Arjay | Security Specialist
April 25, 2025
Hybrid Penetration Testing: What’s New in 2025
Penetration testing (pentesting) remains a critical component of cybersecurity.
With the growing complexity of IT environments, organizations are adopting hybrid penetration testing approaches that blend automated tools with manual techniques.
This combined approach allows organizations to focus their remediation efforts on the most critical vulnerabilities, ensuring efficient resource allocation and reducing overall risk exposure.
This comprehensive article delves into hybrid pentesting approaches for 2025 and outlines how they help organizations stay resilient against modern threats.
What is Hybrid Penetration Testing?
Hybrid penetration testing, also known as a hybrid testing approach, combines the speed and efficiency of automated scanning tools with the depth and intuition of manual testing.
This dual approach ensures comprehensive security assessments by quickly identifying known vulnerabilities and uncovering complex, context-specific security flaws that automated tools may miss.
This leads to faster remediation cycles and more effective risk management.
How to Perform Hybrid Penetration Testing?
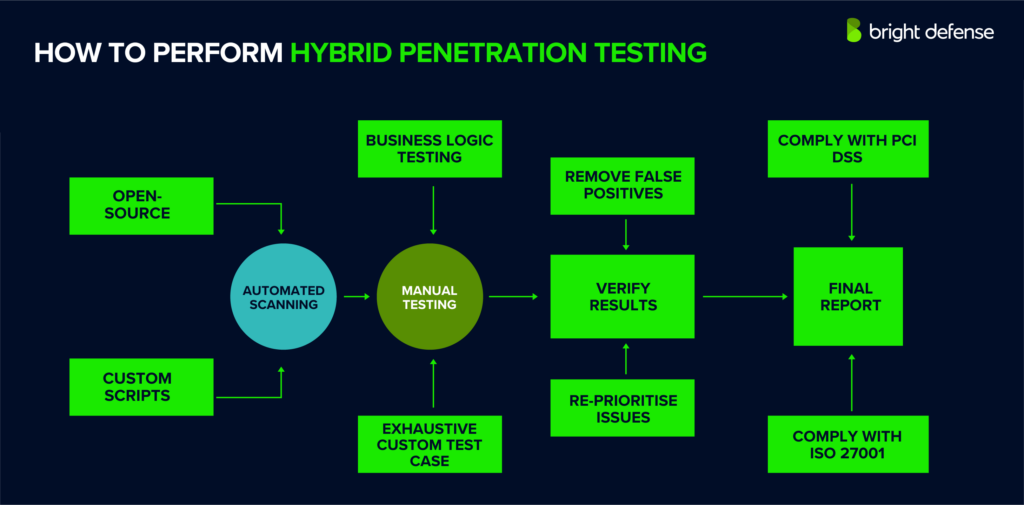
Hybrid penetration testing combines automated tools and manual techniques to identify security weaknesses in a system. This approach leverages the speed and efficiency of automated scans with the thoroughness and expertise of manual testing.
Using both methods together gives organizations a fuller picture of their security. The key is to prioritize the most serious vulnerabilities so time and resources aren’t wasted, and risk stays under control.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to run a hybrid pentest the smart way, balancing automation with human insight to get real results:
Step 1 – Start with Automated Scanning
The first step in any serious penetration test is automated scanning. This stage leverages a mix of open-source tools like:
- Nmap
- Nikto
- OWASP ZAP
To rapidly scan for known vulnerabilities such as open ports, outdated software, exposed services, or misconfigured settings.
Alongside these tools, custom scripts written in languages like Python, Bash, or PowerShell can be used to target specific behaviors or environments unique to your infrastructure. Automated scanning helps establish a baseline quickly, providing a wide-angle view of the attack surface. But make no mistake: automation is only a starting point. It’s fast and noisy, but not deep or context-aware.
Step 2: Dig Deeper with Manual Testing
Once the automated scan results are in, it’s time to go manual. This is where real value is added. Manual testing is where you hunt down the nuanced, creative vulnerabilities that scanners can’t detect.
This includes business logic flaws such as skipping checkout steps, manipulating account roles, or bypassing validation mechanisms. It also involves building exhaustive, custom test cases that explore how the application handles unexpected inputs, misuse of functionality, or chained exploits.
A good tester here doesn’t just think like a hacker. They think like a malicious user with access to your app’s inner workings. This is often where critical issues are uncovered.
Step 3 – Eliminate False Positives
Automated tools are notorious for generating false positives, alerts that look dangerous but turn out to be nothing. That’s why the next step is to weed them out. Each finding must be reviewed to confirm whether it’s a legitimate vulnerability.
You’ll re-test manually to determine whether it’s actually exploitable or just an error in the scanner’s logic. Removing false positives keeps the final report clean and focused, helping developers stay efficient and preventing stakeholders from being overwhelmed by noise. A cluttered report screams “rookie.” A clean, accurate one shows professionalism.
Step 4- Re-prioritize the Issues
With the junk filtered out, the next task is to re-prioritize the validated vulnerabilities to address the most critical ones. Not all real issues carry the same weight. Some may be rare edge cases with minimal impact, while others could be gaping holes in security.
This step involves assessing risk based on context: what’s exposed, how likely it is to be exploited, and what the business impact could be. It’s not just about CVSS scores. You need to understand how vulnerabilities interact. Two medium-risk bugs might combine into a critical flaw when chained. This step helps teams focus on what actually matters first.
Step 5 – Re-verify the Results
Before the report is finalized, each confirmed issue should be retested and verified one last time. This ensures nothing slipped through by mistake and gives you the chance to clean up reproduction steps, capture proof-of-concept examples, and collect any relevant screenshots or logs.
If the dev team can’t reproduce a finding with the information you’ve provided, it slows down remediation. Verification is your quality control step. It ensures the report isn’t just accurate, but usable.
Step 6 – Prepare the Final Report
Now it’s time to put everything together in a final report. This isn’t just a tech document. It’s a communication tool for both developers and business stakeholders. It should start with an executive summary that clearly outlines the overall risk posture and key takeaways.
Then, for each finding, include a detailed description, risk rating, steps to reproduce, potential impact, and suggested mitigation strategies. The report should also describe your testing methodology and include appendices with raw data, logs, or scripts if needed. A good report doesn’t just list problems. It guides solutions.
Step 7 – Meet Compliance Standards
The last step ties everything into regulatory compliance. Whether your organization is aiming to comply with PCI DSS for payment security or ISO 27001 for broader information security governance, your report should show that the penetration testing process aligns with these standards.
Findings should map to specific controls or compliance criteria. This gives stakeholders and auditors confidence that you’re not just patching vulnerabilities. You’re following a disciplined, standards-based approach to security.
Why Hybrid Pentesting Matters in 2025
In 2025, maintaining a robust security posture is crucial as cyber threats become more sophisticated.
Hybrid penetration testing, which combines automated and manual assessments, provides a comprehensive evaluation of potential threats and weaknesses. This approach ensures that organizations can effectively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, keeping their security measures up to date with evolving threats.
Additionally, it helps in addressing the most critical vulnerabilities by prioritizing security threats based on their potential impact and exploitability.
If you’re serious about tightening your defenses, here’s why hybrid pentesting should be part of your playbook:
1. Combines Speed and Depth in One Framework
Automated testing tools are fast. They can scan massive environments such as cloud platforms, APIs, and IoT networks in minutes. They catch low-hanging fruit like open ports, outdated libraries, and known CVEs without breaking a sweat.
But automation has limits. It can’t think critically or simulate a social engineering attack. That’s where manual testing steps in. Ethical hackers bring intuition to the table, digging into business logic flaws, phishing vulnerabilities, and multi-stage attack chains that tools alone can’t catch.
Together, automation handles the heavy lifting, and manual testing adds surgical precision.
2. Tackles the New Breed of Threats
2025’s threat landscape includes AI-generated malware, deepfake-based phishing, and insecure IoT ecosystems. A hybrid model is the only practical response to identify vulnerabilities:
- AI and ML-based tools quickly sort through massive logs and scan data for anomalies.
- Human testers validate and adapt those findings, especially when dealing with unknown or evolving attack vectors.
Cloud-native apps, container-based systems, and smart devices all require this dual approach. Automated scanners may flag issues, but manual testers uncover hidden risks by simulating actual attacker behavior.
3. Cuts Down on False Positives
Automated scanners are known for flagging issues that aren’t actually threats, which can obscure critical vulnerabilities. That’s where human validation comes in. Testers can:
- Confirm whether flagged vulnerabilities, such as potential SQL injection points, are truly exploitable.
- Prioritize real business risks over generic findings, so your security team isn’t chasing noise.
The result? Fewer distractions, clearer insights, and better decision-making.
4. Helps Meet Compliance Without Wasting Time
With tighter regulations in 2025, companies face growing pressure to prove they’re secure. Hybrid pentesting streamlines compliance:
- Automated checks cover password policies, software versions, and encryption standards.
- Manual validation verifies things like access control, data handling, and security controls, ensuring everything holds up during an audit.
This approach satisfies frameworks like GDPR, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001 without slowing teams down.
5. Keeps Up with Continuous Testing and Development
Security can’t be a one-off activity anymore. With agile and DevSecOps in full swing, a comprehensive testing process in hybrid pentesting allows:
- Real-time scanning baked into CI/CD pipelines.
- Scheduled red-teaming to test high-value systems during key release cycles.
That means better coverage without disrupting development flow.
A Quick Look at 2025’s Key Hybrid Trends
| Trend | How Hybrid Pentesting Helps |
| AI-Powered Attacks | Tools detect anomalies; humans handle novel, adaptive threats. |
| Cloud Complexity | Scanners find misconfigs; testers exploit logic gaps. |
| IoT Proliferation | Automation scales tests; humans assess physical interfaces. |
| Regulatory Pressure | Automation handles checks; testers prep for audits. |
Key Practices for Hybrid Pentesting
Security professionals recognize that hybrid penetration testing is quickly becoming the go-to approach for securing today’s complex tech environments.
Here’s a breakdown of five essential practices every team should adopt:

1. AI-Powered Scanning for Initial Reconnaissance
Using AI tools to automatically find targets, map out the attack surface, and catch obvious security gaps like open ports, outdated software, and weak configurations.
Key Practices
- Automated Asset Discovery: Use tools like Shodan, Censys, and Spyse to scan networks, domains, and cloud services.
- Vulnerability Prioritization: Use machine learning to flag high-risk threats (e.g., CVSS 9+).
- Behavioral Analysis: Spot odd patterns like unfamiliar API endpoints using AI.
Why It Matters in 2025
- Speed and Coverage: AI can quickly scan massive systems like IoT devices and hybrid clouds.
- Getting Smarter: It learns from past attacks and picks up on new threats such as zero-days.
ExampleAn AI tool finds an exposed Kubernetes dashboard. Human testers then dig deeper and gain access by taking advantage of weak RBAC settings.
2. Manual Exploitation of Complex Vulnerabilities
This happens when human security experts actively search for and test hard-to-find security weaknesses, such as logic errors or combined flaws, that automated tools typically miss.
Key Practices
- Creative Exploitation: Mimic real attacks (e.g., phishing or session hijacking).
- Contextual Testing: Check if flagged issues are actually usable by attackers.
- Red Teaming: Act like advanced threat groups moving across cloud and on-prem systems.
Why It Matters in 2025
- Evolving Threats: Sophisticated tactics like AI-generated phishing require human judgment.
- Compliance Pressure: Regulations demand that controls are checked by skilled professionals.
ExampleAutomation finds a broken login endpoint. Human testers connect it with a weak JWT setup to escalate access.
3. Actionable Reporting and Fix Guidance
Creating security reports that are easy to understand and useful, especially when derived from penetration tests. These reports explain which issues matter most, how they affect the business, and what steps teams should take to fix them.
Key Practices
- Risk Context: Mark issues by how serious they are and what they affect (e.g., “Critical: Exposed PII”).
- Clear Fixes: Include how-to steps, like code tweaks or config edits.
- Team Collaboration: Share results with DevOps and compliance via tools like Dradis or Confluence.
Why It Matters in 2025
- Regulation-Ready: Reports line up with standards like NIST CSF 2.0 and ISO 27001:2022.
- Practical Focus: Helps teams focus on what actually needs fixing first.
ExampleA report highlights an open S3 bucket and also suggests adjusting the code review process to avoid future mistakes.
4. Integration with DevSecOps Workflows
Making security checks a built-in part of the software development process, including conducting a penetration test, ensures testing for issues early and often—right alongside coding, building, and deploying apps.
Key Practices
- Shift-Left Testing: Run scans early in the dev process using tools like Checkmarx or OWASP ZAP.
- Manual Review Points: Pause and require human review for high-risk updates, like anything touching payment systems.
- Toolchain Compatibility: Plug into Jenkins, GitLab, or Azure DevOps without slowing things down.
Why It Matters in 2025
- Keeps Up With Dev Speed: Matches the fast pace of app development.
- Finds Problems Early: Stops bugs before they reach production.
ExampleA scan runs after deployment using the CI/CD setup. Then, a human tester checks the new login system for weak points.
5. Cloud Configuration Testing
Reviewing how cloud platforms (like AWS, Azure, or GCP) are set up involves identifying vulnerabilities to catch risky settings, such as weak access controls or exposed data—that could lead to security problems.
Key Practices
- Automated Cloud Scans: Use tools like Prowler or Wiz to catch public buckets and overly broad permissions.
- Manual Deep-Dives: Security pros test for issues like escaping containers or jumping between accounts.
- Standards Checks: Compare settings with CIS benchmarks and similar guides.
Why It Matters in 2025
- More Moving Parts: Multi-cloud setups and serverless apps leave more room for mistakes.
- Least Privilege: Manual checks confirm that access is limited to what’s actually needed.
ExampleAn automated scan flags an unencrypted RDS instance. A tester then exploits a vulnerable Lambda function to pull data from it.
Solution: Invest in skilled pentesters capable of performing in-depth manual assessments.
Benefits of Hybrid Penetration Testing
Hybrid penetration testing, where automation meets human insight, is now essential for tackling complex security challenges. Here’s why it matters more than ever:
1. Holistic Security Coverage
Hybrid penetration testing catches what either automation or manual methods alone would miss. Automated scans flag surface-level risks like outdated software, exposed ports, or weak encryption.
Meanwhile, manual testing uncovers the trickier stuff: business logic errors, privilege escalation, chained exploits, and user-specific flaws that require human creativity to detect. The result? End-to-end coverage across simple misconfigurations and complex, contextual threats.
2. Scalability Without Sacrificing Depth
Automated tools can handle vast, distributed environments such as cloud workloads, containers, IoT devices, and APIs in one sweep. They scan thousands of assets simultaneously.
This lets human testers spend their time digging into the high-risk or suspicious areas instead of being bogged down by repetitive tasks. Hybrid testing scales horizontally with automation and vertically with manual precision.
3. Cost and Time Efficiency
Automation handles bulk tasks like fingerprinting, vulnerability scanning, and log parsing. That slashes the manual workload significantly. Teams don’t waste time reviewing false alarms or poking at low-priority issues. Instead, they zero in on the vulnerabilities that truly matter.
Fewer billable hours spent chasing ghosts means more focus on actionable threats. Over time, this lowers both operational costs and turnaround time.
4. Fewer False Positives, Cleaner Reports
Automated scanners often produce junk, vulnerabilities that sound scary but aren’t exploitable. Hybrid testing brings in human validation to confirm what’s real and what’s not.
Every flagged issue is manually reviewed, re-tested, and prioritized. This ensures the final report is lean, relevant, and developer-friendly with none of the bloated noise that slows down remediation efforts.
5. Realistic Simulations of Modern Attacks
Hybrid pentesting mimics how real attackers operate. Automation is used for initial reconnaissance and surface mapping. Then, manual techniques simulate deeper exploitation paths such as credential stuffing, session hijacking, lateral movement, and data exfiltration.
It gives organizations a real-world look at how threats would play out across their systems, not just a sanitized list of CVEs.
6. Faster Integration with DevSecOps
Hybrid testing fits cleanly into agile workflows. Automated scans can be triggered by CI/CD pipelines at every push or release, catching low-level issues early.
Manual testing checkpoints can be added for critical updates like payment modules or identity verification systems. This keeps security in lockstep with development without becoming a bottleneck.
7. Improved Compliance Readiness
Many compliance standards require both automated assessments and manual reviews. Hybrid pentesting satisfies both sides of that equation. Automated checks validate password strength, encryption use, and config hygiene.
Manual testers confirm the presence and effectiveness of access controls, user permission boundaries, and data handling safeguards. It helps produce audit-ready evidence without extra effort.
8. Adaptability Across Complex Tech Stacks
Whether it’s a traditional data center, a cloud-native app, a microservices architecture, or an edge computing setup, hybrid pentesting flexes to fit.
It supports rapid scanning of dynamic environments and deep manual exploration of niche systems. No matter how your stack is built, this approach finds a way in.
9. Risk-Based Prioritization
Not all vulnerabilities are created equal. A hybrid approach helps prioritize the most critical vulnerabilities properly. Automated tools assign base scores and flags. Then, human testers contextualize: Is the app public-facing? Can the flaw be chained with others?
Would exploitation compromise sensitive data? This risk-based prioritization ensures that remediation efforts focus on these vulnerabilities, leading to efficient resource allocation and reduced overall risk exposure. The result is a triaged list that focuses on impact, not just severity labels.
10. Better Collaboration Between Teams
Hybrid pentest reports are more than just data dumps. They’re structured to help both technical and non-technical stakeholders take action.
Clear reproduction steps, proof-of-concept code, remediation guidance, and business impact summaries make it easier for developers, security teams, and execs to align. No translation needed.
Challenges and Solutions in Application Security Testing
Modern application security testing comes with a unique set of hurdles, including the need to implement and continuously test security controls.
The good news is, with the right strategies, they’re manageable.
Let’s break down the key challenges and what you can do about them.
1. Balancing Automation and Manual Effort
Application security testing often struggles to find the right balance between automated tools and human-driven analysis, especially when it comes to identifying and prioritizing critical vulnerabilities. Relying too much on automation can lead to false negatives, missing logic flaws and business context vulnerabilities, while manual testing alone is too slow and expensive for large-scale systems. Teams may also lack clarity on when to use automation versus manual methods, leading to inefficiencies and gaps in coverage.
Solution
A risk-based hybrid approach optimizes resource allocation:
- Automate repetitive tasks using SAST and DAST tools for continuous code scanning, dependency analysis, and baseline security checks (e.g., OWASP Top 10). Tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx streamline this process.
- Manually test high-risk areas such as payment gateways, authentication systems, and complex attack scenarios like chained exploits and social engineering.
- Use risk assessment frameworks like NIST SP 800-30 or FAIR to categorize risks and allocate testing proportionally. Low-risk internal apps might require 80% automation, while customer-facing financial systems may need 50% manual testing.
- Iterate and refine by analyzing test results and automating recurring manual findings.
2. Tool Compatibility
Cybersecurity tools often don’t integrate well, leading to siloed data, redundant efforts, and blind spots. Security professionals play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by implementing strategies to enhance tool compatibility. Proprietary tools may lack APIs or custom workflow support, delaying remediation. Legacy systems add to the complexity, forcing teams to manually correlate results.
Solution
Building an interoperable toolchain streamlines workflows:
- Choose tools with open standards like SARIF (for vulnerability sharing) or OpenAPI (for integrations).
- Use extensible platforms such as Burp Suite (for web apps) or Nessus (for network vulnerabilities) that support plugins and APIs for integration with SIEMs (e.g., Splunk), CI/CD pipelines (e.g., Jenkins), and issue trackers (e.g., Jira).
- Centralize visibility using orchestration platforms like ThreadFix or DefectDojo to aggregate and deduplicate findings.
- Automate data transfer with custom scripts (Python, PowerShell) to bridge incompatible tools, such as exporting Nessus results into a GRC system.
- Validate compatibility early during procurement to avoid vendor lock-in and closed ecosystems.
3. Skill Requirements
The shortage of skilled security testers is a major hurdle. Manual testing demands deep expertise in exploit development, reverse engineering, and threat modeling. These skills are both rare and expensive. Identifying security weaknesses often requires a human perspective, since automated tools may overlook complex scenarios and vulnerabilities. Relying too heavily on automation can leave organizations exposed to advanced attacks that call for human intuition.
Solution
Building and retaining expertise strengthens security capabilities:
- Upskill existing teams with certifications like OSCP, CISSP, or SANS GPEN, and encourage participation in CTF competitions and bug bounty programs.
- Hire specialists in areas like mobile app pentesting, cloud security, and industry-specific risks (e.g., fintech, healthcare).
- Leverage external expertise by partnering with boutique security firms for targeted assessments while keeping routine tasks in-house.
- Foster a security culture by training developers in secure coding to minimize low-level vulnerabilities and free up testers for complex threats.
- Combine human and machine intelligence with tools like BloodHound (for Active Directory analysis) or Cobalt Strike (for adversary emulation) to augment manual testing.
Final Considerations
- Track KPIs such as time-to-remediate, coverage gaps, and exploit success rates to measure security effectiveness.
- Stay adaptive to evolving threats, as AI-driven attacks will require AI-augmented defenses.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001 to avoid legal and financial risks.
Final Thoughts
Hybrid penetration testing approaches, also known as the hybrid testing approach, provide the best of both worlds: efficiency through automation and depth through manual expertise. In 2025, as cyber threats become more sophisticated, adopting hybrid pentesting methods ensures that organizations can effectively identify and remediate vulnerabilities. By combining AI-powered tools, skilled manual testers, and continuous integration practices, businesses can build a strong cybersecurity posture to protect their digital assets.
FAQs
VA identifies security flaws without exploiting them. PT goes further by actively exploiting those flaws to show the real-world impact of an attack.
Pentesters in the U.S. earn around $126,000 per year on average. Beginners make less, but experienced testers can earn much more, especially in high-demand areas.
Penetration testing includes planning, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and reporting. It starts with gathering info and ends with a report detailing how the system was breached and how to fix it.
Get In Touch



