
August 3, 2025
What is Compliance Monitoring? Why is it Important?
Non-compliance costs businesses an average of $14.82 million annually, and data breaches can cripple SMBs, sometimes leading to permanent closure.
In 2025, compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes for an annual audit anymore, it’s about maintaining a strong security posture every single day. With regulatory requirements tightening, companies face hefty fines and reputational damage if they fall short.
Compliance monitoring tools offer a proactive solution by providing real-time visibility into compliance status. This helps organizations stay ahead of regulatory obligations, minimizing the risk of costly breaches. Plus, they foster a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that compliance isn’t just maintained but consistently strengthened.
In this article, we will cover:
- The shift from periodic to continuous compliance monitoring
- Key components of an effective monitoring system including automated checks, real-time alerts, and customizable dashboards
- Challenges in implementing compliance monitoring systems and how to overcome them
- Best practices for maintaining continuous compliance
What is Compliance Monitoring?
Compliance monitoring is a systematic approach that evaluates and ensures that a company’s operational processes continuously meet regulatory and cybersecurity standards. This proactive practice is fundamental to maintaining a company’s integrity and security. This is particularly true for those required to adhere to compliance frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA.

At its core, compliance monitoring involves regular assessments that help identify and rectify compliance gaps in real-time. Unlike traditional methods, which often rely on annual reviews and external audits, compliance monitoring integrates daily operations with compliance goals, creating a seamless overlap between business processes and compliance requirements.
This integration allows for immediate adjustments, reducing the risk of compliance breaches.
The Shift from Periodic to Continuous Compliance
The evolution from periodic compliance checks to continuous monitoring marks a significant shift in regulatory practice. Periodic checks, while useful, often lead to a “checklist” mentality. People see compliance as an obligation to fulfill at specific times rather than a constant priority. Continuous compliance monitoring moves away from this episodic approach by embedding compliance into an organization’s daily workflow.
This shift is driven by several factors:
- Technological Advancements: New technologies have enabled automated systems that can monitor compliance in real-time, allowing for immediate responses to potential infringements.
- Regulatory Expectations: Increasingly, regulatory bodies expect continuous monitoring and have framed their guidelines to favor this approach, recognizing that risks in today’s digital world are constant and ever-evolving.
- Business Continuity and Risk Management: Continuous monitoring provides an ongoing assurance that all business practices are compliant, which in turn protects the company from potential fines, legal repercussions, and reputational damage.
In essence, compliance monitoring is not just a defensive tactic against non-compliance. It is a strategic approach that enhances overall business operations, promotes transparency, and builds stakeholder trust.
Key Components of an Effective Compliance Monitoring Program
To build an effective compliance monitoring program, organizations must incorporate several critical components that ensure the system is comprehensive, responsive, and adaptable.
Here are the key elements that contribute to the efficacy of a compliance monitoring system:
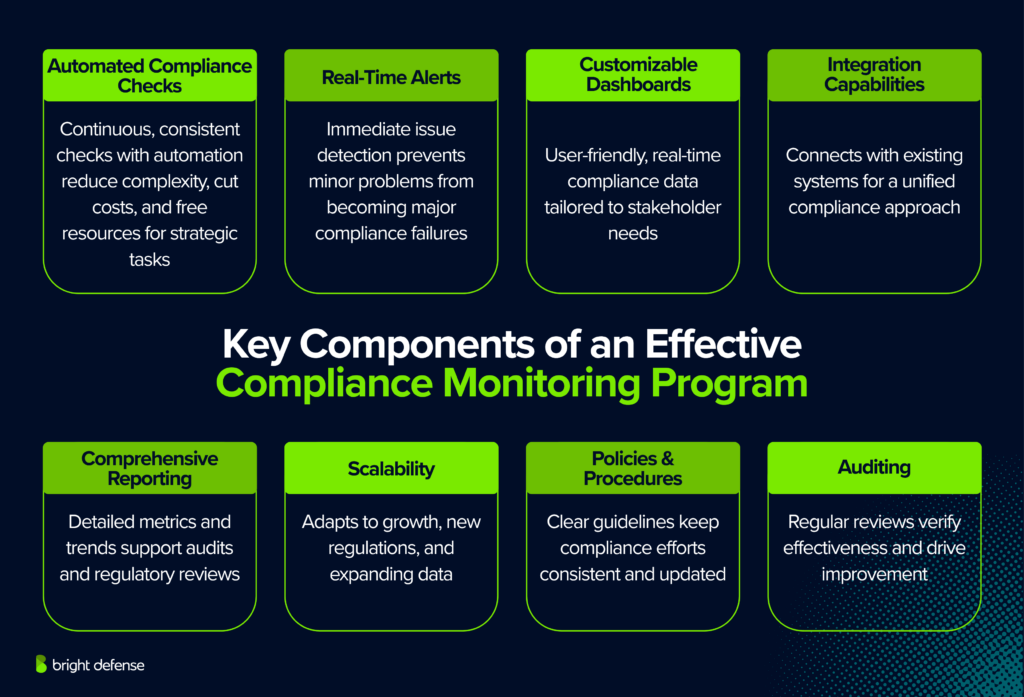
1. Automated Compliance Checks
Automation is a cornerstone of modern compliance monitoring, providing the ability to perform continuous, consistent checks without manual intervention. 65% of corporate risk and compliance professionals said automating manual processes with technology would cut both complexity and cost.
Automated systems scan for deviations from compliance standards and alert the necessary personnel to any anomalies. This not only increases the accuracy of compliance activities but also frees up resources to focus on more strategic tasks.
2. Real-Time Alerts
Real-time alerts are essential for immediate identification and response to potential compliance issues. 23% of security leaders are already monitoring partners and vendors in real time for cybersecurity threats.
Real time alerts enable organizations to address problems as they arise, preventing minor issues from escalating into significant compliance failures. This rapid response capability is critical in maintaining uninterrupted compliance and ensuring that corrective actions are taken swiftly.
3. Customizable Dashboards
Customizable dashboards provide a user-friendly interface for viewing real-time data on compliance status. These dashboards can be tailored to show key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to different stakeholders within the organization, from IT staff to executive management.
4. Integration Capabilities
A robust compliance monitoring system must seamlessly integrate with existing organizational systems and software. This integration ensures that compliance processes are embedded within all business operations, facilitating a unified approach to compliance management.
Effective integration also helps in maintaining a holistic view of the organization’s compliance posture across various departments and functions.
5. Comprehensive Reporting
Comprehensive reporting capabilities are vital for tracking compliance over time and preparing for audits. These reports should provide detailed insights into compliance metrics, highlight trends, and identify areas needing improvement.
Such documentation is invaluable not only for internal review but also for demonstrating compliance to regulators and other external stakeholders.
6. Scalability
As organizations grow and evolve, their compliance monitoring systems must adapt accordingly. Scalability ensures that the system can handle increased loads and complexity without compromising performance.
This means adding new regulations, more extensive data sets, or additional business units without disrupting existing compliance processes.
7. Compliance Policies and Procedures
A strong compliance monitoring program is built on well-defined policies and procedures. These documents outline how compliance is maintained daily, providing clear guidelines for all organizational activities related to compliance.
To be effective, these policies and procedures should be clearly written, easily accessible, and regularly updated to reflect changes in both regulations and business operations.
8. Auditing
Regular auditing is essential to verify the effectiveness of compliance policies and procedures. Audits help identify compliance gaps and inconsistencies, providing opportunities for continuous improvement.
Effective auditing involves scheduled reviews and random checks, ensuring that the organization adheres to both internal standards and external regulatory requirements. This rigorous approach not only reinforces compliance but also underscores the organization’s commitment to operational integrity.
Challenges in Implementing Compliance Monitoring
While compliance monitoring is a crucial component of modern business strategy, implementing it effectively presents a number of challenges. Understanding these obstacles is the first step toward developing strategies to overcome them.
Here are some of the most common challenges businesses face when setting up a compliance monitoring system:
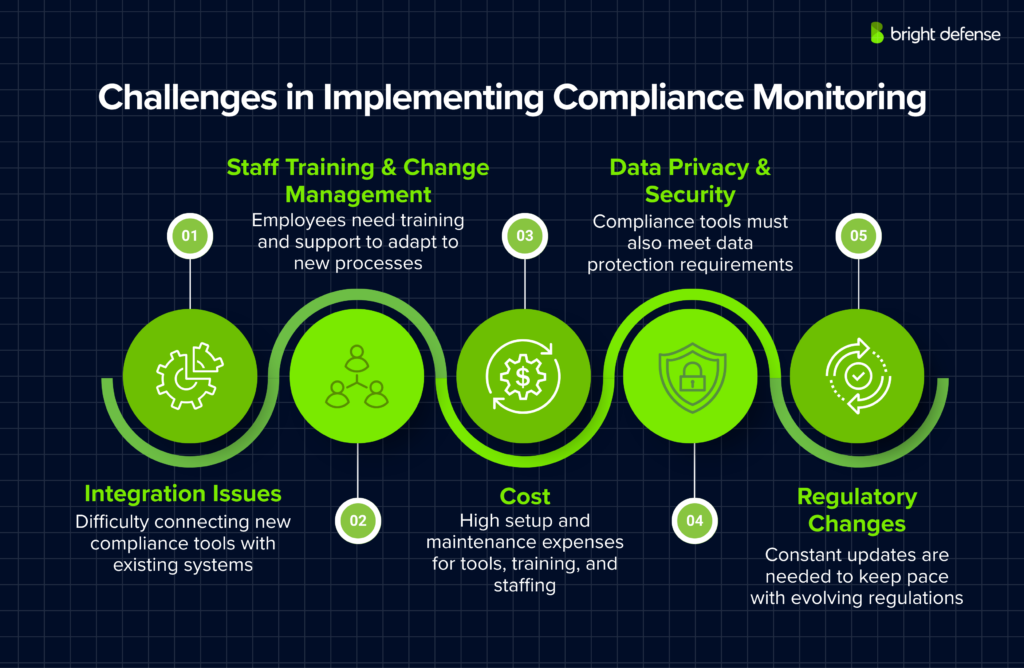
1. Technological Integration Issues
One of the primary challenges is integrating new compliance monitoring tools with existing systems. Organizations often use a variety of software solutions that may not be immediately compatible with new compliance technologies.
Ensuring these systems work harmoniously requires careful planning, potentially significant modifications to existing infrastructures, and sometimes, the adoption of new technologies.
2. Staff Training and Change Management
Implementing a new system is as much about managing people as it is about managing technology. Employees need to be trained not only on how to use new tools but also on the importance of compliance monitoring.
Additionally, change management practices must be employed to help staff transition from old methods to new procedures, which can be a significant hurdle in organizations with a strong adherence to traditional practices.
3. Cost Considerations
The initial cost of setting up a comprehensive compliance monitoring system can be high. This includes the expenses related to purchasing software, integrating systems, training employees, and possibly hiring new staff or consultants.
Businesses need to consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term benefits and savings associated with improved compliance and security.
4. Data Privacy and Security
With the increased collection and monitoring of data, there are heightened concerns about data privacy and security. Organizations must ensure that their compliance monitoring systems themselves comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
5. Keeping Up with Regulatory Changes
The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, and keeping a compliance monitoring system up to date can be challenging.
Organizations must continuously update their systems to adapt to new or amended regulations, which can be resource-intensive and require ongoing attention from compliance and IT teams.
Overcoming These Challenges
To effectively tackle these challenges, organizations can adopt several strategies:
- Invest in Scalable Solutions: Choose compliance monitoring tools that can grow and adapt with the organization and easily integrate with existing systems.
- Prioritize Training and Support: Develop comprehensive training programs and ongoing support for employees to help ease the transition to new systems.
- Plan Financially: Budget for both the initial setup and ongoing costs of the compliance monitoring system, considering potential ROI from avoiding non-compliance penalties and operational disruptions.
- Enhance Security Measures: Implement and regularly update security protocols to protect data integrity and privacy within the compliance monitoring system.
- Stay Informed: Regularly review and adjust compliance strategies to align with current regulations, leveraging updates from regulatory bodies and industry best practices.
Essential Tools for Effective Compliance Monitoring
In the realm of regulatory compliance, leveraging the right tools can significantly streamline processes, enhance security, and ensure continuous adherence to standards. Organizations across industries can benefit from a diverse array of tools designed to automate compliance tasks, manage user identities, train employees, and more. Below, we explore some of the key categories and specific tools that help businesses maintain robust compliance systems.
1. Compliance Automation Tools
These tools are specifically designed to reduce the complexity of achieving and maintaining compliance with regulatory frameworks by automating continuous monitoring and evidence collection.
- Drata: Drata’s compliance management software automates the compliance monitoring process, significantly reducing the effort required to track and manage adherence to standards such as SOC 2 and ISO 27001. It provides real-time insights and automated evidence collection to streamline audit preparation and sustain compliance transparency.
- Vanta: Vanta focuses on security and compliance automation, offering features that automatically track system changes and assess them against compliance criteria for frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA. Their tool simplifies the process of preparing for audits by continuously scanning for vulnerabilities and compliance drift.
- Secureframe: Secureframe streamlines the path to obtaining and maintaining SOC 2 and ISO 27001 certifications with its suite of integrated compliance tools. It helps manage the complexities of compliance by providing continuous monitoring and automated control assessments, reducing the time and effort involved in audits.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Tools
Effective management of user access is critical for maintaining the security and integrity of data systems, playing a crucial role in compliance.
- JumpCloud: Offers a comprehensive open directory platform that manages and secures user access across any device, enhancing an organization’s ability to comply with stringent security standards while simplifying user management.
- Okta: Provides robust identity management solutions that ensure secure and compliant user access, supporting automated compliance processes across multiple applications and environments.
3. Security Awareness Training Automation Platforms
Educating employees on security best practices is essential for a comprehensive compliance strategy. These platforms automate the training process, ensuring continuous employee education and compliance.
- KnowBe4: This platform automates the management of security awareness training and simulated phishing tests, crucial for preparing employees to recognize and respond to security threats, thereby supporting an organization’s overall compliance framework.
- Proofpoint Security Awareness Training: Helps organizations manage the human element of security by automating the delivery of targeted training programs and measuring the effectiveness of these programs in enhancing employee awareness and compliance.
4. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
SIEM tools play a vital role in the continuous monitoring of security events, crucial for maintaining compliance and managing risks.
- Splunk: Provides powerful real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities that enhance an organization’s ability to meet compliance and security requirements.
- IBM QRadar: Offers extensive security intelligence capabilities that help protect business assets while complying with complex regulatory requirements.
5. GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) Platforms
These platforms offer a holistic approach to managing governance, risk, and compliance, essential for maintaining an overarching compliance posture.
- MetricStream: Provides a comprehensive suite of GRC solutions that facilitate robust compliance management across the organization.
- RSA Archer: Features configurable GRC tools that automate risk management and compliance processes, streamlining compliance across various frameworks.
6. Data Protection and Privacy Management Tools
These tools ensure that organizations adhere to data protection laws and manage the privacy of sensitive information effectively.
- OneTrust: Helps businesses comply with international regulations like GDPR by managing privacy, security, and third-party risks through a unified platform.
- TrustArc: Offers tools for privacy management and compliance, ensuring that organizations can meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining trust with their customers.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the complexities of regulatory compliance requires more than adherence to rules. It demands a strategic integration of robust tools across the organization. Businesses can maintain a sustainable compliance posture by utilizing compliance automation tools, identity management systems, and security awareness training platforms.
The right tools streamline compliance processes, ensure continuous monitoring, and fortify the human element of security, creating a proactive environment where compliance is integrated into daily operations. As regulations evolve and complexities increase, adopting these sophisticated tools is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and maintaining stakeholder trust. This strategic approach mitigates risks and positions businesses for long-term success in an ever-changing regulatory landscape.
Bright Defense Delivers Continuous Compliance Monitoring!
If you are ready to implement continuous compliance, Bright Defense can help. Our monthly engagement model combines our vCISO expertise with compliance automation to help you meet frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI, CMMC, and more. We help you build the policies and procedures to meet your compliance requirements and work with you through the audit process and beyond.
FAQs
Compliance monitoring is the ongoing process of checking and verifying that an organization’s operations meet all relevant regulations and internal policies. It involves routine reviews or tests to ensure compliance and to identify any areas of non-compliance early.
In the context of AP Government, compliance monitoring refers to activities by bureaucratic agencies to ensure that companies or other regulated entities are following laws, regulations, and requirements as intended by public policy. It’s essentially the bureaucracy checking that those under its jurisdiction comply with external standards or rules.
Compliance monitoring is continuous, meaning it’s an ongoing activity, not a one-time check. It is dynamic, as it adjusts to regulatory changes and operational shifts. It is also collaborative, involving compliance officers, management, and employees working together. It is risk-focused, targeting high-risk areas for closer monitoring. It is technology-driven, using tools and software for real-time tracking and reporting.
A compliance monitoring report details the findings from compliance checks. It includes identified risks, compliance status, areas of non-compliance, and suggested actions to resolve issues. This helps organizations understand their compliance position and take necessary steps to improve it.
Internal monitoring involves continuous review of daily operations to spot and fix compliance risks as they arise. Compliance auditing is a formal, periodic evaluation to check if regulations are followed and to assess the effectiveness of the compliance monitoring system.
Compliance monitoring is important because it helps catch and correct issues early, ensuring the organization’s activities remain within legal and policy bounds. This proactive oversight protects the organization from legal penalties and reputational damage, improves operational performance by addressing gaps, and demonstrates accountability to regulators and stakeholders.
Monitoring and enforcing compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule is the responsibility of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR). This federal office oversees adherence to HIPAA’s requirements and can take action if entities fail to comply.
The Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW) is the entity responsible for overseeing and monitoring institutional compliance with Public Health Service (PHS) policy.
Compliance monitoring introduces oversight and accountability for bureaucratic agencies, ensuring they implement policies as intended by lawmakers. However, this oversight can also pose a challenge to policy implementation by the bureaucracy, potentially slowing down or complicating an agency’s ability to carry out policies efficiently. In sum, it holds the bureaucracy accountable but may constrain how freely agencies can operate.
Get In Touch



