
250+ Cybercrime Statistics for 2026
Get the facts on the latest cybercrime statistics, updated till May 2025. This report provides key data on current cyberattack trends and vulnerabilities, helping you understand and mitigate digital risks.

1. Global Financial Impact
- Global cybercrime costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- Cybercrime costs are growing by 15% each year leading up to 2025. ( Cybercrime Magazine )
- By 2027, cybercrime is projected to cost the world $23 trillion (a 175% increase from 2022). (MSSP Alert)
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) reports that cybercrime ranks as the third-biggest economy globally, trailing only the United States and China. (World Economic Forum )
- Americans reported $12.3 billion in cybercrime losses in 2023. (FBI IC3)
- The global average cost of a data breach fell to USD 4.44 million in 2025, compared to USD 4.88 million in 2024, representing a 9 percent decline. (Data Breach Stats 2025 – Bright Defense)
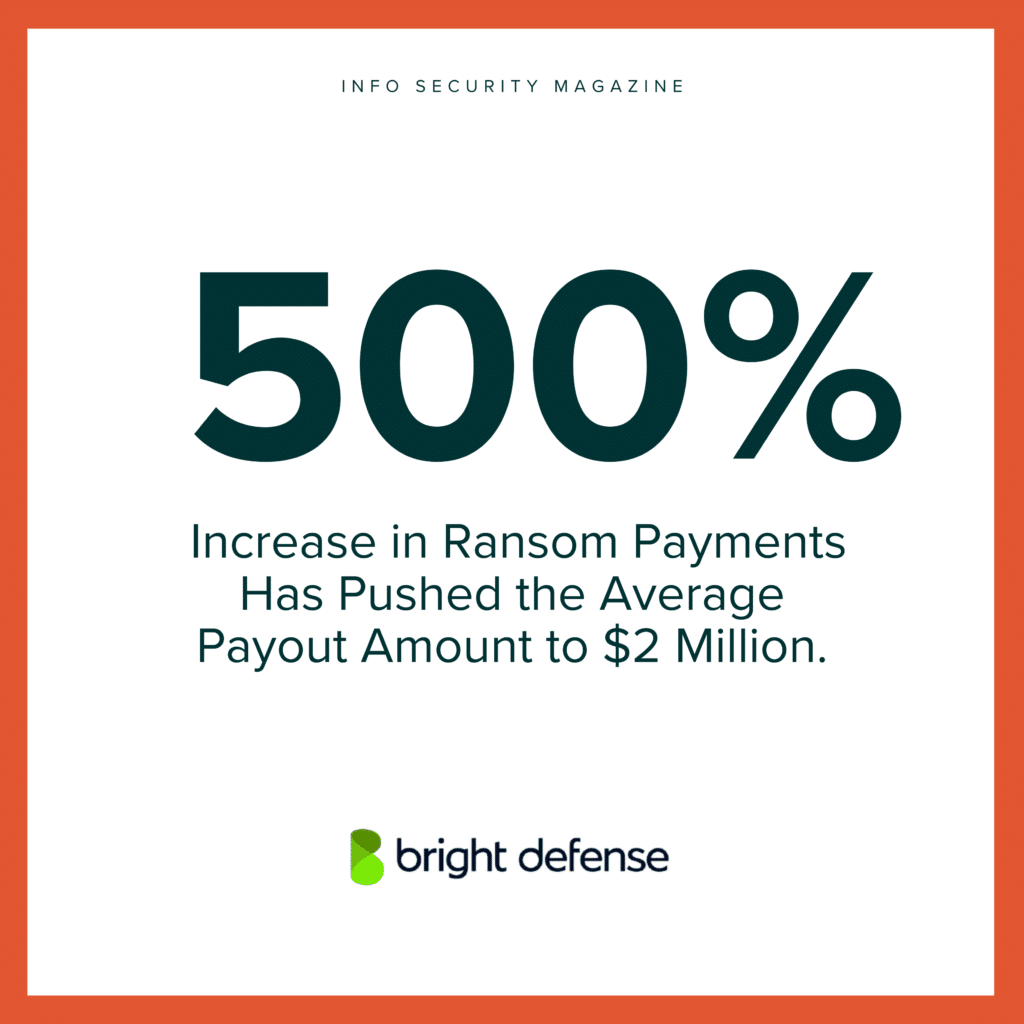
- Ransom payments have increased by 500%, reaching an average of $2 million. ( Info Security Magazine)
- Cyber insurance premiums are projected to grow from $14 billion in 2023 to $29 billion by 2027. (Munich RE)
- Ransomware damages are expected to hit $265 billion annually by 2031. (Cybersecurity Ventures)
- Claims from businesses earning less than $25 million in revenue dropped by 4%, averaging $73,000 per incident. However, businesses earning between $25 million and $100 million saw a 23% rise in claims, with average losses hitting $129,000 per incident. ( The HIPAA Journal)
- Investment scam losses grew 38% between 2022 and 2023 (from $3.31 billion to $4.57 billion) (FBI IC Report).
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) caused over $2.9 billion in losses in 2023 (21,489 complaints). (FBI IC Report).
- In Ransomware attacks only 32% of the total financial impact is from the ransom itself, most costs come from other damages. (Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- Nearly 80% of large enterprises worldwide plan to raise cybersecurity budgets to offset mounting breach costs. ( Gartner )
- Small and medium-sized businesses allocate between 5% and 20% of their overall IT budget to cybersecurity. ( Strong DM )
- Average ransom payment in Q4 2023: $568,705.
- The global cybersecurity market is projected to reach $424.97 billion by 2030 (13.8% CAGR from 2024).( Grand View Research )
- Companies spend an average of $2,700 per employee annually on cybersecurity measures. (Deloitte)
- The cryptojacking solution market is expected to grow from $17.02 billion in 2023 to $64.87 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.2%. ( Future Market Insights )
- The average ransom payment in 2024 reached $2.73 million, nearly $1 million higher than in 2023. (Varonis)
- Global spending on information security is forecasted to reach $212 billion, a 15.1% increase compared to 2024. ( Elisity )
- The technology industry was the most targeted by hackers for the seventh year in a row. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- The median ransom demand was 1.34% of the victim organization’s revenue. For 80% of ransomware demands, the percentage of revenue demanded ranged between 0.13% and 8.30%. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Only 4% of ransomware complaints in the FBI’s IC3 data involved actual financial loss, down from 7% last year. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Ransomware/extortion actions made up 62% of financially motivated breaches. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Financial penalties from phishing attacks rose 144% year-over-year. (Proofpoint State of the Phish Report 2024)
- According to a survey by Accenture involving 600 bank cybersecurity executives, 80% believe that generative AI is empowering hackers faster than their banks can respond. ( Business Insider )
- Global average cost: $4.88M (up 10% from $4.45M in 2023. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
2. Frequency & Scope of Cyber Attacks
- One cyberattack occurs every 39 seconds on average, according to real-time threat monitoring. ( Cobalt)
- The FBI’s IC3 received 880,418 complaints in 2023 (10% increase from 2022). (FBI IC3)
- Cybercrime losses reported to the FBI increased 22% between 2022 and 2023. (FBI IC3)
- Global cyberattacks rose by 30% in Q2 2024 vs. Q2 2023 (the highest jump in two years). (Cobalt)
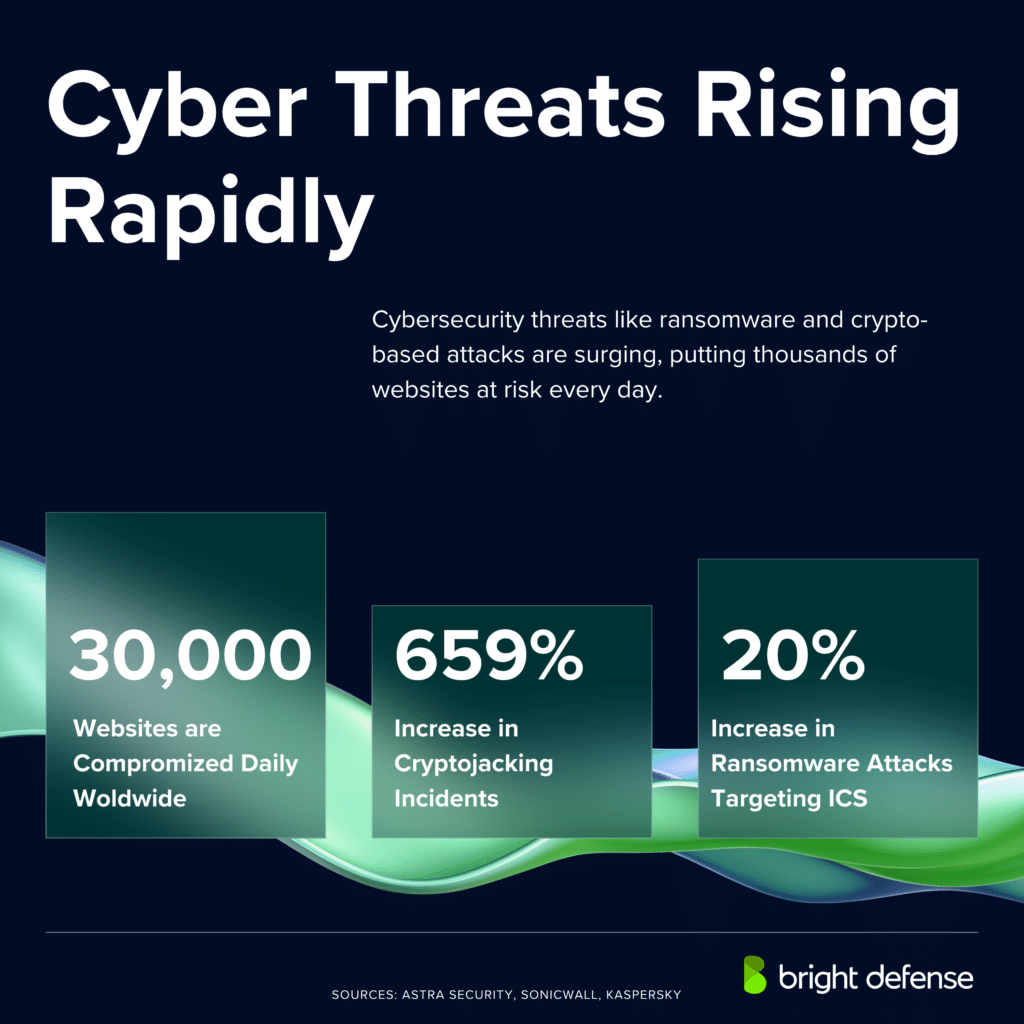
- 30,000 websites are compromised daily worldwide. ( Forbes )
- 236.1 million successful ransomware attacks occurred globally in H1 2022. ( AAG )
- Ransomware attacks in the U.S. increased by 22% in 2023, while related costs rose 74% from 2022. (FBI IC3)
- Supply chain attacks climbed 42% in 2024, targeting weaker vendor security protocols. ( Purplesec )
- In 2023, ransomware attacks impacted 81% of surveyed organizations, with nearly half (48%) opting to pay the ransom. ( Cobalt )
- Top Threats by Industry:
- Public Sector: 57% of threats come from unsafe networks.
- Financial Services: 68% of threats are due to sideloaded apps.
- Healthcare: 39% of mobile threats are phishing-related.
- Retail: 48% of threats come from mishing attacks. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Intrusions targeting cloud environments rose by 75% within the last year. ( National University )
- Over 6,000 new software vulnerabilities were added to the NIST database in the first half of 2024. NIST NVD
- According to AV-TEST, over 450,000 new malware and potentially unwanted programs are detected every day, with the total number of known samples surpassing 1.56 billion as of March 2025. Each month, an average of 14 to 16 million new threats are discovered. Windows remains the most targeted platform, while threats on Android and macOS continue to grow but stay far behind in volume. (AV-TEST Institute )
- The rise in mobile network threats is clear, with a 45% increase in devices connecting to unsecured networks, a 100% spike in rogue access point connections, and one-third of threats caused by man-in-the-middle attacks. Plus, each device now connects to an average of 17 risky networks annually.
( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024) - Massive Spike in DDoS Attacks: Up 550% in 2024 Amid AI Use and Global Tensions ( Security Brief)
- 79% of organizations experienced at least one API-related attack in 2023. ( The HIPAA Journal)
- Over 859,000 malware samples were found in the wild by researchers. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 83% of phishing websites were designed specifically to go after mobile users. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 80% of iOS versions in 2023 had at least one known exploit during the year. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 70% of companies aren’t doing enough to secure employees’ personal devices used for work. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 71% of workers admit they’ve knowingly taken risky actions on their devices. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 90% of successful cyberattacks begin from endpoint devices like phones or laptops. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Apps downloaded from outside official app stores are 200% more likely to contain malware. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- In 2024, once a hacker broke into a system, it took them just 48 minutes on average and in the fastest case, only 51 seconds to start moving deeper into the network. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- The number of online ads offering to sell stolen access to companies rose by 50%. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- 35% of cloud-related cyber incidents happened because hackers got hold of real user login details. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- In 2024, the North Korea-linked group FAMOUS CHOLLIMA was responsible for 304 security incidents, nearly 4 out of 10 involving an insider, used 7 types of custom-built malware, and in one case, tricked a company into transferring $25.6 million using a deepfake video of its CFO.
( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 ) - Cyberattacks linked to China rose by 150% overall in 2024, with some industries like media, manufacturing, and finance seeing increases of up to 300%, even as heavily targeted sectors experienced another 50% surge, and CrowdStrike identified seven new Chinese hacker groups during the year. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
3. Ransomware & Malware Trends
- 72.7% of organizations were hit by ransomware attacks in 2023. (Statista)
- 1 in 4 protected devices encountered malware during the year. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Only 54% of organizations recover their data after paying ransom. (Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- Cloud-based attacks grew by 26% in 2024, showing that hackers are paying more attention to cloud systems. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- Hackers got into cloud systems most often by using stolen usernames and passwords, which were behind 35% of all cloud-related incidents in the first half of the year. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- Users who sideload apps are 200% more likely to end up with malware. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Nearly 8 out of 10 cyberattacks in 2024 didn’t use any malware, meaning hackers used other methods like stolen passwords or pretending to be real users. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- Vishing attacks, where hackers call victims pretending to be IT support, exploded by 442% from the first half to the second half of 2024. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- The number of hands-on attacks, where hackers manually take action after breaking in, grew by 35% compared to the year before. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- Riskware (73%) and Trojans (11%) dominate sideloaded malware. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Pure Extortion techniques accounted for 9% of breaches. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- In 8.3% of mobile malware cases, the source was a sideloaded app. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- AI generated phishing emails, those fake messages designed to steal your login info, tricked 54% of people into clicking, while only 12% fell for ones written by humans.
( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 ) - Ransomware and Extortion attacks made up 32% of breaches. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Ransomware alone was responsible for 23% of breaches. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- The median financial loss for ransomware victims who paid was $46,000. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- The smallest reported ransomware loss was $3, and the largest was $1,141,467. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Business Email Compromise (BEC), mostly resulting from Pretexting, appeared in 24% to 25% of financially motivated breaches. The median BEC loss was approximately $50,000. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- 43% of Android devices in the APAC region sideload apps. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- By October 2024, there have already been 137 confirmed ransomware attacks, each causing an average of 11 days of downtime. ( Info Security Magazine )
- Ransomware was listed as a top threat in 92% of industries. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- As your backups become more valuable, they’re also becoming a bigger target. In fact, 96% of attacks now go after backup repositories, and in 76% of those cases, attackers manage to compromise them.(Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- 43% of data impacted by ransomware is ultimately unrecoverable. (Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- The median ransom demand equaled 1.34% of the company’s revenue. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- For 80% of cases, ransom demands ranged between 0.13% and 8.30% of revenue. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- 75% of organizations report multiple cyberattacks (not just once). (Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- 41% of production data is encrypted/affected during attacks. (Veeam Ransomware Trends Report 2024)
- 79% of cyber detections were malware-free, indicating more sophisticated, fileless methods. ( CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024 )
- Phishing was the most common type of intrusion, affecting 76% of organizations, up from 49% last year. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Business email compromise appeared as a new intrusion category in 2024 and impacted 65% of surveyed organizations. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Ransomware and wiper attacks affected 56% of organizations, increasing from 32% the year before. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- DDoS attacks doubled in frequency compared to the previous year. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Malware incidents declined to 38%, down from 56%. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Cryptojacking incidents surged 659% in 2023 (1.06 billion attacks). ( SonicWall )
- In the past year, 31% of organizations experienced six or more cybersecurity intrusions, up sharply from 11% the year before, with all types of intrusions increasing in frequency except for malware, which declined. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- In 2024, Kaspersky detected 33.3 million attacks on smartphone users globally. (Kaspersky)
- On average, cybercriminals launched 2.8 million malware, adware, and unwanted software attacks on mobile devices every month in 2024. (Kaspersky)
- Scams and malvertising made up 87% of all desktop-related threats. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- On mobile devices, scams and malvertising accounted for 93% of threats. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- Web-based threats represented 95% of all threats detected. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- Trojan banker attacks on Android smartphones tripled from 420,000 in 2023 to 1,242,000 in 2024, accounting for 6% of all attacked users and ranking fourth among mobile threats despite their rapid growth. (Kaspersky)
- AdWare was the most common threat in 2024, accounting for 57% of all attacked users, followed by General Trojans at 25% and RiskTools at 12%. (Kaspersky)
- In 2024, Fakemoney scam apps were the most active mobile threat. (Kaspersky)
- Kaspersky reported a 20% rise in ransomware attacks targeting industrial control systems (ICS) in Q2 2024 compared to the previous quarter, with Africa seeing the highest ICS exposure at 30%, followed by the Middle East at 25%. ( Kaspersky )
- Over 1 billion unique attacks were blocked each month in Q2 2024. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- There was a 46% year-over-year increase in attacks. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- More than 1 million users were protected from fake scan scams during the quarter. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- The top 10 countries with the most fake scan attacks blocked were Brazil, the United States, France, Germany, Spain, Mexico, Italy, Poland, the United Kingdom, and Argentina. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- Ransomware attacks increased by 24% compared to the previous quarter. Ransomware spikes were highest in India (379%), followed by the US, UK, and Canada (each 100%), and Australia (66%). (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- AgentTesla accounted for 33.84% of all information stealer malware, with an 11% increase in activity. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- The most common information stealers in Q2 2024 were AgentTesla, Ramnit, FormBook, Fareit, RedLine, Vidar, Azorult, Lumma, Lokibot, and ViperSoftX. (Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report)
- Ransomware actors often gain entry through unpatched vulnerabilities, sometimes within days of a patch being released. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- After one year, 8% of critical vulnerabilities remained unpatched, leaving the door open for ransomware attacks. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities, often linked to ransomware, grew by 180% year over year. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
4. Phishing & Social Engineering Cybercrime Statistics
- Phishing emails increased by 341% in the past six months. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Over the past 12 months, phishing emails have surged by 856%. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Since the launch of ChatGPT in November 2022, phishing emails have risen by a staggering 4151%. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- According to OpSec Security, social media platforms faced the highest number of phishing attacks in Q2 2024, making up 30.5% of all incidents. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- SaaS and webmail services accounted for 21.2% of phishing attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Financial institutions were targeted in 13% of phishing attacks. eCommerce and retail sectors made up 8% of phishing attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Payment services were targeted in 5.8% of phishing attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Text-based Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks increased by 29% since January 2024. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Smishing now accounts for 45% of all mobile threats. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Credential phishing has grown by 217% since October 2023. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- QR-based phishing now makes up 11% of all email phishing threats. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Generative AI has significantly contributed to the rise of phishing and BEC attacks. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- On average, users click on a malicious link just 21 seconds after opening the email. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- It takes only another 28 seconds for users to enter their data after clicking the link. Microsoft SharePoint, AWS, and Salesforce are the most commonly used trusted services for phishing and malware hosting. CAPTCHA-based attacks are on the rise, being used to hide credential harvesting forms. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- Attackers are now targeting multiple channels including email, SMS, Teams, and Slack. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- By 2026, 90% of online content could be AI-generated. (SlashNext 2024 State of Phishing Report)
- 82% of phishing sites are designed specifically for mobile users. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 76% of phishing sites now use HTTPS, making them appear more legitimate. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Loan scams accounted for 4.5% of scam activity. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Interac scams made up 3.8% of all scam activity. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Phishing sites using .dev domains accounted for 40% of detections in 2023. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- Mishing is the 2nd most expensive attack, costing organizations an average of $4.76 million per incident. ( Zimperium Mobile Threat Report 2024)
- 932,923 phishing attacks were reported in Q3 2024. This was an increase from 877,536 phishing attacks reported in the second quarter of 2024. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Phishing was responsible for 41% of data security incidents in 2023. (Verizon DBIR 2024)
- In 2023, 71% of organizations fell victim to phishing, 73% faced Business Email Compromise attacks, yet only 29% trained their users specifically to spot BEC threats. (Proofpoint State of the Phish Report 2024)
- The telecom sector experienced 4.9% of phishing attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Logistics and shipping companies accounted for 3.1% of attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Travel services were targeted in 2.6% of attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Cryptocurrency services made up 2.4% of phishing attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Smishing, or phishing via SMS, increased by more than 22% in Q3 2024. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Vishing, or phishing through voice calls, increased by more than 28% in Q3 2024. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Gift card scams were the most common scam type, making up 40.4% of all scams. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Advance fee fraud scams made up 29.8% of reported attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Payroll diversion scams represented 6.6% of attacks. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Romance scams were responsible for 2.7% of phishing activity. (APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Cryptocurrency extortion scams made up 2.7% of scams, up from 0.6% in the previous quarter.(APWG Phishing Activity Trends Report 2024)
- Nearly all phishing attacks (96%) are sent by email. (National University)
Our article featuring 200+ verified phishing statistics offers the most current data on phishing trends. Check it out for a clear breakdown of the latest figures and insights.
5. Data Breaches & Exposure
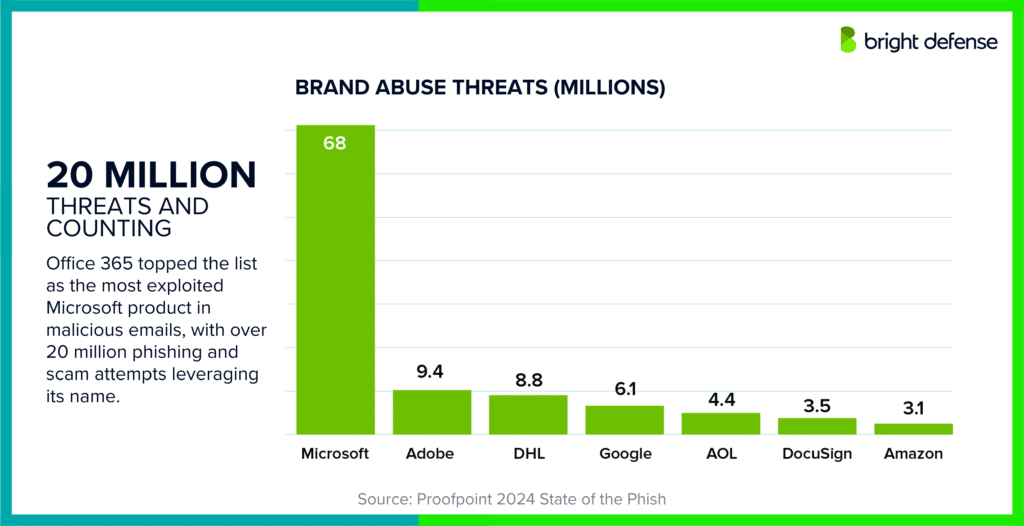
- 3,158 data compromises were tracked in 2024, with 1.3 billion victim notices (a 211% increase). (ITRC Annual Data Breach Report 2024)
- On average, it took organizations 258 days to identify and contain a data breach in 2024. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- The average cost per compromised record rose to $169 globally. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Breaches reported by attackers cost more, averaging $5.53 million, compared to $4.55 million when identified by internal security teams. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- More than 50% of organizations reported their breach within 72 hours, while 34% took longer than that.(IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Ransomware was responsible for 23% of confirmed data breaches, rose to 32% when combined with extortion, and was named a top threat in 92% of affected industries. (Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report)
- 16% of breaches were caused by compromised credentials, which led to an average cost of $4.81 million. 53% of breached organizations reported a high-level shortage of skilled cybersecurity personnel. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Nearly 1 billion emails were exposed in a single year, affecting 1 in 5 internet users. (Sprinto)
- Russia had the highest number of cybercrime incidents, topping the World Cybercrime Index with a score of 58.39. Ukraine followed in second place with a score of 36.44, while China came third at 27.86. ( Oxford University )
- In 2024, companies took an average of 194 days to identify data breaches, which is 4% faster than the year before. Containment took another 64 days. In comparison, it took 207 days to detect and 70 days to contain breaches back in 2022.( Statista )
- The healthcare sector experienced the highest breach costs, averaging $10.93 million in 2024. (Accutive Security)
- Nearly half (46%) of all breaches involved customer PII (releasing personal information online) (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- A decline in brand awareness was reported by 52% of respondents, a sharp increase from 34% in previous assessments, highlighting the growing reputational damage caused by cyberattacks. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Approximately 43% of organizations reported the loss of business-critical data or intellectual property, up from 34%, indicating a rise in the severity of breaches. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- As outlined in Fortinet’s 2024 State of Cybersecurity Report, 55% of respondents said their organization experienced productivity outages, making it one of the most widespread impacts of cyber incidents.
(Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024) - Revenue-impacting outages were reported by 52% of organizations, showing that the financial consequences of cyber incidents are becoming more common. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- 48% of respondents in the Fortinet’s 2024 cybersecurity study reported physical safety risks linked to cyber-related outages, pointing to how digital threats can cause real-world harm.
(Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024) - Compliance failures were experienced by 44% of organizations, potentially exposing them to legal consequences and regulatory penalties. (Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
- Only 3% of respondents in the 2024 State of Cybersecurity Report by Fortinet said their organization experienced no impact from intrusions, showing just how rare it is to remain untouched by cyber threats today.
(Fortinet State of Cybersecurity Report 2024)
Data breaches continue to surge, affecting businesses and users worldwide. Check out 120 data breach stats that reveal how often they happen, what causes them, and the scale of the damage.
7. Geopolitical & Regional Insights
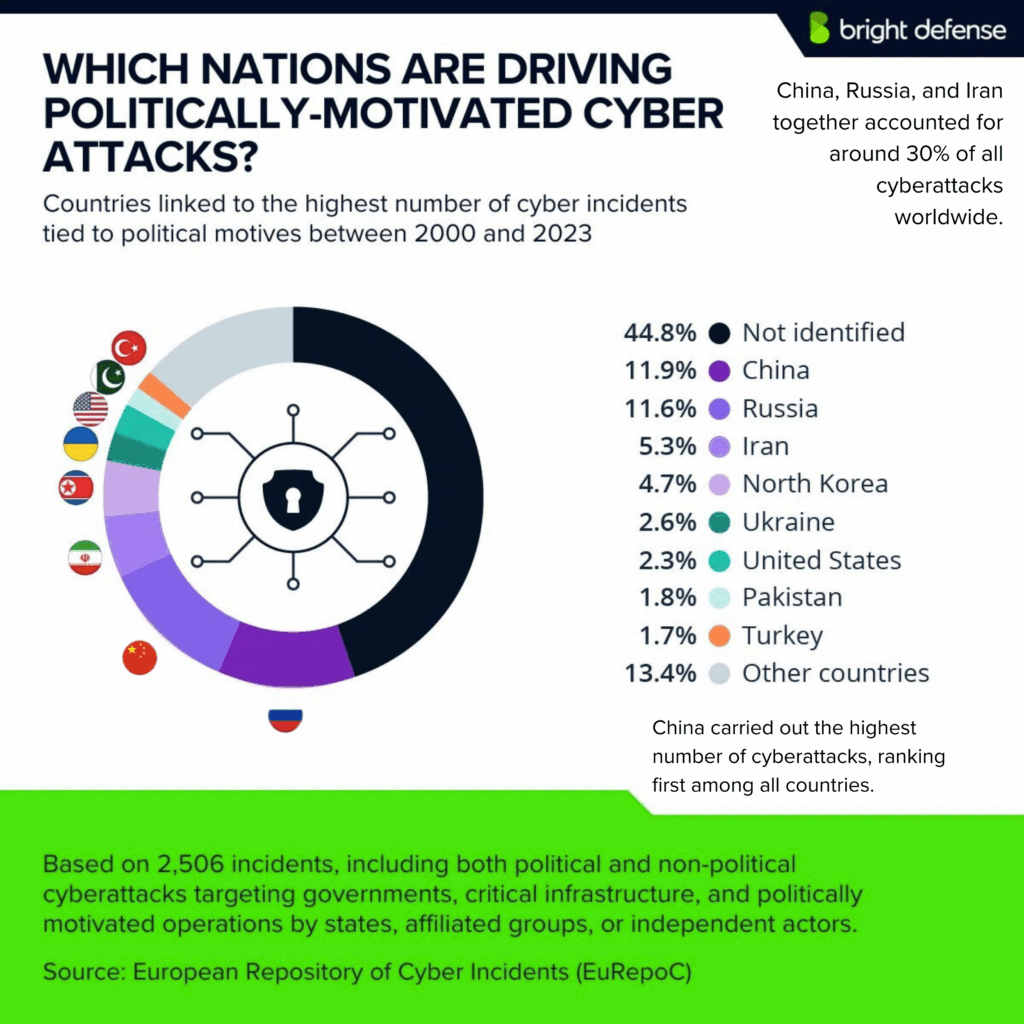
- State-sponsored attacks accounted for 35% of all breaches in 2024. (TechTarget)
- Cyberattacks within the European Union surged during the reporting period, with ENISA documenting approximately 2,580 incidents across member states. Of those, 220 specifically targeted two or more EU countries simultaneously. ( ENISA Threat Landscape )
- India saw a 115% surge in cyberattacks in Q2 2024 vs. Q2 2023.(Indusface)
- Latin America faces higher cyberattack rates compared to global averages, with organizations experiencing nearly 40% more attacks weekly (Dark Reading)
- In the lead-up to its invasion, Russia intensified cyber operations starting in 2021. By 2022, Russian government-backed attackers had increased their targeting of Ukrainian users by 250% and users in NATO countries by over 300% compared to 2020. ( Google Blog)
- Brazil ranks as the world’s second most targeted nation for cyberattacks, trailing only the United States. (Forbes)
- UK remains a significant target for cyberattacks, with a 100% increase in ransomware incidents in Q2 2024 compared to the previous quarter. (Statista)
- In February 2025, North Korean state-sponsored hackers executed the largest cryptocurrency heist to date, stealing approximately $1.5 billion in Ethereum from the Dubai-based exchange Bybit. (Wikipedia)
Cybersecurity never stands still. Take a look at 200+ security stats that capture the latest trends, risks, and defenses shaping today’s digital world.
8. Emerging Threats & Future Projections
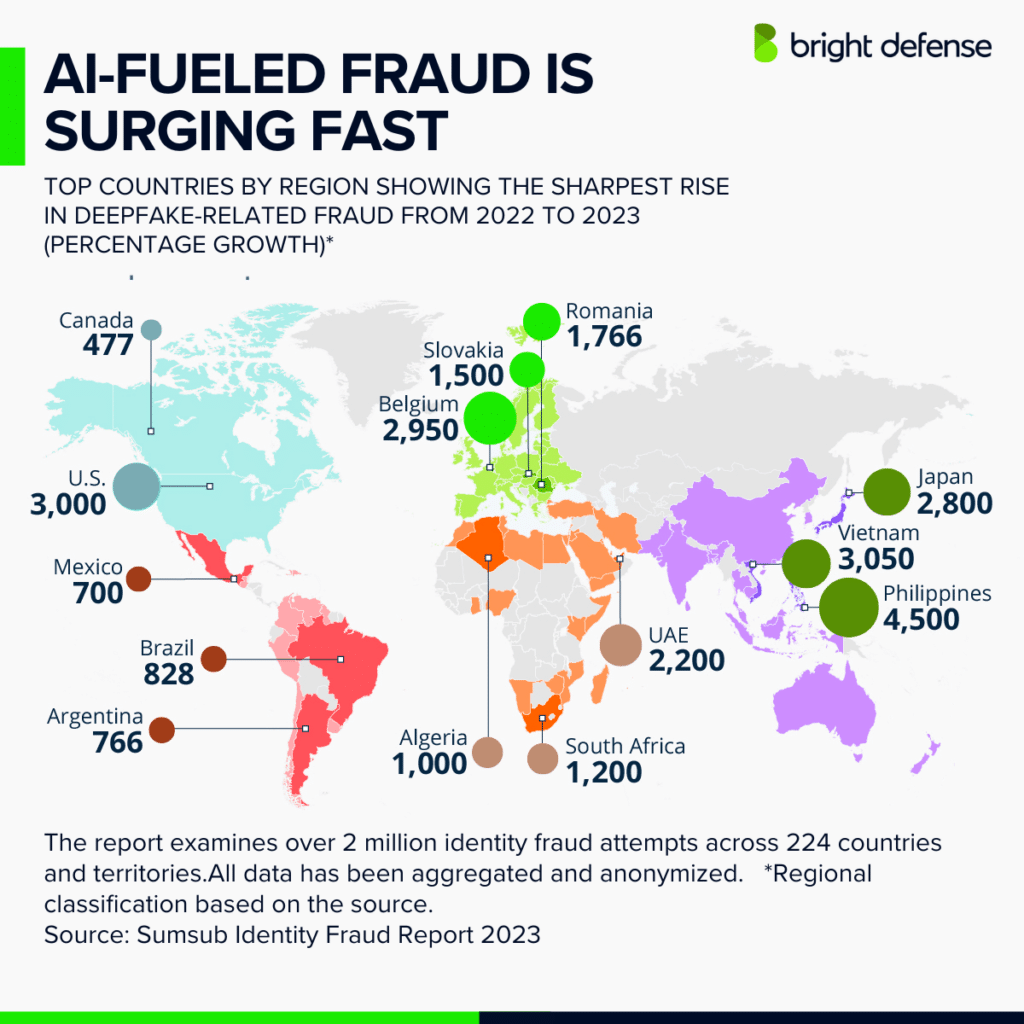
- 31% of organizations reported using AI and automation extensively in their security operations in 2024. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Organizations that didn’t use AI and automation faced an average breach cost of $5.72 million, while those with extensive usage saw the cost drop to $3.84 million. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- Using AI and automation reduced the breach identification and containment time by nearly 100 days on average. (IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
- In the first half of 2023, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks on IoT devices surged by 300%, resulting in global financial losses of $2.5 billion. (Breach Lock)
- IoT and OT networks face a 107% year-over-year rise in cyberattacks. (Sonice Wall)
- As of early 2025, approximately 81% of organizations have either fully or partially implemented a Zero Trust model, with 19% still in the planning phase. (VM Blog)
- Approximately 31% of organizations have adopted a Zero Trust strategy as of 2024. (Statista)
- Approximately 26% of individuals encountered deepfake scams online in 2024, with 9% falling victim to them. (Spiralytics)
- There has been a notable surge in cyberattacks targeting vehicles. VicOne reports a 165% rise in deep and dark web activity connected to the automotive and smart mobility sectors. (Electronica)
- In Germany, cybercrime and sabotage have cost companies approximately €267 billion ($298 billion) over the past year, marking a 29% increase from the previous year. (Reuters)
- Cloud environments have become a primary target, with 72% of respondents in a World Economic Forum survey indicating an increase in cyber risks over the past year, including a rise in phishing and social engineering attacks. (World Economic Forum Reports)
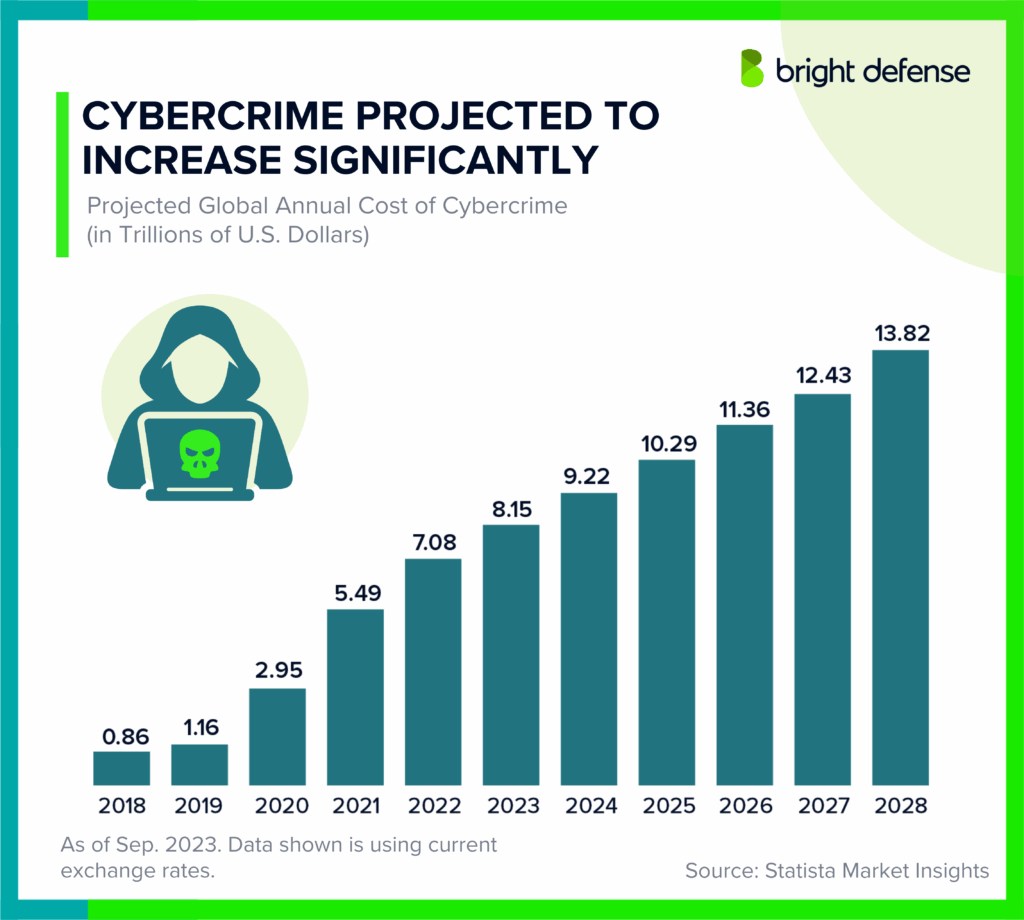
- The annual average cost of cybercrime is predicted to exceed $23 trillion by 2027, up from $8.4 trillion in 2022, indicating a rapidly escalating threat landscape. (Informa TechTarget)
- There is a growing concern over attacks on critical infrastructure, with state-sponsored hackers collaborating with civilian hacking groups to target utilities, transportation, and manufacturing sectors. (Axios)
- The global AI cybersecurity market is expected to grow from $22.4 billion in 2023 to $60.6 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 21.9%. (Cobalt: Offensive Security Services)
- A survey across 10 countries found that 2.2% of respondents had been victims of deepfake pornography, while 1.8% admitted to creating such content. (arXiv)
- Deepfake attacks are anticipated to rise by 50% to 60% in 2024, with an estimated 140,000 to 150,000 global incidents. (Cobalt: Offensive Security Services)
- Losses from deepfake-enabled fraud are projected to reach $40 billion annually by 2027, driven by advancements in generative AI. (Cybersecurity Dive)
- Many businesses lack protocols to handle deepfake attacks, with 80% of companies reportedly unprepared for such threats. (Security.org)
Data breaches keep making headlines, exposing millions of records from major companies and online platforms. Here’s a quick look at the latest data breach incidents and what was compromised.
9. Workforce & Defense Gaps
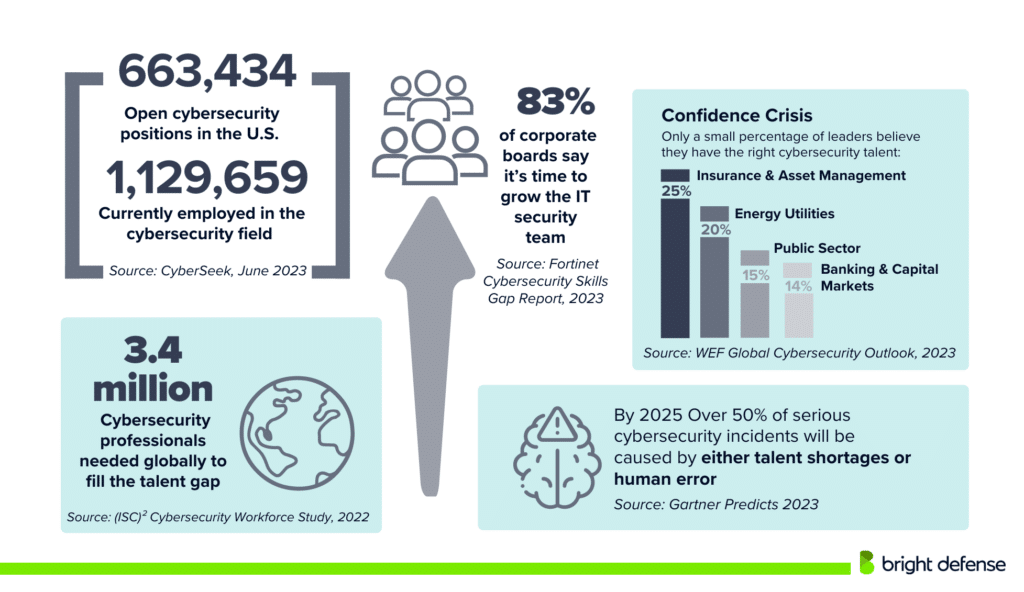
- A Fortanix report indicates that 97% of surveyed companies plan to either buy or build a GenAI solution to automate business processes or create new revenue streams. Concurrently, 87% of security executives reported a breach in the past 12 months, highlighting significant security concerns associated with GenAI adoption. (Security Magazine)
- 80% of executives cite AI-powered malicious attacks as the top emerging threat. (Tech Republic)
- SentinelOne reports that almost all (98%) cyberattacks use social engineering techniques, such as phishing or baiting, to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information. (Sentinel One)
- The 2024 ISC2 Cybersecurity Workforce Study reveals a 19% year-over-year increase in the global cybersecurity workforce gap, totaling approximately 4.8 million vacant positions. While the current workforce includes 5.5 million professionals, the industry requires 10.2 million to meet demand. (ISC2)
- With the global cybersecurity workforce estimated at approximately 4.7 million professionals and a median salary of $80,000, automating 30% of cybersecurity tasks could result in annual workload cost savings of $112 billion. (Watchguard)
- Over 77% of organizations do not have an incident response plan. (Packetlabs)
- Only 32% of businesses perform penetration testing annually or biannually, leaving a significant portion potentially vulnerable due to infrequent testing. (Elite Sec)
- A report by JumpCloud indicates that approximately half of all employees reuse the same passwords for work and personal accounts. (Jump Cloud)
- 74% of all breaches involve a human element, encompassing errors, privilege misuse, use of stolen credentials, or social engineering. (Secureframe)
- According to the Ponemon Institute’s 2023 Cost of Insider Risks Global Report, the average annual cost of insider threats reached $16.2 million per organization, marking a 40% increase over four years. (Sign Post Six)
- Organizations that extensively implemented AI and automation experienced a data breach lifecycle of 214 days, which is 108 days shorter compared to the 322-day lifecycle in organizations without these technologies. (Watchguard)
Cyberbullying has grown fast with the rise of new AI tools. You can review the latest cyberbullying data in our recent cyberbullying statistics report.
10. Cybercrime in Asia
Let’s check out some cybercrime statistics that occurred in different countries in Asia
Cybercrime Statistics for Japan

- There were 19,033 reported cases of cyber and phone scams in 2023 in Japan, an 8.3% increase from the previous year and the highest in a decade. (Source: Agenzianova)
- There were 197 reported ransomware cases in 2023 across Japan. (Source: NPA Japan)
- Between 2019 and 2024, over 200 cyberattacks targeting Japan’s defense and tech sectors were attributed to the Chinese hacking group MirrorFace. (Source: AP News)
- In October 2023, police arrested 18 individuals for laundering more than ¥100 million (~$714,000 USD) through Monero cryptocurrency. (Source: Tokyo Reporter)
- From January to September 2023 alone, credit card fraud caused losses of around ¥40.2 billion (~$287 million USD) in Japan, mostly due to phishing and stolen card data misuse. (Source: NPA Japan PDF)
- The average cost of a data breach for Japanese organizations was ¥460 million (~$3.29 million USD) in 2023. (Source: Infoblox)
- Notable incidents: Between 2021 and 2022, a wave of robberies in Japan was orchestrated by a group led by a man known as “Luffy,” who was directing operations from a detention center in the Philippines. (Source: Wikipedia)
- In 2023, four Japanese nationals associated with the Luffy group were extradited from the Philippines to face charges in Japan. (Source: Wikipedia)
- In 2023, Japanese police resolved over 12,400 cybercrime cases, marking the highest figure on record. (Source: Statista)
- Japan accounted for 23.4% of all deepfake-related crimes reported in Asia in 2023, second only to Vietnam. (Dark Reading)
Cybercrime Stats for India
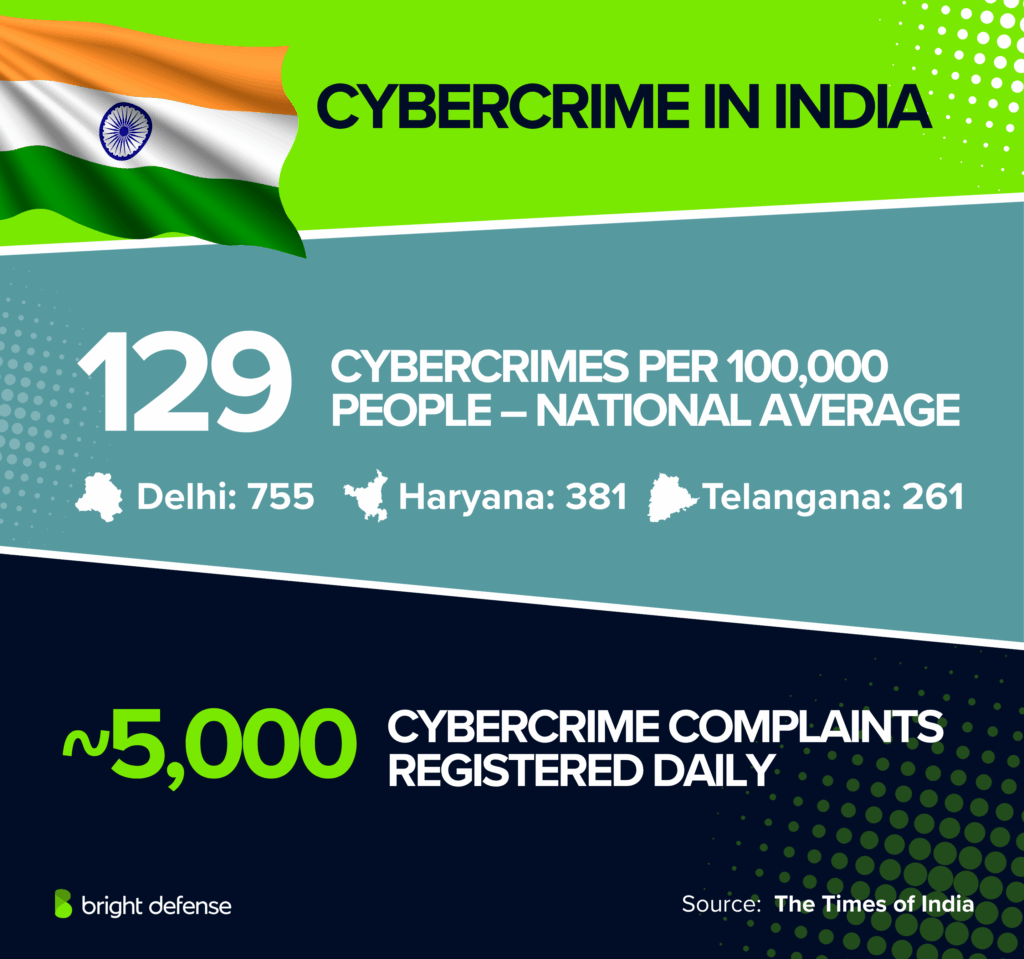
- Per Capita Incidence: The national average stood at 129 cybercrimes per 100,000 people. Delhi reported the highest rate with 755 cases per 100,000, followed by Haryana (381) and Telangana (261). (The Times of India)
- On average, about 5,000 cybercrime complaints were registered daily. (The Times of India)
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) reported approximately 1.59 million cybersecurity incidents in 2023, a significant rise from 53,117 incidents in 2017. (PWOnlyIAS)
- In the fiscal year 2023-24, high-value cyber fraud cases (involving amounts over ₹1 lakh) increased more than fourfold, resulting in losses exceeding ₹177 crore (approximately $20 million). (SecurityWeek)
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plans to revise guidelines to enable banks to temporarily freeze accounts suspected of cybercrime activities, aiming to address the surge in online fraud. (Reuters)
Cybercrime in Singapore

- Singapore reported 50,376 scam and cybercrime cases in 2023, a 49.6% increase from 33,669 cases in 2022. (ZDNET)
- Scams, including malware-enabled scams, accounted for 92.4% in Singapore, totaling 46,563 incidents. (Singapore Police)
- Victims lost approximately S$651.8 million in 2023, a slight decrease from S$660.7 million in 2022. (Reuters)
- Job Scams alone in Singapore saw 9,914 cases with losses totaling S$135.7 million. (CNA)
- E-commerce Scams: 9,783 cases resulting in S$13.9 million lost. (The Straits Times)
- Fake Friend Call Scams: 6,859 cases with S$23.1 million in losses. (Singapore Police Force)
- Phishing Scams: 5,938 cases leading to S$14.2 million lost. (Singapore Police Force)
- Investment Scams: 4,030 cases with the highest total losses at S$204.5 million. (Singapore Police Force)
- Authorities froze more than 19,600 bank accounts linked to scam activities, recovering over S$100 million. (Singapore Police Force)
- A new law enacted in January 2025 empowers police to freeze bank accounts of Singaporean scam victims to prevent further losses. (Reuters)
Cyber Attacks in China

- Cyberattacks in China resulted in estimated losses of $1.79 trillion in 2024, with projections indicating a rise to $2.16 trillion in 2025. (Sci-Tech Today)
- China accounted for approximately 17% of global data breaches in 2024, with nearly 1,800 accounts compromised per minute. (Cybernews)
- Increased Activity: State-backed cyber espionage activities surged by 150% in 2024, targeting sectors such as finance, manufacturing, media, and critical infrastructure. (Cyber Magazine)
- China experienced a substantial increase in cyber fraud cases in 2023. The Supreme People’s Procuratorate reported a 36.2% rise in computer crimes, including social media fraud, involving approximately 323,000 individuals. Telecom fraud indictments also surged nearly 67% to about 51,000 cases. (AP News)
- In response to the rise in overseas cybercrime, China intensified its crackdown on scam operations. Notably, over 1,200 Chinese nationals suspected of involvement in cybercrime were repatriated from Myanmar, reflecting China’s commitment to addressing cross-border cyber threats. (AP News)
Cybercrime Stats for Pakistan

- Cyber threats in Pakistan rose by 17% in 2023 compared to the previous year. Kaspersky reported blocking 16 million cyberattacks in the country during this period, with approximately 24.4% of users affected by online threats. (propakistani.pk)
- Global Cybersecurity Index Ranking: Pakistan advanced to a Tier-1 (Role-Modeling) rating in the 2024 Global Cybersecurity Index by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), placing it among the top 40 countries, reflecting significant progress in cybersecurity measures. (The Neutral)
11. Cyber Attacks in Europe
As one of the wealthiest and most digitally interconnected regions globally, Europe has become a prime target for cybercriminals seeking financial gain and influence.
With its vast digital infrastructure and economic power, the region faces a growing number of cyber threats.
Let us examine the current landscape of cyberattacks across Europe and evaluate how effectively it is positioned to confront these evolving challenges:
The State of Cybercrime in the UK

- In 2024, the Crime Survey for England and Wales (CSEW) estimated approximately 1.3 million incidents of computer misuse, which includes hacking and computer viruses. This represents a decrease compared to previous years. (Office for National Statistics)
- The CSEW estimated around 4.1 million incidents of fraud in 2024, marking a 33% increase compared to the previous year. (Office for National Statistics)
- Action Fraud received over 35,000 reports of social media and email account hacking in 2024. (Action Fraud)
- The total combined loss from ticket fraud increased nearly 50% from 2023 to £9.7 million in 2024. (Action Fraud)
- Holidaymakers lost a combined total of £11.18 million to holiday fraud in 2024, slightly less than the £12.3 million lost in 2023. (Action Fraud)
- In 2023, the Suspicious Email Reporting Service (SERS) received nearly 11.6 million reports of phishing emails, a 44% increase from 2022. (Action Fraud)
Cybercrime in Germany
- Cybercrime and sabotage inflicted approximately €267 billion ($298 billion) in damages on German companies in 2023, marking a 29% increase from the previous year. (Reuters)
- According to a Bitkom survey, 81% of companies reported being victims of data theft, espionage, or sabotage.(heise online)
- Phishing attacks were reported by 53% of affected German companies, attacks on cloud services by 42%, and data leaks by 37%. (KPMG)
- Approximately 45% of German companies attributed at least one cyber attack to China, and 39% to Russia. (Reuters)
- The clearance rate for cybercrime offenses in Germany increased by three percentage points in 2023, reaching 32.2%. (BKA)
- In a significant international operation named “Operation Endgame,” coordinated by Europol and involving Germany, authorities dismantled major ransomware networks, arrested four suspects, and took control of over 2,000 internet domains. (AP News)
- Companies have increased their IT security budgets, allocating 17% of their IT expenditures to digital security, up from 14% the previous year. (Reuters)
- Despite the increased investment, only 37% of companies have developed emergency plans to address supply chain security incidents. (Reuters)
Cybercrime in France
- The French National Cybersecurity Agency (ANSSI) reported a 30% rise in ransomware incidents compared to 2022. A total of 3,703 security events were recorded, with 1,112 classified as confirmed incidents. (cyber.gouv.fr)
- Phishing remained the most common threat in France, accounting for 38% of assistance requests. (CYBERMALVEILLANCE.GOUV.FR)
- Account hijacking incidents in France increased by 22% from the previous year. (CYBERMALVEILLANCE.GOUV.FR)
- APT28, linked to Russian military intelligence, targeted French government agencies, local authorities, and organizations involved in the 2024 Paris Olympics. (AP News)
- ANSSI identified cyber actors associated with China, Russia, and organized cybercrime as major threats to critical national infrastructure. (cyber.gouv.fr)
- There was a notable increase in attacks targeting mobile devices, particularly those used by individuals handling sensitive information. (cyber.gouv.fr)
What is Cyber Crime?
Cyber crime, also known as cybercrime, refers to any type of criminal activity that involves the use of computers, computer networks, or other digital technologies to commit or facilitate illicit activities. These crimes can range from the theft of personal and financial data to sophisticated attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids or financial systems.
Cyber crimes can be perpetrated by individuals, groups, or even state-sponsored organizations, and they can have severe consequences for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. The theft of financial data, identity theft, and various forms of online fraud are common examples of cyber crime, highlighting the need for robust cyber security measures to protect sensitive information.
Recent Notable Cyber Attacks
In recent times, the cybersecurity landscape has been marked by a series of sophisticated and impactful cyberattacks targeting various sectors globally. Notable incidents include:
1. Attack on X (formerly Twitter)
On March 10, 2025, X faced major service issues, especially on its mobile app, where users struggled to load posts. Elon Musk, the platform’s owner, stated that the disruption was the result of a large-scale cyberattack, possibly carried out by a well-organized group or even a nation.
The incident, which some security leaders have described as indicative of a broader cyber threat landscape, led to two major waves of user complaints and widespread downtime. The most impact was reported on the U.S. coasts, where internet users experienced significant delays.
While official statements did not confirm the involvement of government agencies, the scale and precision of the attack raised concerns over national emergency readiness and the evolving capabilities of modern threat actors.
2. Bybit Cryptocurrency Exchange Hack
On February 21, 2025, a major security breach hit Bybit, one of the top cryptocurrency exchanges globally. Hackers made off with roughly $1.5 billion in Ethereum. The FBI linked the attack to the Lazarus Group, a North Korean state-sponsored cybercrime organization known for targeting financial institutions. The group took advantage of weaknesses in Bybit’s security system, causing massive financial losses and sparking renewed concerns about how well crypto platforms are protected.
3. Medusa Ransomware Attacks
Since 2021, the Medusa ransomware group has been actively targeting sectors such as medical, education, legal, insurance, technology, and manufacturing. Employing phishing campaigns to steal credentials, Medusa operates on a double extortion model, encrypting victim data while threatening public release if ransoms are unpaid.
The group’s data-leak site lists victims and offers a countdown to data release, with the option to delay the timer for a $10,000 cryptocurrency payment. To mitigate risks, officials recommend updating operating systems, software, and firmware, employing multifactor authentication for all services, and using long, secure passwords.
4. SiegedSec’s Hacktivist Operations
Between 2023 and 2024, the hacktivist group SiegedSec conducted several high-profile cyberattacks, including breaches of NATO portals, the Idaho National Laboratory, and The Heritage Foundation. The group targeted organizations to protest anti–gender-affirming-care bills and other political issues, leading to significant data leaks and operational disruptions. In July 2024, SiegedSec announced its disbandment to avoid closer scrutiny.
5. Rhysida Ransomware Group Activities
The Rhysida ransomware group has been active in targeting large organizations, including the British Library and Insomniac Games. The group encrypts data on victims’ systems and threatens to make it publicly available unless a ransom is paid. In November 2023, U.S. agencies published an alert about Rhysida, detailing the techniques the ransomware uses to infiltrate targets and its mode of operation.
6. MOVEit Data Breach
In June 2023, a vulnerability in the MOVEit file transfer software led to a series of cyberattacks affecting thousands of organizations and nearly 100 million individuals. The Russian-affiliated cyber gang Cl0p exploited this vulnerability, launching a series of cyberattacks that compromised sensitive information across numerous organizations globally.
7. Cyberattack on the Polish Space Agency (POLSA)
On March 2, 2025, Polish cybersecurity services detected unauthorized access to the IT infrastructure of the Polish Space Agency. The systems were quickly secured, and operational investigations were launched to identify those responsible. The incident brought to light ongoing vulnerabilities in the systems of critical infrastructure providers.
8. Surge in DDoS Attacks Across Europe
In early 2025, cybersecurity analysts reported a significant rise in Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks across Europe. The frequency of these attacks jumped by 137% year-over-year, with attackers deploying more precise and powerful strikes. The largest attack recorded reached a staggering 1.4 terabits per second, crippling services and causing financial losses.
9. Coordinated Exploitation of SSRF Vulnerabilities
On March 9, 2025, cybersecurity firms observed a coordinated surge in exploitation of Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerabilities. Over 400 IP addresses were found actively targeting these flaws across systems in the U.S., Germany, Singapore, India, Lithuania, and Japan. These widespread probes signaled a major offensive likely driven by organized threat actors.
10. Cyberattack on Mission, Texas
On February 28, 2025, the city of Mission, Texas, experienced a cyberattack that disrupted municipal operations, including law enforcement’s ability to access mobile data terminals and scan license plates. In response, city officials declared a state of emergency. This incident highlights how even smaller municipalities can be heavily impacted by cyber threats.
These incidents underscore the evolving nature of cyber threats and the critical importance for organizations to bolster their cybersecurity measures to protect against such sophisticated attacks.
Cyber Crime in the US and UK
Cyber crime is a significant problem in both the US and the UK, with both countries experiencing high levels of cyber attacks and data breaches. According to cyber crime statistics, the US is one of the most targeted countries for cyber attacks, with an estimated 53.35 million US citizens affected by cyber crime in the first half of 2022 alone. The UK is also a major target, with an estimated 32% of UK businesses reporting a cyber attack or data breach in 2023. These statistics highlight the pervasive nature of cyber crime and the urgent need for robust cyber security measures to protect personal and financial data in both countries.
How to Prevent Cyber Crime
Cybercrime can hit anyone, but most threats are preventable. With a few smart habits and tools, you can stay protected. Here’s what to do:
1. Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Creating complex passwords is your first line of defense. Avoid using common phrases, birthdays, or easily guessable sequences like “123456.” Instead, use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Don’t reuse passwords across different sites. If one gets exposed, the rest are at risk. Password managers like Bitwarden or 1Password can help you store and generate secure passwords.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a second step, like a text code or app notification, making it much harder for hackers to gain access, even if they know your password.
2. Regularly Update Software and Systems
Cybercriminals often exploit known software bugs. That’s why software companies constantly release patches to close those gaps.
Make sure your operating system, antivirus programs, browsers, and even mobile apps are up to date. Enable auto-updates when possible, and don’t ignore those system restart reminders. They’re usually triggered by important patches.
In a business setting, IT teams should maintain a patch management schedule to ensure all devices are updated consistently.
3. Be Cautious with Emails and Links
Phishing emails remain one of the most common cyberattack methods. These emails often look legitimate and may even appear to come from trusted brands or coworkers.
Always double-check the sender’s email address and look for spelling errors or urgent calls to action like “Click now to avoid suspension.” If it feels off, it probably is.
Hover over links to see where they really lead. If you’re unsure, contact the sender directly through a different channel before clicking anything.
4. Watch for AI Generated Scams and Deepfakes
Fraudsters now use AI to mimic voices, faces, and writing styles. These tools can create fake emails, clone voices in phone calls, or generate realistic videos to impersonate trusted individuals.

Always verify unexpected requests for money, credentials, or sensitive information, especially if they claim urgency. Use a separate and known method to confirm. In workplaces, train employees to recognize AI generated phishing and set up verification steps for wire transfers or password resets.
5. Use Security Software
Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware programs. These tools scan your system for known threats, block malicious websites, and even warn you about risky downloads.
Some advanced security suites also offer ransomware protection, a secure VPN, and firewall management. For business use, endpoint protection platforms (EPPs) like CrowdStrike or SentinelOne can help monitor and protect multiple devices at once.
6. Back Up Important Data
If ransomware locks you out of your files, having a recent backup can save you. Backups should be stored in at least two locations: one offline, like an external hard drive, and one online, such as a cloud service.
Schedule regular automatic backups to avoid relying on manual reminders. Make sure you test your backups too. They’re useless if they’re corrupted or incomplete when you need them.
For businesses, using solutions like Veeam or Acronis can help automate and secure backups across your entire network.
7. Secure Your Network
Start with a strong password on your Wi-Fi and ditch the default login credentials. Use WPA3 encryption if your router supports it. Set up a guest network for visitors, and keep smart home devices separate from your work or personal devices.
For businesses, invest in firewalls and virtual private networks (VPNs) to secure remote access. Regularly scan the network for unknown devices or open ports that could serve as entry points.
8. Educate and Train Users
Human error is one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. That’s why regular training is so important. Teach staff and family members how to spot phishing, why they shouldn’t use personal devices for sensitive tasks, and how to report suspicious activity.
Interactive training sessions, phishing simulations, and clear cybersecurity guidelines go a long way in reducing accidental security breaches.
For parents, talk to your kids about safe internet habits. Don’t just install parental controls without explaining why. They need to understand the risks, not just follow rules.
9. Develop and Enforce Security Policies
If you’re running a business, have clear rules about device usage, data access, password protocols, and how to handle sensitive information.
Make sure your employees know what to do if they suspect a breach. Incident response plans should be documented, rehearsed, and updated regularly.
Even for personal use, having your own rules, like never logging into bank accounts on public Wi-Fi, can make a big difference.
10. Monitor and Analyze Network Activity
Use tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor real-time traffic and catch threats before they escalate.
For small businesses and tech-savvy individuals, tools like Wireshark, Splunk, or Security Onion can help you track unusual behavior. Look for unexplained spikes in data usage, failed login attempts, or unauthorized access requests.
The sooner you detect suspicious activity, the quicker you can contain it.
11. Collaborate with Authorities and Organizations
If you do get attacked, report it to local authorities or cybersecurity agencies. In the U.S., that’s the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3). Many other countries have similar bodies.
Businesses should stay connected with cybersecurity organizations and information-sharing groups like ISACs (Information Sharing and Analysis Centers). Being part of these communities can give you early warnings and help you respond more effectively.
Cybercrime Cost and Impact
Cybercrime is a massive and growing global threat. By 2025, it’s projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually, up from $3 trillion in 2015.
The average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million globally in 2024, marking a 10% increase from the previous year. In the United States, the average cost per breach was even higher, at $9.36 million.
Ransomware attacks are particularly costly. In 2023, the average cost of a ransomware attack exceeded $5 million, not including ransom payments. Organizations that paid the ransom reported an average payment of $2 million, up from $400,000 in 2023.
Cybercrime’s impact extends beyond financial losses. Businesses suffer from lost productivity, reputational harm, and operational disruptions. Individuals face identity theft and financial data theft, leading to personal financial losses and emotional distress.
Phishing attacks are a common vector for cybercrime. In 2023, ransomware attacks accounted for 24% of all breaches, with the median cost per attack doubling to $26,000 over the past two years.
Importance of Cyber Security
After going through over 200 hard-hitting stats, one thing is clear. Cybercrime isn’t just rising. It’s evolving. Attacks are getting more frequent, more sophisticated, and more damaging. From phishing scams to billion-dollar data breaches, the numbers don’t lie.
This isn’t just a warning bell for IT teams. It’s a wake-up call for every business leader, organization, and individual who operates online. Cybersecurity is no longer a technical add-on. It’s a core part of staying in business and staying trusted.
The tools are out there. Firewalls, encryption, AI-driven threat detection, and more. But the real advantage comes from making cybersecurity a daily habit and a strategic priority. Because in today’s digital world, the cost of doing nothing is far greater than the cost of staying prepared.
FAQ
The FBI’s IC3 reported $16.6 billion in losses from 859,532 complaints in 2024, with 256,256 complaints reporting an actual loss and an average reported loss of $19,372.
Investment fraud led reported losses at $6.57 billion in 2024, followed by Business Email Compromise at $2.77 billion, and tech support scams at $1.46 billion.
Yes. Verizon’s 2025 DBIR executive summary says ransomware was present in 44% of reviewed breaches, up from 32%, with a reported median amount paid of $115,000 and 64% of victim organizations not paying.
Yes. Verizon’s 2025 DBIR executive summary reports exploitation of vulnerabilities as an initial access vector reached 20% of breaches, up 34% from the prior report, while only about 54% of edge-device and VPN vulnerabilities were fully remediated with a median of 32 days to remediate.
The UK Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2025 estimates UK businesses experienced about 8.58 million cyber crimes in the last 12 months, including about 7.87 million phishing cyber crimes and about 595,000 hacking cyber crimes.
Call the vendor using a phone number you already have on file and confirm the change, since business email compromise commonly uses fake “updated payment instructions” to redirect funds.
Contact the fraud department for any affected financial account, follow your internal incident process, and set fraud alerts with major credit bureaus when personal accounts are involved.
Contact your bank or the payment provider immediately, report the transfer as fraudulent, and ask for a reversal, then file a report with the FTC.
The FBI IC3’s 2024 report lists these as the top complaint categories by count: Phishing/Spoofing, Extortion, Personal Data Breach, Non-Payment/Non-Delivery, Investment, Tech Support, Business Email Compromise, Identity Theft, Employment, Confidence Fraud/Romance.
More than 90% of successful cyber-attacks start with a phishing email, according to CISA guidance.
Czechia is ranked #1 in the National Cyber Security Index (NCSI), and Canada is ranked #2 in that same index.
The “95%” figure is most often used to mean human error is involved (mistakes, manipulation, or misuse) in many breaches in some reports, while other large datasets report a lower share, such as Verizon’s DBIR executive summary saying the human element is involved in about 60% of breaches.
Get In Touch



