John Minnix
April 13, 2025
FERPA Compliance Checklist (April – 2025)
Protecting student education records isn’t optional. It’s a legal requirement. Schools, colleges, and universities must follow the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), a federal law that outlines how student records should be handled. FERPA gives students and parents specific rights over those records and demands strict safeguards from institutions.
But staying compliant isn’t as simple as locking a filing cabinet. With rising cybersecurity threats, schools need more than just good intentions. They need a clear plan. That’s where a solid FERPA compliance checklist comes in.
This article lays out that checklist and shows how adopting proven cybersecurity frameworks can help you stay compliant, protect sensitive data, and build trust with students and families.
Key Takeaways
- FERPA protects student education records, granting rights to access, amend, and control disclosures.
- Schools must provide annual FERPA rights notifications via accessible channels like handbooks and emails.
- Access and amendment requests must be handled within 45 days, with clear procedures in place.
- Written consent is required for most disclosures, with specific exceptions outlined in FERPA.
- Staff must receive regular FERPA training, and institutions must maintain clear policies and procedures.
- Strong record-keeping practices (encryption, secure storage, and controlled access) ensure data protection.
- Cybersecurity frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001 help strengthen FERPA compliance and prevent breaches.
What is FERPA?
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law enacted in 1974 designed to protect the privacy of student education records. FERPA applies to all educational institutions that receive funding from the U.S. Department of Education. The primary objectives of FERPA are to ensure that students and their parents have access to their education records, the right to seek amendments to those records and some control over the disclosure of information from those records.
Who is Covered by FERPA?
FERPA covers all students who are or have been in attendance at an educational institution that receives federal funding. This includes public and private elementary and secondary schools, post-secondary institutions, and state education agencies. Under FERPA, parents or eligible students (students who are 18 years old or attending a post-secondary institution) have specific rights regarding the student’s education records.
Rights Granted to Students and Parents Under FERPA
FERPA grants several key rights to students and parents to ensure the protection and privacy of education records:
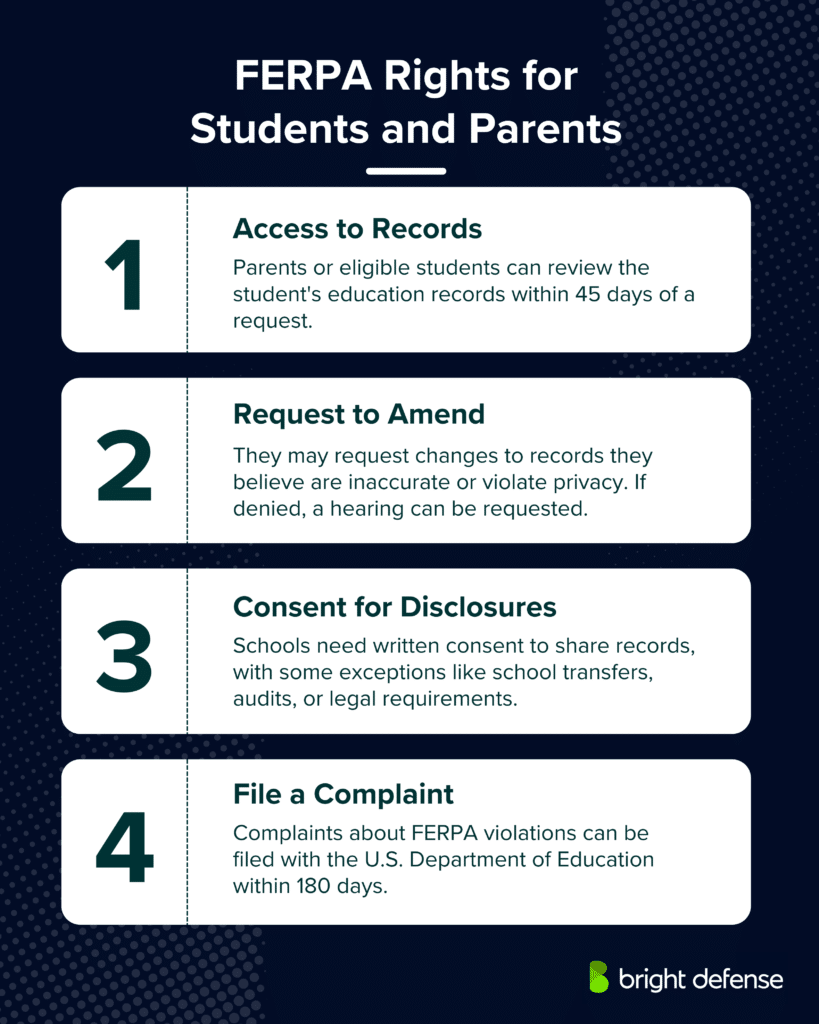
- Right to Access Education Records:
- Parents or eligible students have the right to inspect and review the student’s education records maintained by the school. Schools are required to provide access within 45 days of receiving a request.
- Right to Request Amendment of Records:
- If parents or eligible students believe that information in the education records is inaccurate, misleading, or violates the student’s privacy rights, they can request that the school amend the records. If the school decides not to amend the record, the parents or eligible students have the right to a formal hearing.
- Right to Consent to Disclosures:
- Schools must have written permission from the parent or eligible student to release any information from a student’s education record. However, several exceptions to this rule exist, including disclosures to school officials with legitimate educational interests, other schools to which a student is transferring, specified officials for audit or evaluation purposes, appropriate parties in connection with financial aid, organizations conducting certain studies for the school, accrediting organizations, and in compliance with a judicial order or lawfully issued subpoena.
- Right to File a Complaint:
- Parents or eligible students have the right to file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education if they believe their rights under FERPA have been violated. The complaint must be submitted within 180 days of the alleged violation.
Understanding these rights and implementing appropriate policies and procedures help schools comply with FERPA and protect student privacy.
FERPA Compliance Checklist
To help educational institutions ensure they meet FERPA requirements, the following comprehensive checklist covers key areas of compliance:

1. Annual Notification of Rights
Schools must notify students and parents each year about their FERPA rights. Provide this notification through multiple channels, such as student handbooks, websites, and emails.
Before you notify, you should:
- Verify that your notification explains the right to inspect and review student records, request amendments, consent to disclosures, and file complaints with the U.S. Department of Education.
- Track and confirm the annual distribution of these notices.
These notifications must be clear and timely to avoid potential noncompliance.
2. Access and Amendment Requests
Document the procedures for students and parents to request access to education records. Publish these procedures in a straightforward format, and respond within the 45-day timeframe.
When you get an access or amendement request, try to:
- Maintain a record of each request, including the date, type of request, and the school’s response.
- Log any amendments made to student records. Include the rationale for each change to provide transparency if disputes arise.
Proper documentation proves compliance and helps address issues quickly.
3. Information Disclosure
Review and document how staff should disclose student education records. Staff must get written consent from parents or eligible students unless a FERPA exception permits release without consent.
- Confirm your process for disclosing directory information and allow students and parents to opt out.
- Ensure the opt-out procedure is easy to understand and complete.
Record the reasons for each disclosure. Unauthorized sharing of personal information can expose you to legal consequences.
4. Policy and Training Implementation
Keep FERPA policies current and readily available to students, parents, and staff. Outdated or hard-to-find policies increase the chance of violations.
While implementing policies and training, you should:
- Conduct frequent FERPA training for staff and faculty who handle student records.
- Track and document training participation. Require follow-up if policies change or if an employee fails to comply.
Regular training and clear policies encourage consistent adherence to FERPA requirements.
5. Additional Compliance Measures
Safeguard student education records through robust data security protocols. Implement encryption, secure storage solutions, and role-based access restrictions.
- Create and maintain an incident response plan to handle potential data breaches.
- Outline procedures for notifying affected individuals and authorities during a breach.
Use real-time monitoring tools to identify threats. Schedule regular security audits to detect and fix vulnerabilities. Demonstrate a strong commitment to protecting student information.
Educational institutions can use this FERPA compliance checklist to cover all necessary requirements, ensuring student education records remain protected and in line with federal regulations. Taking a structured approach not only helps maintain compliance but also reinforces trust with students and parents. Plus, it strengthens the institution’s reputation for handling sensitive information responsibly.
5 Key FERPA Compliance Requirements
To comply with FERPA, educational institutions must follow specific guidelines that protect student education records and uphold privacy rights. These requirements ensure that students and parents have access to important information while maintaining strict controls over data disclosure.
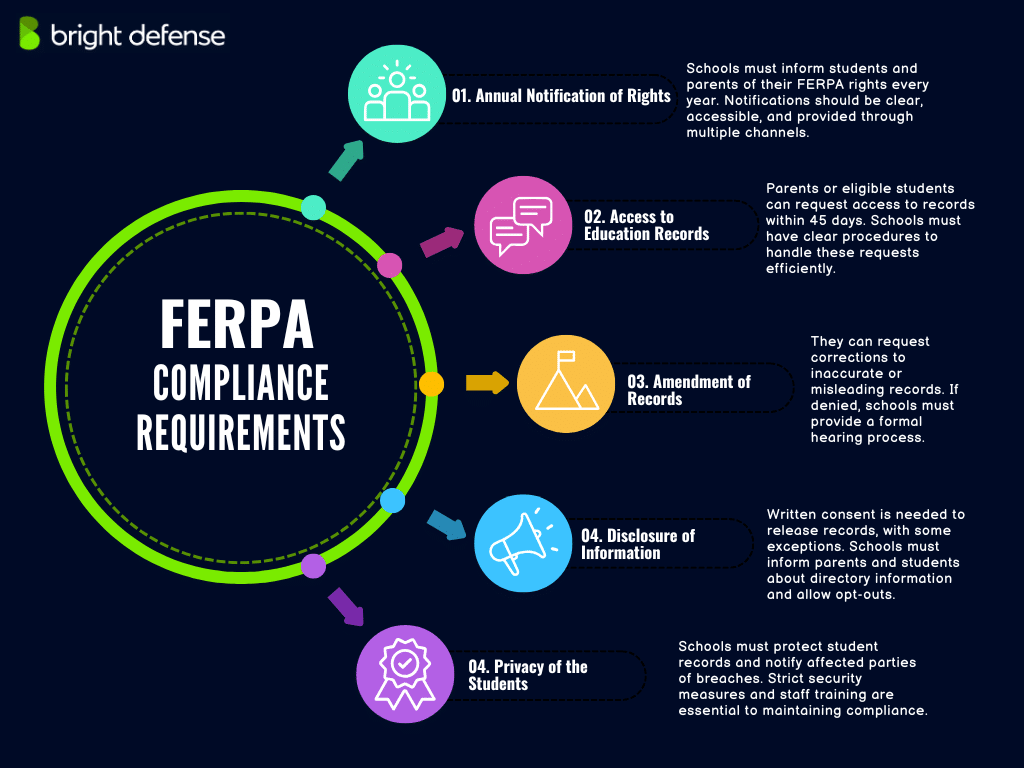
Below are the key compliance measures schools must implement.
1. Annual Notification of Rights
Educational institutions must annually inform students and their parents of their rights under FERPA. This notification must include information about the right to inspect and review education records, the right to request amendments, the right to consent to disclosures, and the right to file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education.
Schools can use various methods to notify parents and students, including school handbooks, websites, emails, and direct mail. The notification must be clear, concise, and accessible to all parties.
2. Access to Education Records
Under FERPA, parents or eligible students can inspect and review the student’s education records. Schools must comply with requests for access within a reasonable time, not exceeding 45 days from the date of the request.
Schools should establish clear procedures for handling requests to review records. This includes identifying the appropriate contact person, specifying how requests should be submitted, and providing access promptly.
3. Amendment of Records
If parents or eligible students believe that information in the education records is inaccurate, misleading, or violates the student’s privacy rights, they can request that the school amend the records. The school must decide whether to amend the record as requested within a reasonable time.
Schools must have a formal process for handling requests to amend records. This includes notifying the requester of the decision and providing the right to a formal hearing if the request is denied.
4. Disclosure of Information
FERPA generally requires that schools have written permission from the parent or eligible student before releasing any information from a student’s education record. However, FERPA allows schools to disclose records, without consent, to the following parties or under the following conditions (34 CFR § 99.31):
- School officials with legitimate educational interests
- Other schools to which a student is transferring
- Specified officials for audit or evaluation purposes
- Appropriate parties in connection with financial aid
- Organizations conducting certain studies for or on behalf of the school
- Accrediting organizations
- To comply with a judicial order or lawfully issued subpoena
- Appropriate officials in cases of health and safety emergencies
- State and local authorities within a juvenile justice system, according to specific state law
Schools may disclose, without consent, “directory” information such as a student’s name, address, telephone number, date and place of birth, honors and awards, and dates of attendance. However, schools must inform parents and eligible students about directory information and allow them a reasonable amount of time to request that the school not disclose directory information about them.
5. Privacy of the Students
Protecting student privacy is a fundamental requirement under the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). Educational institutions must ensure that student education records remain confidential and are accessible only to authorized individuals. This involves implementing strict access controls, training staff on privacy protocols, and establishing clear guidelines for handling sensitive student information.
In addition to these measures, institutions must be transparent about data breaches. Recent investigations have revealed that some schools, after experiencing cyberattacks, have withheld critical information about these breaches from students, parents, and staff. This lack of transparency can leave affected individuals vulnerable to identity theft and fraud, as they remain unaware of the exposure of their personal and sensitive information.
To uphold FERPA’s standards, schools should not only prevent unauthorized disclosures but also promptly inform affected parties in the event of a data breach. By doing so, institutions demonstrate a commitment to student privacy and maintain trust within the academic community.
Following these key FERPA compliance requirements helps educational institutions protect students’ education records while preserving the trust of both students and parents. Maintaining compliance isn’t just about legal obligations, it reinforces confidence in the institution and safeguards sensitive information.

What Is a FERPA Violation?
A FERPA violation occurs when an educational institution or its employees fail to adhere to the privacy standards and student rights outlined in the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). Common violations include:
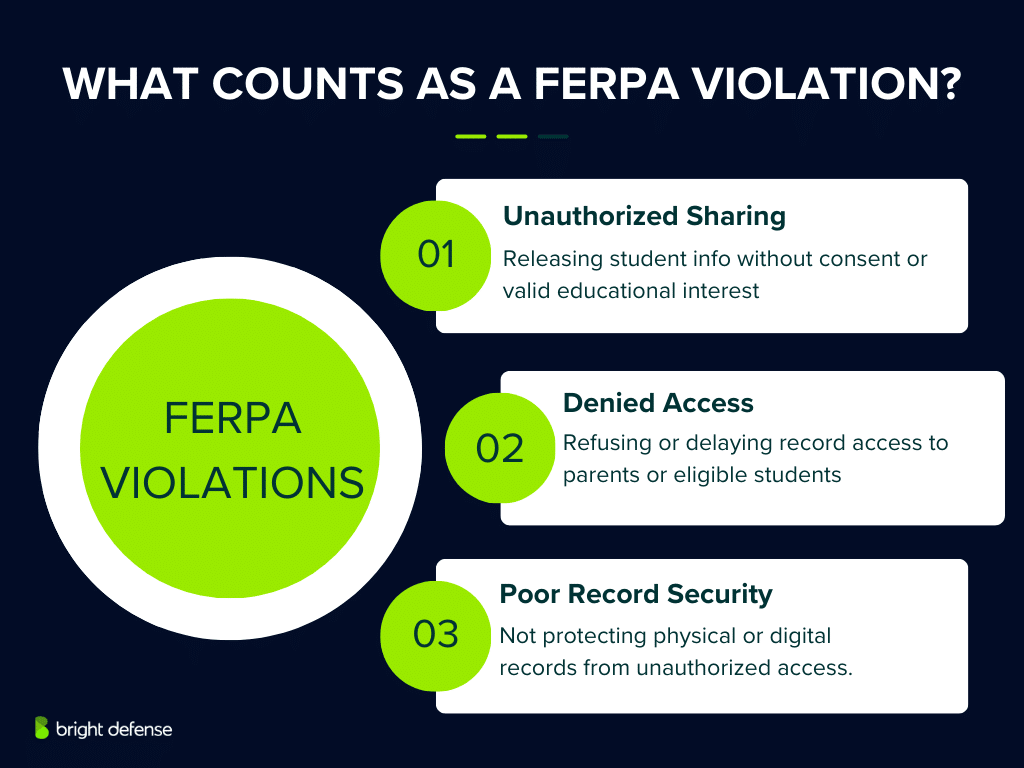
- Unauthorized Disclosure of Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Sharing or releasing student records or PII to individuals who do not have legitimate educational interests or without the student’s/parent’s consent.
- Failure to Provide Access to Records: Illegitimately denying or delaying a parent’s or eligible student’s right to inspect and review education records.
- Improper Management of Records: Neglecting to secure both physical and digital records, leading to unauthorized access.
Essentially, any action that compromises the confidentiality of student educational records or infringes on the rights granted to students and parents under FERPA can be considered a violation.
Penalties for Violating FERPA
If you violate FERPA, following pernalties can be incurred:
1. Loss of Federal Funding
The most serious consequence of violating FERPA is the potential loss of federal funding from the U.S. Department of Education. While this penalty is rarely enforced in full, the risk is enough to ensure that institutions take compliance seriously.
2. Legal Action
FERPA doesn’t always allow individuals to sue directly, but those affected by a violation may seek legal action under related state or federal privacy laws if they can prove harm from the disclosure.
3. Department of Education Enforcement
The Department of Education has the authority to investigate complaints, demand that violations stop, impose fines, or require corrective actions to bring institutions into compliance.
4. Accreditation Impact
Repeated or serious violations can affect an institution’s accreditation, damaging its reputation and potentially impacting its ability to operate.
5. Employee Disciplinary Measures
Staff members responsible for FERPA violations may face consequences such as a formal warning, suspension, or even termination, depending on the severity of the breach and the institution’s policies.
How to Implement FERPA Policies and Procedures
Compliance with FERPA starts with clear policies and structured procedures for handling student records. Schools must outline rights, access protocols, and privacy safeguards to ensure compliance and build trust. Below are the detailed steps for effective policy implementation:
1. Developing Clear FERPA Policies
To ensure compliance with FERPA, educational institutions must develop and implement clear, comprehensive policies regarding handling student education records. These policies should outline the rights of students and parents under FERPA, the procedures for exercising these rights, and the responsibilities of school officials in protecting student privacy.
- Key Elements to Include in FERPA Policies:
- Procedures for notifying students and parents of their FERPA rights
- Guidelines for accessing and reviewing education records
- Steps for requesting amendments to education records
- Rules for the disclosure of education records, including exceptions
- Process for handling complaints and disputes regarding FERPA compliance
- Ensuring Policies are Accessible:
- Policies should be readily available to all students, parents, and school staff. The school can achieve this by publishing them on its website, including them in student handbooks, and distributing them via email or direct mail.
2. Training and Awareness
Regular training and awareness programs ensure that all school staff understand their responsibilities under FERPA and are equipped to handle student education records appropriately.
- Regular Training Sessions:
- Schools should conduct regular training sessions for staff and faculty, covering key aspects of FERPA compliance. Training should be mandatory for all new employees and include periodic refresher courses for existing staff.
- Resources and Tools for Ongoing Education:
- Provide staff with access to resources such as online FERPA training modules, compliance manuals, and U.S. Department of Education guidelines. Encourage staff to stay informed about any updates or changes to FERPA regulations.
3. Record-Keeping Practices
Maintaining accurate and secure education records is a fundamental aspect of FERPA compliance. Schools must implement robust record-keeping practices to protect the integrity and confidentiality of student information.
- Best Practices for Electronic Records:
- Use secure, password-protected systems for storing electronic education records. Implement encryption to protect data during transmission and storage. Regularly back up records and ensure that backup systems are secure.
- Best Practices for Physical Records:
- Store physical education records in locked, secure locations. Limit access to authorized personnel only. Implement a sign-in/sign-out system for tracking records.
- Data Retention and Disposal:
- Establish clear policies for the retention and disposal of education records. Ensure that records are retained for the required period and securely disposed of when no longer needed, such as through shredding or secure electronic deletion.
Educational institutions can safeguard student records and stay FERPA-compliant by establishing clear policies, conducting regular training, and maintaining secure record-keeping practices. These steps not only protect student privacy but also reinforce the institution’s commitment to data security and trust.

How to Achieve FERPA Compliance in 10 Steps
Here are 10 quick tips to get you FERPA-compliant fast:
1. Understand FERPA
FERPA is a federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. It gives specific rights to parents or guardians while their child is under 18. Once the student turns 18, rights shift to the student unless an exception applies.
FERPA aims to prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive student data, such as grades or disciplinary records. Schools must secure and maintain these records with strict confidentiality.
2. Confirm That FERPA Applies
FERPA applies to all schools receiving federal funding from the US Department of Education. This includes most public and charter schools at the elementary, secondary and post-secondary levels. Private and parochial schools rarely meet this criterion. Failure to comply can lead to loss of federal funding, which can devastate a school’s budget.
3. Identify Protected Information
FERPA covers two types of student data:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): This information identifies a student directly or indirectly. It includes details like social security numbers, student ID numbers, date of birth and more.
- Directory Information: This includes data that typically isn’t harmful if disclosed. Examples include student names, addresses and phone numbers. Some details (like a student’s name) can appear in both categories, so schools must be careful when linking any public data with other sensitive records.
4. Know Student and Parental Rights
Parents and eligible students have the right to inspect, review and request changes to student records. They can block disclosure of directory information and must give explicit permission before the school can release personally identifiable data.
Schools must provide annual notification of these rights and a copy of their policy for handling education records. Schools must also explain how parents or students can file a complaint if they suspect a FERPA violation.
5. Understand Common Exceptions
Schools can release PII without consent in specific scenarios. These include disclosing information for financial aid, accreditation, health and safety emergencies or compliance with court orders. Schools can also share records with local authorities for audit or evaluation purposes. Reviewing these exceptions keeps staff from accidentally violating FERPA or withholding data when they’re legally required to disclose it.
6. Choose FERPA-Compliant Vendors
Schools must ensure that third-party vendors handle student data appropriately. Conduct thorough screening to confirm that they know FERPA rules. Avoid free services that rely on data mining. Outline clear responsibilities and penalties in contracts. It is the school’s responsibility to track and monitor all outside data handling, and any vendor mishap falls back on the school.
7. Train Staff
Untrained staff are the biggest risk to FERPA compliance. Offer yearly training covering the handling of student data, record-keeping, disclosure protocols and responses to parent or student requests. Emphasize the consequences of violating FERPA, which can include lawsuits, fines and loss of federal funding. Make sure new hires receive immediate FERPA training.
8. Develop & Implement Policies
Clear policies and procedures guide teachers and administrators on proper record storage, retention and destruction. Keep a list of individuals and organizations that request or obtain student records. Document why they wanted the information. Plan for accidental disclosure and data breaches. This includes who to notify, how to limit damage and when to alert affected students or parents.
9. Encrypt Files & Emails
Encryption secures data on lost or stolen devices and reduces risk if staff accidentally leave computers unlocked. Encryption tools protect email attachments containing sensitive data. Many schools still allow unprotected transmission of PII, which is reckless. Combining encryption with regular staff training can prevent major data breaches.
10. Employ Security Tools
Use routine vulnerability scans to detect weak points in cloud-based record systems. Apply compliance-monitoring software to track how staff handle sensitive files. Automate security patches to close system loopholes quickly. These measures reduce the likelihood of FERPA violations and demonstrate that the school takes data privacy seriously.

Final Thoughts
Ensuring compliance with the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a critical responsibility for educational institutions. Protecting the privacy of student education records not only fulfills legal requirements but also fosters trust and confidence among students and parents. Institutions can effectively safeguard sensitive information by understanding FERPA’s key objectives, implementing clear policies and procedures, providing regular training, and leveraging established cybersecurity frameworks.
As the data privacy landscape evolves, staying informed and proactive is essential. Regularly reviewing and updating FERPA policies, embracing best practices in cybersecurity, and committing to continuous improvement will ensure that your institution remains compliant and well-prepared to protect student records.
Bright Defense: Your Partner in Education Compliance Solutions
At Bright Defense, we understand the critical importance of protecting student education records and ensuring compliance with FERPA. Our monthly engagement model delivers a robust cybersecurity program that aligns with various compliance frameworks, including SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, CMMC, and PCI. This comprehensive approach ensures that your institution achieves compliance certification and continuously enhances its security posture to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape and compliance standards.
Our compliance automation toolset is designed to provide complete visibility into your compliance status. This innovative solution saves time and money, streamlining the compliance process and allowing you to focus on your core educational mission. With Bright Defense, you can trust that your institution’s data is secure and that your compliance efforts are efficient and effective.
Contact Bright Defense today to get started!
FAQs
Yes, the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) applies to all students who are or have been in attendance at educational institutions that receive federal funding, including postsecondary institutions. Once a student turns 18 or attends a postsecondary institution, the rights under FERPA transfer from the parents to the student, now referred to as an “eligible student.”
If a teacher violates FERPA by improperly disclosing or handling a student’s education records, the educational institution may face consequences such as the potential loss of federal funding. While FERPA doesn’t provide a private right of action for individuals, complaints can be filed with the U.S. Department of Education’s Family Policy Compliance Office. The institution is responsible for ensuring compliance and may take disciplinary action against the teacher, which could include termination, depending on the severity of the violation.
Yes, a teacher can be terminated for violating FERPA, especially if the violation is severe or part of a pattern of non-compliance. The specific consequences depend on the institution’s policies and the nature of the violation.
FERPA knowledge is essential for various groups. Educational institutions, including administrators, teachers, and staff at federally funded schools, must understand FERPA to ensure compliance and protect student information. Parents and students also need to be aware of their rights regarding access to and control over education records. Additionally, third-party service providers that handle educational data must comply with FERPA regulations to maintain student privacy and prevent unauthorized disclosures.
Yes, HIPAA excludes education records from its coverage. Education records protected by FERPA are not subject to HIPAA regulations.
Get In Touch



