Data Security and Compliance: What You Need to Know in 2026
2025 is a critical turning point for data security and compliance.
The average cost of a single data breach in 2025 is a staggering $4.44 million!
Meanwhile, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) reports that 80% of countries now have or are working on data protection and privacy legislation.
This growing focus on data security and compliance underscores the increasing risks and regulatory pressures businesses face.
Staying ahead of the curve requires a proactive approach, understanding emerging trends, and adapting to new regulatory landscapes.
In this post, we’ll explore the key shifts you need to anticipate and strategize for to ensure your organization’s data remains safe and compliant.
Key Stats to Watch Out
- 45% of Americans have had their personal information compromised in the last five years.
- Organizations facing a shortage of security skills saw a 20% rise in the costs associated with data breaches.
- Breaches caused by stolen credentials were the most time-consuming to detect and resolve, with an average duration of 292 days. In contrast, breaches that were identified and contained within 200 days incurred 23% lower costs.
- In March 2020, the Cam4 data breach compromised 10.88 billion records.
- Data theft and leaks account for 32% of all cyber incidents.
- According to the 2023 Definitive Risk & Compliance Benchmark Report by Navex Global, 83% of risk and compliance professionals emphasized that maintaining organizational compliance with applicable laws, policies, and regulations is a critical or indispensable factor in the decision-making process.
- The 2023 Thomson Reuters Risk & Compliance Survey Report indicates that 80% of corporate risk and compliance professionals acknowledge their organization’s recognition of risk and compliance as valuable business advisory functions. Additionally, 74% concurred that risk and compliance requirements play a crucial role in facilitating and supporting business activities.
What is Data Security Compliance?
Data Security Compliance means following data protection laws, regulations, and industry standards to keep sensitive information safe. It ensures that organizations implement proper security measures to safeguard data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse.
Compliance frameworks—such as GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001—set clear data security standards for data handling, storage, and transmission to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These frameworks often cover data compliance standards to ensure consistency and accountability in data management practices.
Failure to comply with data security laws can lead to legal penalties. Ignoring these regulations not only violates regulatory compliance but also exposes organizations to hefty fines, financial losses, and reputational damage. For instance, HIPAA violations can cost anywhere from$100 to $50,000 per incident, with a yearly cap of $1.5 million for repeated offenses.
Data Compliance Vs. Data Security Compliance
While data compliance and data security compliance are closely related, they serve distinct purposes in managing and protecting data.
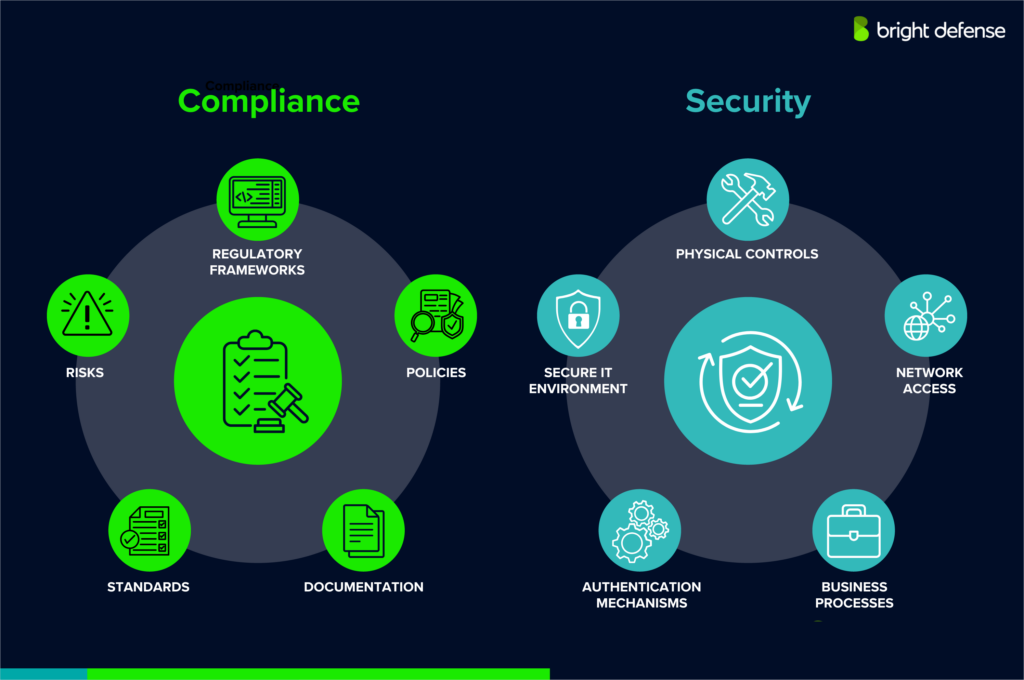
- Data Compliance focuses on the legal, regulatory, and ethical obligations an organization must follow when collecting, storing, processing, and sharing data. It ensures that businesses handle data in a lawful and responsible manner, covering aspects like user consent, data retention policies, and cross-border data transfers. Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA define how organizations must manage personal and sensitive information to protect individuals’ rights.
- Data Security Compliance, on the other hand, is specifically concerned with protecting data from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and breaches. It involves implementing security measures like encryption, firewalls, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. Standards such as PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and NIST outline best practices for securing sensitive information and preventing cyberattacks.
In simple terms, data compliance ensures organizations handle data legally and ethically, while data security compliance ensures that data remains protected from threats and breaches. Both are essential for maintaining trust, avoiding legal penalties, and safeguarding business operations.
Data Privacy and Why It’s Important
Data privacy is the practice of ensuring that personal and sensitive information is collected, processed, and stored responsibly, with strict controls over who can access it and how it’s used. It focuses on protecting individuals’ rights to control their own data, and preventing unauthorized sharing, misuse, or exploitation.
In the context of data security and compliance, privacy plays a crucial role because compliance regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA exist primarily to enforce privacy protections. Without proper data privacy policies, organizations risk violating these laws, leading to heavy fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
Why Is Data Security Important for Businesses?
As one cyberattack happening every 39 seconds. data security is a more critical concern for businesses of all sizes right now more than ever.
Here are the main reasons why having execptional data security is imrportant for your business:
1. Prevents Financial Losses
Data breaches can be financially devastating. In 2023, the average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high of USD 4.45 million.
Small businesses are not exempt; in Australia, the average cost per incident is at least $50,000.
2. Maintains Customer Trust and Business Reputation
Reputational damage from data breaches can lead to significant customer loss. Studies reveal that up to one-third of customers in retail, finance, and healthcare might stop doing business with a company. The impact doesn’t stop there; 85% of customers will discuss the incident through word of mouth, and one-third will share details about it on social networking platforms.
3. Ensures Compliance with Regulations
Failing to follow data protection regulations can lead to hefty fines. Under GDPR, companies risk fines of up to 4% of their annual global revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher.
4. Protects Intellectual Property
Insider threats pose a significant risk to intellectual property. Studies show that 81% of insiders commit malicious acts for financial gain, often stealing sensitive information.
5. Prevents Operational Disruptions
Data breaches can cause extensive operational downtime. Identifying and containing a breach takes an average of 277 days, during which severe disruptions can impact business operations.
6. Reduces the Risk of Insider Threats
Insider threats are a growing concern, with 53% of companies confirming insider attacks against their organization in the previous 12 months.
7. Enhances Competitive Advantage
A strong data security framework not only protects assets but also enhances a company’s reputation. In the wake of high-profile cyberattacks, rigorous cybersecurity due diligence has become essential in maintaining a competitive edge, especially during mergers and acquisitions.
8. Mitigates Legal Liability
Data breaches can lead to legal actions and significant financial penalties. In 2024, organizations reported 3,158 data breach incidents, marking a 70% increase since 2021. This surge underscores the growing legal risks linked to inadequate data security measures.
7 Steps To Achieve Data Security Compliance
Data security compliance is about protecting sensitive information and staying within the rules set by laws and regulations. It helps you avoid legal trouble, protect customer data, and maintain trust.
Here are seven straightforward steps to help you achieve data security compliance and keep your information safe:
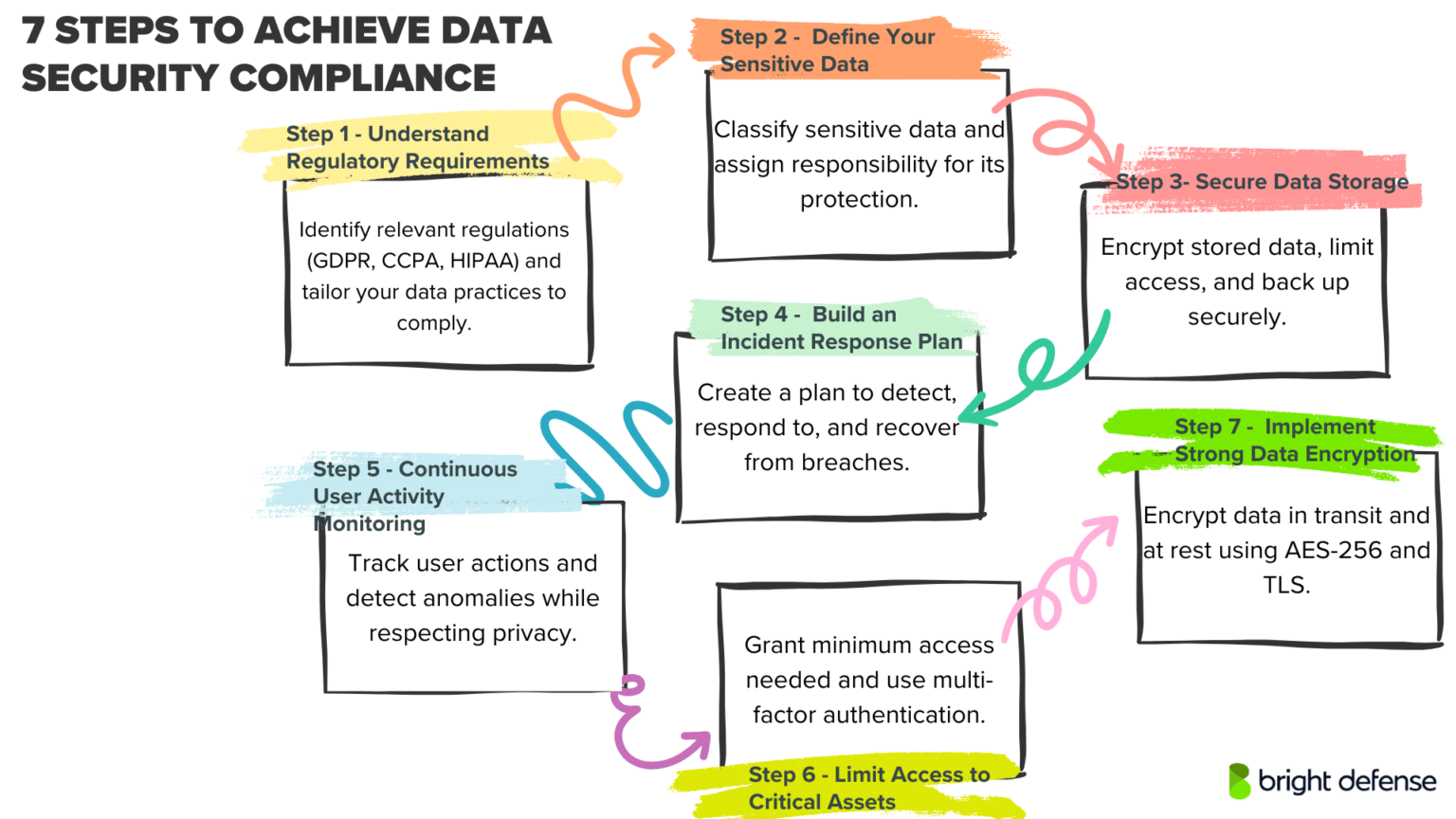
Step 1 – Understand Regulatory Requirements
Recognizing the regulatory environment that shapes your organization’s data protection obligations establishes a solid foundation for compliance. Industries and regions enforce distinct laws, whether you operate under GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or other frameworks.
Which requirements affect your storage processes, your approach to data sharing, or your methods of collecting personal information? Not every rule applies universally, so identify the standards that influence your day-to-day operations.
In-depth awareness of these mandates helps avert steep penalties, cultivates customer trust, and upholds industry best practices. Seek guidance from legal counsel or compliance professionals; evaluate any location-specific and cross-border data transfer stipulations.
With clarity on your obligations, each subsequent measure in your data security plan becomes more precise and manageable.
Pro Tip: Use regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions that automatically update compliance requirements as laws change. This proactive approach keeps your organization compliant without the constant need for manual updates, minimizing the risk of non-compliance due to outdated policies.
Step 2 – Define Your Sensitive Data
Before you can protect your data, you need to know exactly what needs protection. Classify and categorize your data based on its sensitivity and regulatory requirements. Identify personal information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, and other critical assets that require heightened security measures. Establish data ownership and assign accountability for each data type to ensure proper handling and protection.
Pro Tip: Use data discovery tools with AI-driven classification capabilities to automatically identify and label sensitive data, even within unstructured data sources like emails and documents. This not only saves time but also minimizes human error in the classification process.
Step 3 – Secure Data Storage
Storing data securely is crucial for preventing unauthorized access, breaches, and data loss. Use encryption at rest to protect sensitive information from being accessed even if storage devices are stolen or compromised. Implement role-based access controls to restrict data access to only those who need it. Regularly back up data to secure, off-site locations and test recovery procedures to ensure data integrity and availability.
Pro Tip: Use decentralized storage solutions like blockchain-based storage systems to distribute data across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of a single point of failure or centralized attack.
Step 4 – Build an Incident Response Plan
Having a solid incident response plan helps minimize the impact of security breaches. In practice, develop a clear, step-by-step plan outlining how to detect, respond to, and recover from data security incidents. To make this effective, assign specific roles and responsibilities to team members and establish communication protocols for internal and external stakeholders. On top of that, regularly review and update the plan to adapt to evolving threats and, to ensure readiness, conduct simulations to test the effectiveness of the response strategies.
Pro Tip: Integrate threat intelligence feeds into your incident response plan to receive real-time alerts on emerging cyber threats, allowing your team to proactively defend against potential attacks.
Step 5 – Continuous User Activity Monitoring
Monitoring user activity helps detect unauthorized access and suspicious behavior in real time. Implement logging and auditing systems to track user actions, such as logins, data access, and modifications. Use automated tools with machine learning capabilities to identify anomalies and potential threats. Ensure that monitoring respects user privacy while maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.
Pro Tip: Set up honeytokens—decoy data that acts as a bait to track unauthorized access attempts, enabling you to identify malicious insiders or external attackers.
Step 6 – Limit Access to Critical Assets
Restricting access to critical data assets reduces the risk of insider threats and unauthorized data exposure. Use the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to grant users the minimum access required to perform their duties. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing sensitive systems and regularly review access permissions to revoke unnecessary privileges.
Pro Tip: Implement Just-In-Time (JIT) access, which grants temporary access privileges to users only when needed, significantly reducing the attack surface for critical assets.
Step 7 – Implement Strong Data Encryption
Encryption safeguards data both in transit and at rest, ensuring that unauthorized parties cannot read it even if intercepted or stolen. Use strong encryption protocols like AES-256 for data storage and TLS for data transmission. Regularly update encryption keys and algorithms to maintain security against emerging threats. Encrypting sensitive information helps achieve compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Pro Tip: Use homomorphic encryption to allow data processing and computations while keeping the data encrypted, enhancing security without compromising functionality.
8 Data Security Regulations and Key Considerations
Data security regulations and standards provide essential frameworks that protect sensitive information and guide organizations in handling data responsibly. Here are eight prominent data security regulations and standards:
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), in effect since May 2018, is a key EU law that protects data privacy for people in the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). It also controls the transfer of personal data outside these regions. GDPR’s main goal is to give individuals more control over their personal information while simplifying data privacy rules for international businesses across the EU.
Key Considerations:
- Consent Management: GDPR emphasizes the need for clear and affirmative consent to process personal data. Organizations must ensure that consent is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous, with easy-to-understand terms and conditions.
- Data Subject Rights: Under GDPR, individuals have several rights, including accessing their data, requesting data deletion, transferring their data to another service, and being informed about data breaches. Organizations must have processes in place to address these rights promptly.
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): When processing data that is likely to result in high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms, organizations are required to perform DPIAs to identify and mitigate these risks effectively.
- Data Protection Officers (DPOs): For certain organizations, the appointment of a Data Protection Officer is mandatory. The DPO is responsible for overseeing data protection strategies and compliance with GDPR requirements.
- Breach Notification: GDPR requires that data breaches likely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals must be reported to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of the organization becoming aware of it.
2. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), established in 1996, sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. Any organization handling protected health information (PHI) must have and follow the necessary physical, network, and process security measures. HIPAA includes provisions for the protection and confidential handling of protected health information.
Key Considerations:
- Privacy and Security Policies: It’s essential to develop comprehensive policies that comply with HIPAA’s Privacy and Security Rules. These policies should clearly outline how PHI is used, disclosed, and protected.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting PHI both at rest and in transit is crucial for safeguarding patient information. This helps prevent unauthorized access in the event of data breaches or other security incidents.
- Employee Training: Regular training programs are vital for ensuring that all personnel understand HIPAA requirements and the importance of protecting patient information. This reduces the risk of accidental breaches or non-compliance.
- Risk Assessments: Conducting periodic risk assessments is a proactive measure to identify vulnerabilities in the handling of PHI. These assessments help organizations prioritize their security efforts and ensure compliance with HIPAA standards.
3. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) sets security rules for companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information to ensure a secure environment.Established by major credit card brands, PCI DSS helps reduce credit card fraud through increased controls around data and its exposure to compromises.
Key Considerations:
- Secure Network Infrastructure:To protect cardholder data, organizations need a secure network infrastructure. This means setting up and maintaining a firewall and avoiding the use of default passwords and security settings provided by vendors.
- Cardholder Data Protection: Cardholder data must be protected wherever it is processed, stored, or transmitted. Encryption, truncation, masking, and hashing are critical techniques in protecting cardholder data.
- Access Management: Access to system information and operations should be restricted and controlled. Organizations need to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to cardholder data based on their job role.
- Regular Monitoring and Testing: Networks must be regularly tested to ensure security measures and controls are effective. This includes tracking and monitoring all access to network resources and cardholder data to ensure that no unauthorized individuals gain access.
- Information Se
- curity Policy: Organizations must maintain a policy that addresses information security for employees and contractors. This policy should be updated regularly and should effectively communicate security procedures and guidelines to all relevant staff.
4. ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001is an international standard on how to manage information security. It provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). The standard is designed to ensure the selection of adequate and proportionate security controls that protect information assets and give confidence to interested parties, particularly customers.
Key Considerations:
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: A crucial element of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard is the need to conduct regular risk assessments to identify threats and vulnerabilities that affect company information. This process involves the systematic evaluation of information risks, considering the impacts and likelihood, followed by the implementation of appropriate measures to manage or treat these risks.
- Security Policy and Objectives: Organizations need to establish clear information security policies and objectives that are aligned with their business goals. These policies serve as a directive for implementing and operating the ISMS and should be reviewed and updated regularly.
- Employee Awareness and Training: Employees play a critical role in maintaining information security. Regular training and awareness programs are essential to ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities within the ISMS and the broader security efforts of the organization.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO/IEC 27001 emphasizes the importance of continual improvement through the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. Organizations should regularly review and refine their ISMS to adapt to new security threats or changes in the organization.
- Internal Audits and Management Reviews: Conducting internal audits is essential for evaluating the ISMS against the set policies and objectives. Management reviews, conducted at planned intervals, ensure the continued suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the information security management system.
5. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Frameworkprovides guidelines and best practices for managing cybersecurity-related risk. Originally developed for industries vital to national and economic security, the framework has been widely adopted across various sectors due to its flexible and cost-effective approach to enhancing cybersecurity.
Key Considerations:
- Identify: The framework starts with the identification process, where organizations need to catalog their physical and software assets to understand the resources that support critical functions. This includes understanding the business environment, governance, and associated risk management strategies.
- Protect: This core function emphasizes the need to implement appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical services. This involves protecting access to assets, data security measures, maintenance of security protections, and management of protective technologies.
- Detect: Detection processes are crucial for timely discovery of cybersecurity events. Organizations should implement continuous monitoring systems, anomaly detection mechanisms, and conduct security event assessments to identify potentially malicious activity swiftly.
- Respond: When a cybersecurity event is detected, having a response plan in place is vital. This includes response planning, communications during and after an incident, analysis of the incident to understand its impact, and mitigation strategies to prevent expansion or recurrence.
- Recover: The recovery function focuses on restoring any capabilities or services impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. Recovery planning and improvements are crucial, as is managing communications with external parties including stakeholders and regulators.
6. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which took effect in January 2020, is a law that strengthens privacy rights and consumer protection for California residents. The CCPA provides California residents with the right to know about the personal data collected about them, the right to request the deletion of their personal data, the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal data, and the right to non-discrimination for exercising their CCPA rights.
Key Considerations:
- Consumer Rights: Organizations need to ensure they provide clear mechanisms for consumers to exercise their rights under CCPA. This includes the rights to access their personal information, request the deletion of their personal information, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
- Data Inventory and Mapping: To comply with CCPA, organizations should maintain a comprehensive inventory of personal information they collect, use, and share. Data mapping helps in understanding and managing how data flows through the organization, which is crucial for addressing consumer requests effectively.
- Privacy Notices and Policies: Updating privacy notices and policies to comply with CCPA requirements is essential. These notices must be clear, accessible, and must detail the specific categories of personal information being collected, the purpose for the collection, and how consumers can exercise their rights.
- Vendor Management: Organizations must ensure that their service providers and third-party vendors who handle personal information on their behalf are also in compliance with CCPA. This may involve revising contracts to include terms that require these vendors to uphold the privacy protections required by CCPA.
7. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), enacted in 2002, is a federal law that enhances corporate accountability and financial transparency in the United States. It was established to restore investor confidence after high-profile corporate scandals, such as Enron and WorldCom. SOX mandates strict reforms to improve financial disclosures, prevent accounting fraud, and ensure the accuracy of financial reporting for publicly traded companies.
Key Considerations:
- Financial Reporting and Accuracy: Organizations must implement stringent processes to certify the accuracy of financial statements. This includes the personal accountability of executives, who are required to certify the correctness of financial reports under Section 302. This increases scrutiny in financial disclosures, ensuring that financial data is truthful and free of material misstatements.
- Internal Controls and Audits: SOX Section 404 mandates the establishment of internal controls for financial reporting. Organizations must document and evaluate these controls, and external auditors must validate their effectiveness. This involves regular internal audits, increased documentation, and enhanced IT security measures to safeguard financial data integrity.
- Compliance and Documentation: Detailed documentation of financial transactions and internal control procedures is mandatory. Organizations are required to maintain records for at least seven years, ensuring they are readily accessible for audits and inspections. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment for executives.
- Real-Time Disclosures: Section 409 requires organizations to disclose significant changes in financial condition in real-time, ensuring transparency for investors. This involves updating financial systems to provide accurate and timely disclosures of material events that may impact financial performance.
- Training and Awareness: Employees involved in financial reporting, auditing, and IT security must be trained on SOX requirements. Regular training ensures that all personnel are aware of compliance obligations and understand how to implement internal controls effectively. This promotes consistent compliance practices across the organization.
8. Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
The Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), enacted in 2002 as part of the E-Government Act, establishes a comprehensive framework to protect government information, operations, and assets from cybersecurity threats. FISMA requires federal agencies, contractors, and other organizations handling federal data to implement robust security measures, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems.
Key Considerations:
- Risk Management Framework: FISMA mandates the use of a risk management framework to identify, assess, and mitigate security risks. Organizations must categorize information systems based on impact levels (low, moderate, or high) and implement security controls accordingly. Continuous monitoring and regular risk assessments are crucial for maintaining security posture.
- Security Controls and Compliance: Organizations are required to implement and document security controls that meet the standards outlined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). These controls cover areas such as access control, incident response, and data encryption. Compliance with NIST guidelines is mandatory for maintaining FISMA certification.
- Information Security Plan: Agencies must develop and maintain an information security plan that outlines the policies, procedures, and controls in place to safeguard federal information. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to address emerging cybersecurity threats and changes in operational requirements.
- Security Authorization and Accreditation: Before an information system is deployed, it must undergo a security authorization process, including testing and evaluation of implemented security controls. The system must be accredited by an authorized official, verifying that it meets all security requirements and is safe for operation.
- Continuous Monitoring and Reporting: FISMA requires continuous monitoring of information systems to detect security incidents and vulnerabilities in real-time. Organizations must implement automated tools for monitoring and regularly report security status to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and Congress.
Final Thoughts
Prioritizing your organization’s data security and compliance is not just about avoiding fines. It’s about showing that your organization values data security and takes responsibility for safeguarding customer information. This builds credibility and trust, which are essential for long-term success.
As regulations and cyber threats continue to change, staying proactive is key. Review and update your data security practices regularly. Doing so not only keeps your organization compliant but also reinforces your commitment to data protection and customer confidence.
Bright Defense Offers Data Security and Compliance Services
At Bright Defense, we provide comprehensive Data Security and Compliance Services tailored to safeguard your sensitive information and maintain regulatory standards. Our solutions include SOC 2, HIPAA, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and NIST compliance to ensure your organization meets the highest security benchmarks.
We also offer a range of security solutions such as Continuous Cybersecurity Compliance, Virtual Chief Information Security Officer (vCISO) services, Penetration Testing, Vulnerability Management, Managed Security Awareness Training, and Security Assessment & Remediation. Our goal is to protect your data, strengthen your security posture, and keep your business compliant and resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help secure your data and maintain compliance.
FAQs
A: The four elements are Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, and Authenticity. Confidentiality ensures only authorized access. Integrity maintains data accuracy. Availability guarantees access when needed. Authenticity verifies user identity and data sources.
A: Implement encryption, access controls, and firewalls. Establish clear security policies, conduct regular audits, train employees on best practices, and use tools like intrusion detection systems and data loss prevention software.
A: Security safeguards data from unauthorized access and threats using technical and administrative measures. Compliance involves meeting legal and industry standards for data protection and privacy.
A: It protects sensitive information, builds customer trust, avoids legal penalties, enhances brand reputation, and ensures business continuity by minimizing security risks.
A: Data security compliance ensures data is protected according to laws and industry standards. It prevents unauthorized access and breaches while meeting legal obligations. This involves using encryption, access controls, and regular audits to safeguard sensitive information.
A: Data compliance focuses on following legal and regulatory standards for data management. Data security compliance is about implementing security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and threats, ensuring these measures meet regulatory requirements.
A: It reduces security risks, ensures legal compliance, and prevents fines. It also enhances brand reputation, boosts operational efficiency, and creates a competitive edge by building customer trust and attracting strategic partnerships.
Get In Touch