Tim Mektrakarn
February 26, 2025
Continuous Vulnerability Management: Embracing a Proactive Approach
Organizations face a constant threat from various vulnerabilities in their systems. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the need for an effective vulnerability management program has never been more critical. A core aspect of modern vulnerability management is the concept of Continuous Vulnerability Management (CVM), a proactive approach to identify, assess, and address security vulnerabilities in real-time. This article delves into the key elements of a successful vulnerability scanning and vulnerability management program, specifically focusing on integrating Continuous Vulnerability Management.
Understanding Continuous Vulnerability Management
Continuous Vulnerability Management is an ongoing process of identifying, classifying, prioritizing, remediating, and mitigating vulnerabilities in software and firmware. CVM, a dynamic and continuous process, contrasts with traditional periodic scans and assessments by ensuring immediate identification and resolution of vulnerabilities upon discovery.
Key Elements of an Effective Vulnerability Management Program
Comprehensive Asset Inventory
- Understanding the Landscape: The foundation of any vulnerability management program is a thorough understanding of the organization’s assets. This includes hardware, software, applications, and data. Continuous monitoring of these assets is vital for identifying new vulnerabilities.
- Automation in Asset Discovery: Automation in asset discovery immediately identifies and assesses vulnerabilities in new assets. Tools that provide real-time visibility of the asset inventory can significantly enhance the efficiency of the vulnerability management process.
Vulnerability Identification and Assessment
- Continuous Scanning: Regular and continuous scanning of assets for known vulnerabilities is a critical component. This process should be automated to ensure timely identification.
- Intelligent Prioritization: Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk. An effective program must include a mechanism for prioritizing vulnerabilities based on factors such as exploitability, severity, and the criticality of the affected asset.
- Vulnerability Scanning Programs
Vulnerability scanning is a crucial component of any cybersecurity strategy. These programs proactively identify and report potential security vulnerabilities within an organization’s network, software, and systems.
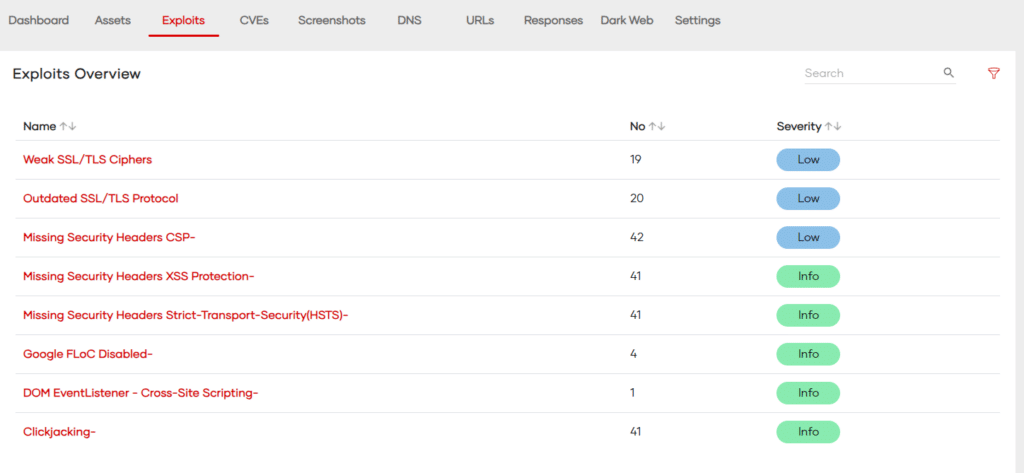
Key Features of Vulnerability Scanning Programs:
- Automated Scanning: These programs perform regular, automated scans of networks and systems to detect vulnerabilities. This automation ensures continuous monitoring and timely identification of security gaps.
- Comprehensive Coverage: They scan for a wide range of vulnerabilities, including unpatched software, open ports, insecure configurations, and potential malware infections.
- Prioritization and Reporting: Post-scan, they categorize vulnerabilities based on severity, helping IT teams prioritize remediation efforts. Detailed reports are generated, outlining vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and recommendations for mitigation.
- Integration with Other Tools: Many vulnerability scanners integrate with other security tools, such as intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, for enhanced security monitoring.
CVE Scoring System
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system is a publicly available catalog of known security vulnerabilities. The CVE database actively assigns each vulnerability a unique CVE ID, description, and references. Importantly, the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) often scores these vulnerabilities.
Understanding CVSS:
The CVSS is a standardized framework for rating the severity of security vulnerabilities. Scores are calculated based on various metrics, which fall into three main groups:
- Base Metrics: These assess the intrinsic qualities of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments. This includes factors like the complexity of the attack, the need for user interaction, and the impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Temporal Metrics: These consider factors that change over time but not among user environments, like the availability of exploits and the existence of patches.
- Environmental Metrics: These account for the characteristics of a particular user’s environment, tailoring the CVSS score to reflect the severity of the vulnerability in the specific context of an organization.
CVSS v2.0 Score Ranges:
- 0.0-3.9: Low severity
- 4.0-6.9: Medium severity
- 7.0-10: High severity
CVSS v3.0 Score Ranges:
- 0.1-3.9: Low severity
- 4.0-6.9: Medium severity
- 7.0-8.9: High severity
- 9.0-10.0: Critical severity
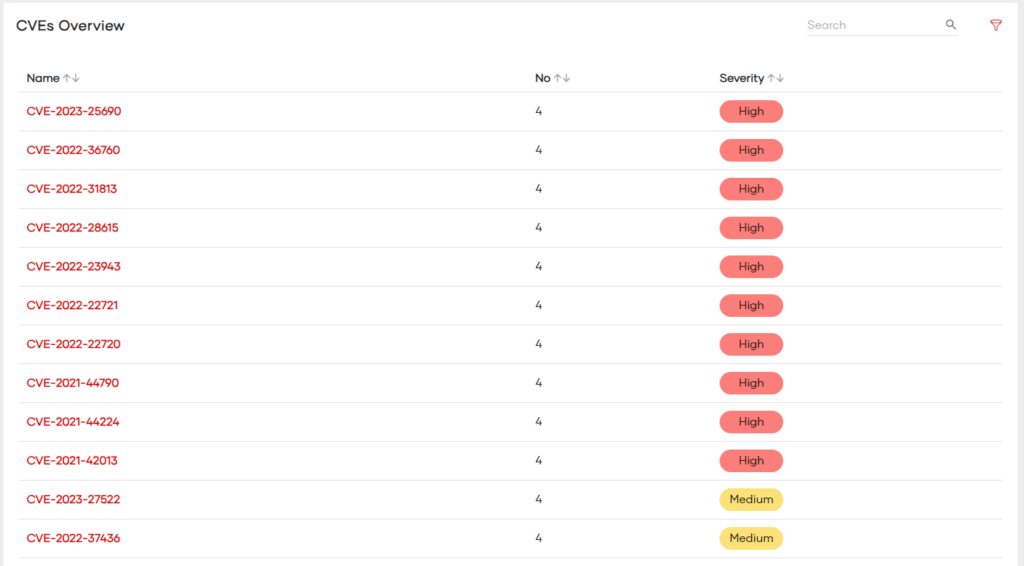
These scores actively guide organizations to prioritize vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention and identify those that can be deprioritized. Tying the CVSS score to SLAs for patch management reinforces a robust Continuous Vulnerability Management Program.
Sample Vulnerability Management SLA
- As-Needed: Low severity
- 90 days: Medium severity
- 30 days: High severity
- 7 days: Critical severity
Integration with Threat Intelligence
- Staying Ahead of Threats: Integrating real-time threat intelligence into the vulnerability management process allows organizations to understand the evolving threat landscape and anticipate potential attacks.
- Automated Responses: By leveraging threat intelligence, organizations can automate certain responses to common or critical vulnerabilities, thus reducing the time between discovery and remediation.
Patch Management and Remediation
- Efficient Patch Management: A robust patch management process is crucial. This involves not only the timely application of patches but also testing them to ensure they do not disrupt existing systems.
- Automated Patch Deployment: Automation tools can significantly streamline the patch management process, ensuring that vulnerabilities are patched promptly and consistently.
Compliance and Reporting
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements: An effective vulnerability management program must ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
- Continuous Reporting and Documentation: Automated reporting tools help maintain a continuous overview of the vulnerability management process, aiding in decision-making and compliance reporting.
Employee Training and Awareness
- Building a Security Culture: Employees should be trained to understand the importance of vulnerability management and their role in it. This includes recognizing potential security risks and adhering to best practices.
The Marriage of Security and Compliance
While continuous vulnerability management inherently enhances an organization’s security posture, it also serves as a linchpin for maintaining continuous compliance. Compliance standards and regulations, whether industry-specific or general, often mandate a proactive and ongoing approach to security. CVM becomes the conduit that ensures organizations remain in compliance with these standards.
Continuous Compliance aligns seamlessly with the objectives of Continuous Vulnerability Management. By continually scanning for vulnerabilities and promptly addressing them, organizations fortify their defenses and stay in compliance with the ever-evolving regulatory landscape. The synergy between Continuous Vulnerability Management and Continuous Compliance is a force multiplier in the realm of cybersecurity. Organizations that embrace this tandem approach find themselves not only resilient against emerging threats but also well-prepared to navigate the complexities of compliance.
Conclusion
Continuous Vulnerability Management is not just a tool or a set of procedures; it’s a mindset that requires organizations to remain vigilant and proactive in the face of ever-changing cyber threats. By incorporating the key elements outlined above and leveraging automation, organizations can build a robust vulnerability management program that not only protects their assets but also supports their overall cybersecurity strategy.
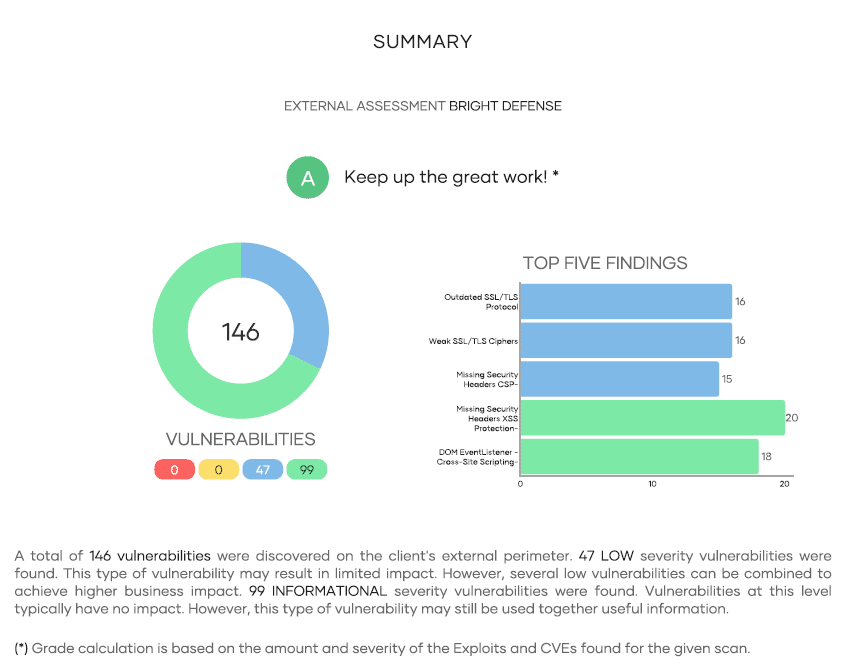
Bright Defense Vulnerability Management Program
Bright Defense offers Vulnerability Management services with continuous or scheduled scanning of internal assets by Active Directory domain and CIDR ranges, external asset scanning Domain, CIDR range, as well as Dark Web monitoring for leaked credentials. Our vulnerability scanner can also scan public cloud resources in Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services through a read only account. Reports can be delivered on a daily basis but typically our clients prefer to receive them monthly along with a summary of the most important patches to apply.
Bright Defense’s Vulnerability Management services are an extension of our continuous compliance offering. Our monthly engagement model delivers a robust cybersecurity program that meets compliance frameworks including SOC 2, CMMC, HIPAA, NIST, and ISO 27001. Our managed compliance automation platform automates your compliance journey and provides a single platform to continuously monitor your compliance journey.
Get started with Bright Defense today!
Embracing Continuous Vulnerability Management is an essential step towards securing an organization’s digital infrastructure. By continuously monitoring, analyzing, and responding to vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile and ensure a more secure and resilient operation.
Get In Touch



