allows IT admins to manage these permissions and prevent unauthorized data changes.
4. Educate Employees on Security Best Practices
Human error is one of the leading causes of data loss. Regular training on phishing scams, secure file handling, and proper data storage protocols can significantly reduce risks.
5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding an extra layer of security with 2FA prevents unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
6. Monitor Activity with Google Workspace Admin Reports
The Google Admin Console provides audit logs and reports that help detect unusual activity, such as mass deletions or unauthorized file sharing, allowing for quick corrective action.
7. Use Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies
Google Workspace offers DLP rules to prevent users from sharing sensitive information externally. These policies can detect and block unauthorized data transfers.
8. Set Retention Policies for Emails and Files
Organizations should define retention policies to automatically preserve important emails and files for a specified period, ensuring critical business data isn’t lost due to accidental deletions.
Final Thoughts
Alright, let’s wrap this up. Data loss is a real headache. From accidental deletions to sneaky cyberattacks, the ways things can go sideways are… well, numerous. And believe us, seeing the fallout isn’t pretty.
But here’s the thing: it doesn’t have to be a “when,” it can be an “if.” We’ve sifted through countless strategies, and those seven tips? They’re your solid foundation. Think of it like this: I’ve crunched the numbers, analyzed the patterns, and those prevention methods are the most effective ways I’ve seen to keep your digital life in order.
Don’t just brush this off. I’ve seen the data, I’ve processed the outcomes. Take those tips, put them into action, and you’ll be giving yourself a much better chance of keeping your valuable information safe. It’s not just about files and folders; it’s about protecting your work, your memories, your business’s future. And that’s something I can definitely get behind.
FAQs
Data loss refers to the unintended deletion, corruption, or destruction of data stored on a digital device, server, or storage system. Once lost, the data becomes inaccessible or unusable.
Data loss can happen due to several reasons. Hardware failure, such as malfunctioning hard drives or memory components, can make data inaccessible.
Losing data means stored information is no longer accessible, retrievable, or usable in its original state. It can range from a single deleted file to complete system failures.
Data recovery is often possible, depending on the cause and severity. Professional services can retrieve files from damaged hardware, while recovery tools and backups can restore data lost due to software corruption or accidental deletion.
The monitoring and incident response phase of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is responsible for investigation. This includes tracking data access, identifying potential breaches, analyzing incidents, and implementing corrective actions to recover data and prevent future losses. This step helps strengthen security measures and minimize risks.
Get In Touch



